Hiperwall Introduces Cost-Effective ‘Essentials’ Video Wall Hardware and Software Packages — from hiperwall.com with thanks to Michael Farino for this resource
Hiperwall Essentials video wall bundles eliminate barriers to entry for organizations wanting enhanced collaboration, clearer communication, and the ability to make informed real-time decisions
Excerpt:
February 24, 2021 – IRVINE, Calif., – Hiperwall Inc., an industry-leader in commercialized, IP-based visualization technology, today introduces ‘Hiperwall Essentials,’ two all-inclusive video wall hardware and software bundles that get users started with a full-featured, control-room grade video wall powered by Hiperwall for just $9,995.
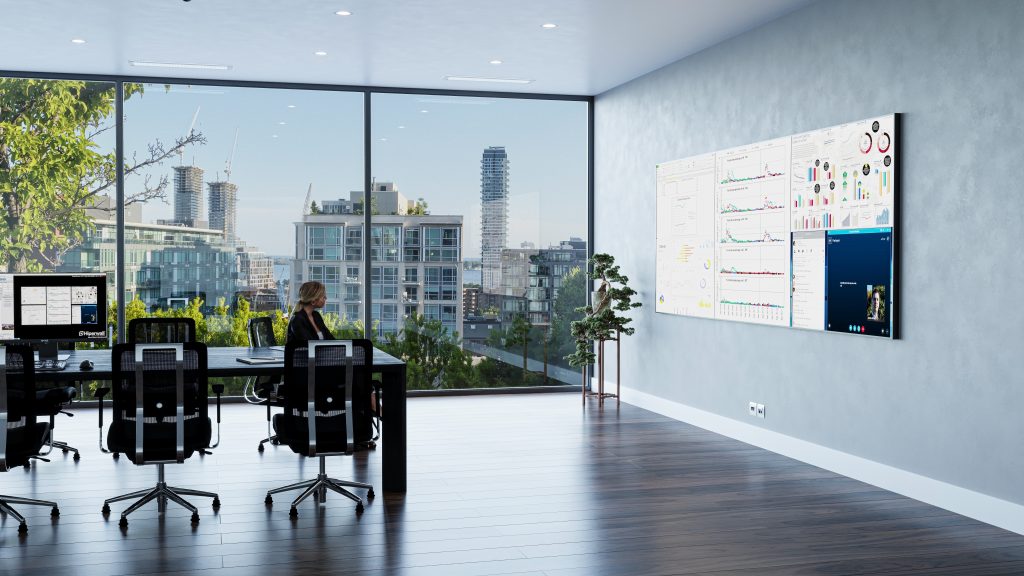
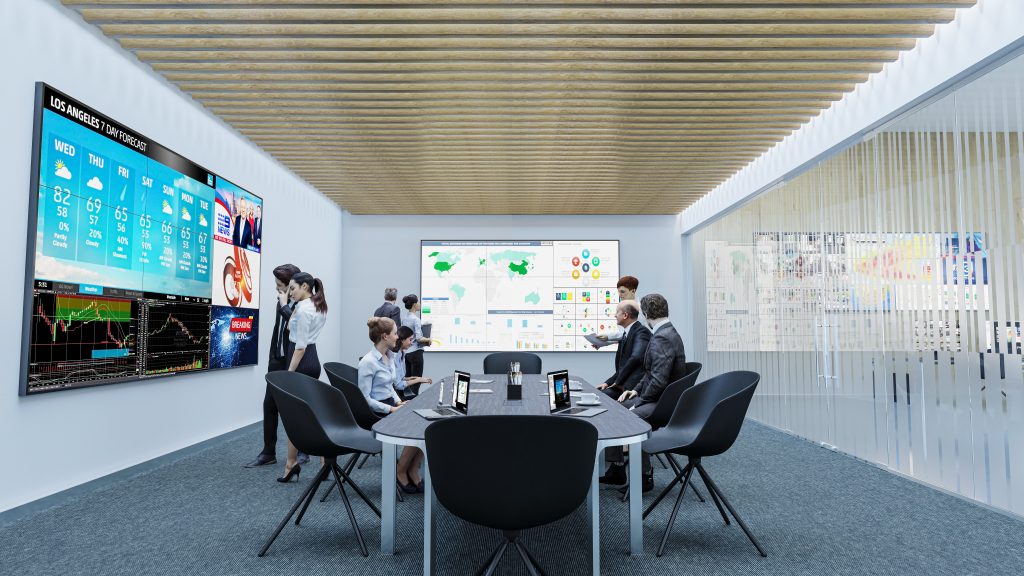
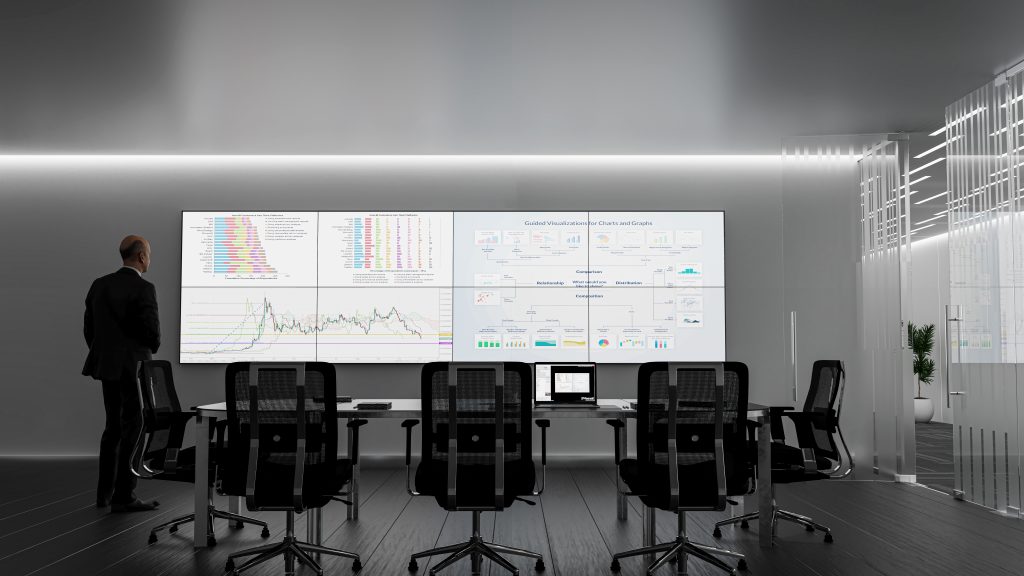
