AI: Embracing the promises and realities — from the Allegis Group
Excerpts:
What will that future be? When it comes to jobs, the tea leaves are indecipherable as analysts grapple with emerging technologies, new fields of work, and skills that have yet to be conceived. The only certainty is
that jobs will change. Consider the conflicting predictions put forth by the analyst community:
- According to the Organization of Economic Cooperation and Development, only 5-10% of labor would be displaced by intelligent automation, and new job creation will offset losses. (Inserted comment from DSC: Hmmm. ONLY 5-10%!? What?! That’s huge! And don’t count on the majority of those people becoming experts in robotics, algorithms, big data, AI, etc.)
- The World Economic Forum27 said in 2016 that 60% of children entering school today will work in jobs that do not yet exist.
- 47% of all American job functions could be automated within 20 years, according to the Oxford Martin School on Economics in a 2013 report.
- In 2016, a KPMG study estimated that 100 million global knowledge workers could be affected by robotic process automation by 2025.
Despite the conflicting views, most analysts agree on one thing: big change is coming. Venture Capitalist David Vandergrift has some words of advice: “Anyone not planning to retire in the next 20 years should be paying pretty close attention to what’s going on in the realm of AI. The supplanting (of jobs) will not happen overnight: the trend over the next couple of decades is going to be towards more and more automation.”30
While analysts may not agree on the timing of AI’s development in the economy, many companies are already seeing its impact on key areas of talent and business strategy. AI is replacing jobs, changing traditional roles, applying pressure on knowledge workers, creating new fields of work, and raising the demand for certain skills.
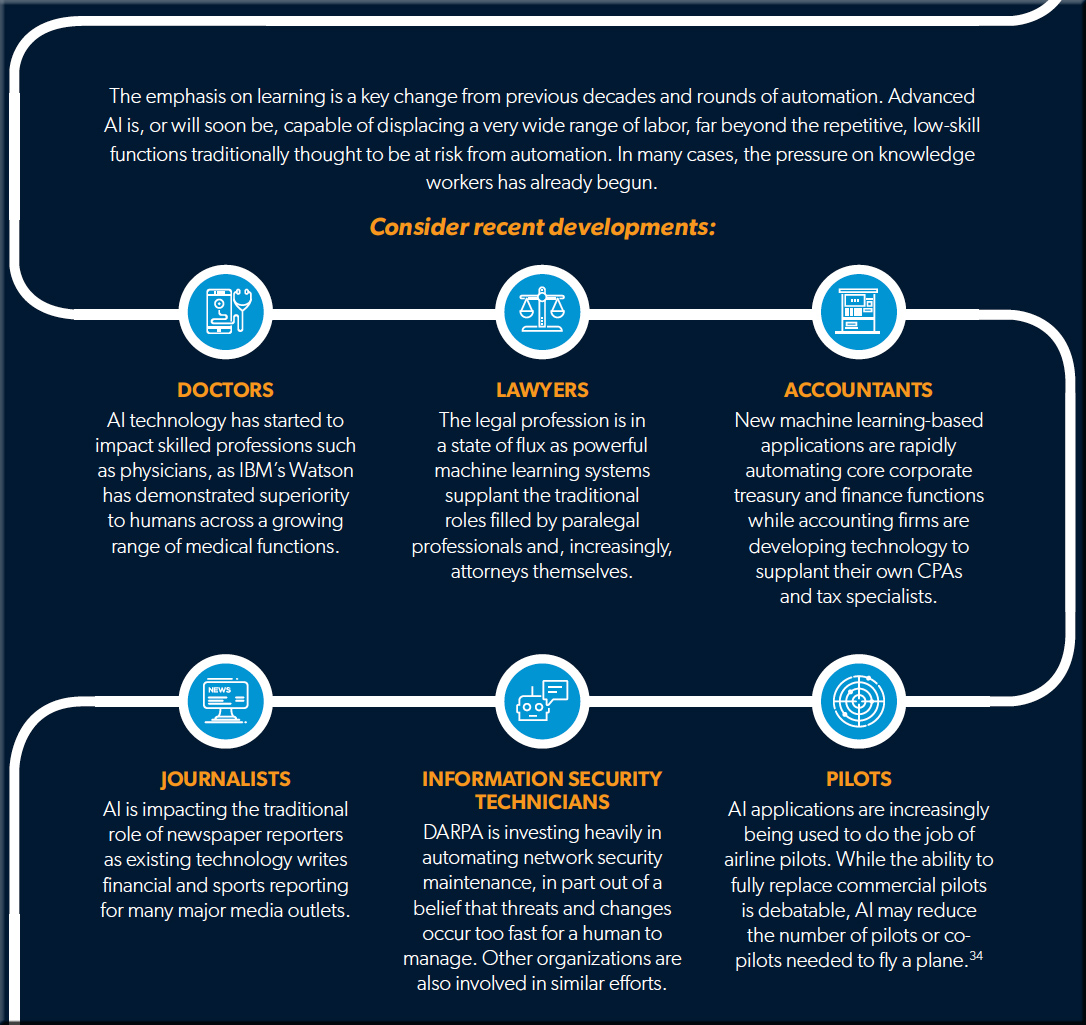
The emphasis on learning is a key change from previous decades and rounds of automation. Advanced AI is, or will soon be, capable of displacing a very wide range of labor, far beyond the repetitive, low-skill functions traditionally thought to be at risk from automation. In many cases, the pressure on knowledge workers has already begun.
Regardless of industry, however, AI is a real challenge to today’s way of thinking about work, value, and talent scarcity. AI will expand and eventually force many human knowledge workers to reinvent their roles to address issues that machines cannot process. At the same time, AI will create a new demand for skills to guide its growth and development. These emerging areas of expertise will likely be technical or knowledge-intensive fields. In the near term, the competition for workers in these areas may change how companies focus their talent strategies.