AI plus human intelligence is the future of work — from forbes.com by Jeanne Meister
Excerpts:
- 1 in 5 workers will have AI as their co worker in 2022
- More job roles will change than will be become totally automated so HR needs to prepare today
…
As we increase our personal usage of chatbots (defined as software which provides an automated, yet personalized, conversation between itself and human users), employees will soon interact with them in the workplace as well. Forward looking HR leaders are piloting chatbots now to transform HR, and, in the process, re-imagine, re-invent, and re-tool the employee experience.
How does all of this impact HR in your organization? The following ten HR trends will matter most as AI enters the workplace…
…
The most visible aspect of how HR is being impacted by artificial intelligence is the change in the way companies source and recruit new hires. Most notably, IBM has created a suite of tools that use machine learning to help candidates personalize their job search experience based on the engagement they have with Watson. In addition, Watson is helping recruiters prioritize jobs more efficiently, find talent faster, and match candidates more effectively. According to Amber Grewal, Vice President, Global Talent Acquisition, “Recruiters are focusing more on identifying the most critical jobs in the business and on utilizing data to assist in talent sourcing.”
…as we enter 2018, the next journey for HR leaders will be to leverage artificial intelligence combined with human intelligence and create a more personalized employee experience.
From DSC:
Although I like the possibility of using machine learning to help employees navigate their careers, I have some very real concerns when we talk about using AI for talent acquisition. At this point in time, I would much rather have an experienced human being — one with a solid background in HR — reviewing my resume to see if they believe that there’s a fit for the job and/or determine whether my skills transfer over from a different position/arena or not. I don’t think we’re there yet in terms of developing effective/comprehensive enough algorithms. It may happen, but I’m very skeptical in the meantime. I don’t want to be filtered out just because I didn’t use the right keywords enough times or I used a slightly different keyword than what the algorithm was looking for.
Also, there is definitely age discrimination occurring out in today’s workplace, especially in tech-related positions. Folks who are in tech over the age of 30-35 — don’t lose your job! (Go check out the topic of age discrimination on LinkedIn and similar sites, and you’ll find many postings on this topic — sometimes with 10’s of thousands of older employees adding comments/likes to a posting). Although I doubt that any company would allow applicants or the public to see their internally-used algorithms, how difficult would it be to filter out applicants who graduated college prior to ___ (i.e., some year that gets updated on an annual basis)? Answer? Not difficult at all. In fact, that’s at the level of a Programming 101 course.
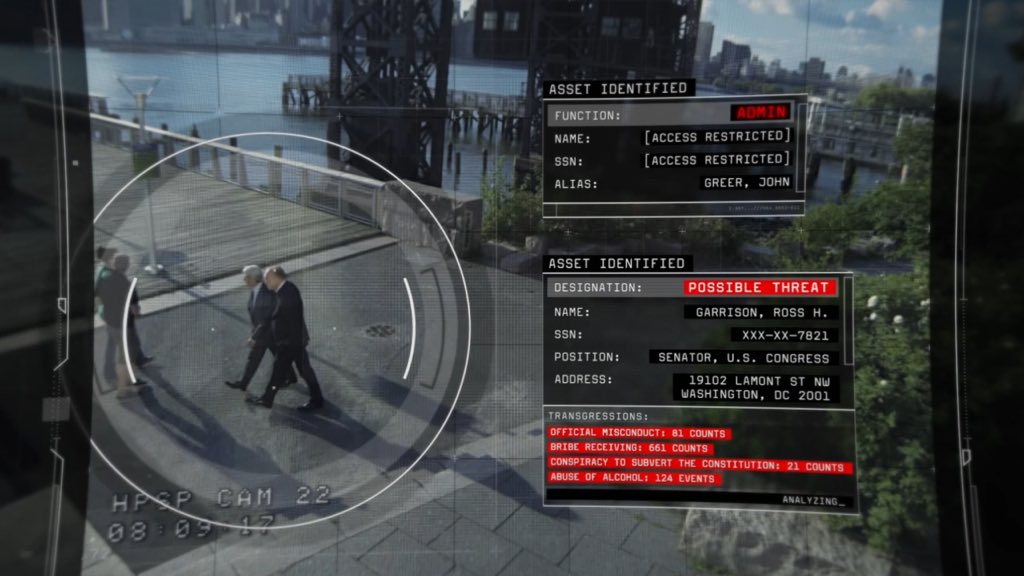
Artificial intelligence is going to supercharge surveillance – from theverge.com by James Vincent
What happens when digital eyes get the brains to match?
From DSC:
“Persons of interest” comes to mind after reading this article. Persons of interest is a clever, well done show, but still…the idea of combining surveillance w/ a super intelligent is a bit unnerving.
Artificial intelligence | 2018 AI predictions — from thomsonreuters.com
Excerpts:
- AI brings a new set of rules to knowledge work
- Newsrooms embrace AI
- Lawyers assess the risks of not using AI
- Deep learning goes mainstream
- Smart cars demand even smarter humans
- Accountants audit forward
- Wealth managers look to AI to compete and grow
Chatbots and Virtual Assistants in L&D: 4 Use Cases to Pilot in 2018 — from bottomlineperformance.com by Steven Boller
Excerpt:
- Use a virtual assistant like Amazon Alexa or Google Assistant to answer spoken questions from on-the-go learners.
- Answer common learner questions in a chat window or via SMS.
- Customize a learning path based on learners’ demographic information.
- Use a chatbot to assess learner knowledge.
Suncorp looks to augmented reality for insurance claims — from itnews.com.au by Ry Crozier with thanks to Woontack Woo for this resource
Excerpts:
Suncorp has revealed it is exploring image recognition and augmented reality-based enhancements for its insurance claims process, adding to the AI systems it deployed last year.
The insurer began testing IBM Watson software last June to automatically determine who is at fault in a vehicle accident.
…
“We are working on increasing our use of emerging technologies to assist with the insurance claim process, such as using image recognition to assess type and extent of damage, augmented reality that would enable an off-site claims assessor to discuss and assess damage, speech recognition, and obtaining telematic data from increasingly automated vehicles,” the company said.
6 important AI technologies to look out for in 2018 — from itproportal.com by Olga Egorsheva
Will businesses and individuals finally make AI a part of their daily lives?










![The Living [Class] Room -- by Daniel Christian -- July 2012 -- a second device used in conjunction with a Smart/Connected TV](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian-July-2012.jpg)