Most major decisions made in the public and private sectors are driven by vast amounts of data. Due to the volume of data sources, data complexity, and different analytics tools, video walls have become the perfect canvas for decision-makers to put all of this data together clearly to arrive at an informed decision faster and more confidently.
At a price point that effectively removes barriers to implementation for small to medium businesses, small government agencies, and local law enforcement, Hiperwall Essentials serves as a great baseline for integrating video wall technology into any organization. As dependence on the video wall grows, Hiperwall’s modular platform makes scaling the video wall footprint and capabilities seamless and cost-effective.
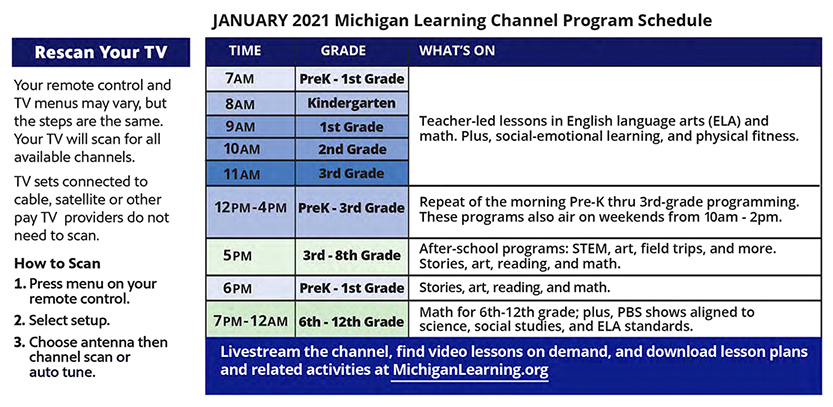
Below are some example settings:

























![The Year TV Leaped Into The Future [Roettgers]](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/BigTrendsStreaming-2020-Janko-Roettgers.jpg)







