Discount Rates At Colleges Continue To Increase As Colleges Explore Alternate Pricing Strategies — from forbes.com by Lucie Lapovsky
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
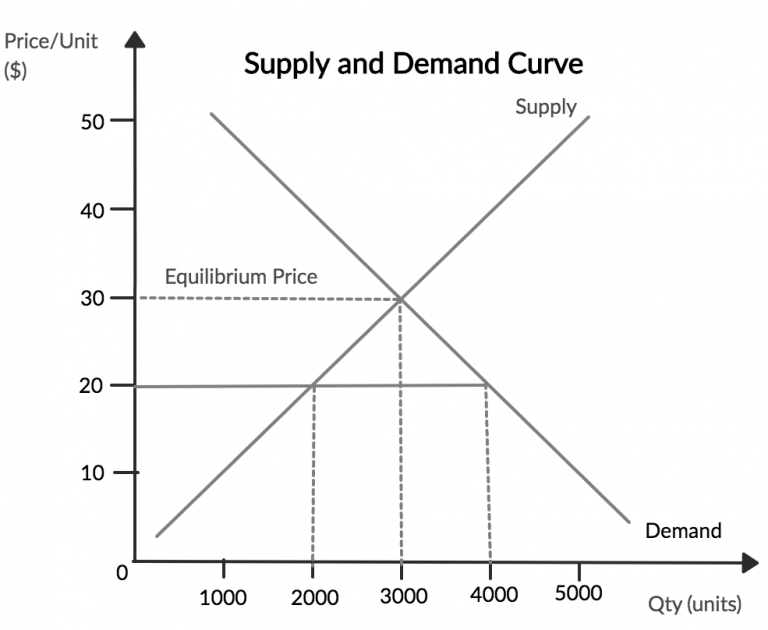
Since 2012, 65 private colleges and universities with enrollment of 500 students or more, that I know of, have reduced their tuition, and commensurately reduced their discount rate. Several more schools are planning price resets for fall 2024. Schools use this strategy to increase the number of students who will consider them, and this approach has been successful for more than 80 percent of the schools which have reduced their published price.
From DSC:
What I learned of economics in college would agree with this last bit. As the price goes down, demand goes up. And conversely, as the price goes up, demand goes down. As Lucie points out, many people don’t know about the heavily discounted prices within higher education. I’ve been fighting for price decreases for over 15 years…clearly, I haven’t had much success in that area.
Excerpts from Kristen Trader’s recent posting on LinkedIn:
(Emphasis DSC)
How liberal arts colleges can make career services a priority — from highereddive.com by John Boyer
Creating internships and focusing on short-term experiences has a big impact, the longtime undergraduate dean at the University of Chicago says.
Virginia to eliminate degree requirements for most state jobs — from hrdive.com/ by Kathryn Moody
State movement on the issue reflects ongoing private sector interest in reducing reliance on four-year degrees for hiring purposes.
GETTING STARTED WITH MICROCREDENTIALS: A PRIMER FOR HIGHER EDUCATION LEADERS — from cps.northeastern.edu by Ellen Stoddard | Allison Ruda | Emilee Trieckel | Sean R. Gallagher; with thanks to Goldie Blenstyk for this resource
3 Ways Campus Leaders Can Prepare Students for Technology Transformation in the Workforce — from campustechnology.comby Sandra Loughlin, Ph.D.
Consider these strategies for equipping students with the tech skills they will need to succeed post-graduation.
TI-ADDIE: A Trauma-Informed Model of Instructional Design — from er.educause.edu by Ali Carr-Chellman and Treavor Bogard
Adjusting the ADDIE model of instructional design specifically to accommodate trauma offers an opportunity to address the collective challenges that designers, instructors, and learners have faced during the current learning moment.











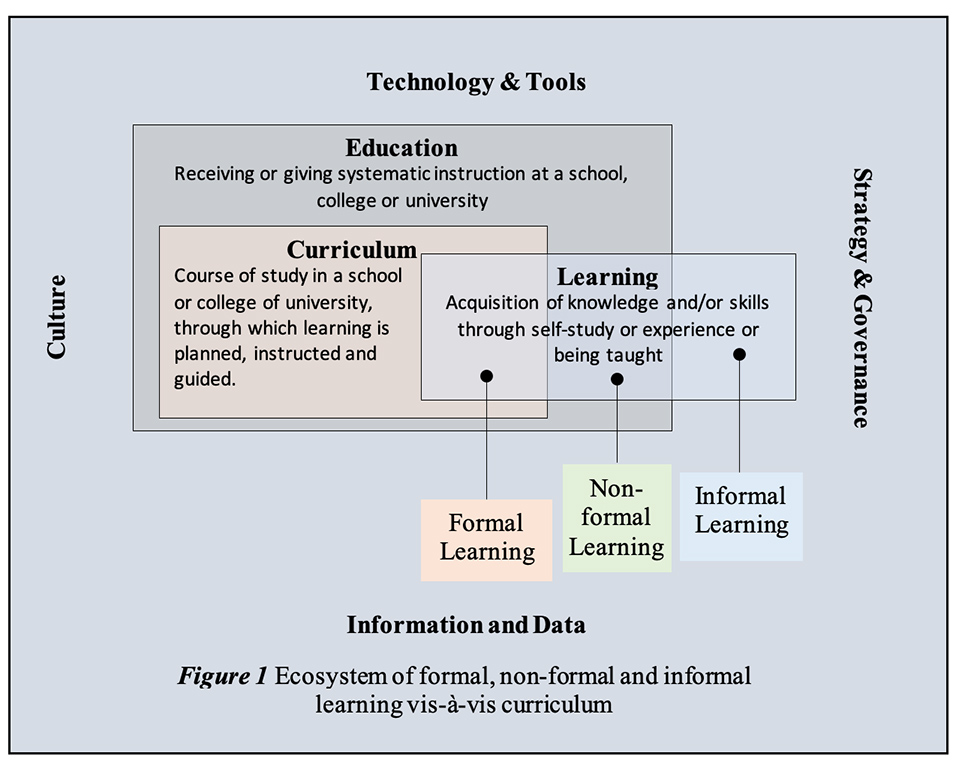
AI-assisted cheating isn’t a temptation if students have a reason to care about their own learning.
Yesterday I happened to listen to two different podcasts that ended up resonating with one another and with an idea that’s been rattling around inside my head with all of this moral uproar about generative AI:
** If we trust students – and earn their trust in return – then they will be far less motivated to cheat with AI or in any other way. **
First, the question of motivation. On the Intentional Teaching podcast, while interviewing James Lang and Michelle Miller on the impact of generative AI, Derek Bruff points out (drawing on Lang’s Cheating Lessons book) that if students have “real motivation to get some meaning out of [an] activity, then there’s far less motivation to just have ChatGPT write it for them.” Real motivation and real meaning FOR THE STUDENT translates into an investment in doing the work themselves.
…
Then I hopped over to one of my favorite podcasts – Teaching in Higher Ed – where Bonni Stachowiak was interviewing Cate Denial about a “pedagogy of kindness,” which is predicated on trusting students and not seeing them as adversaries in the work we’re doing.
So the second key element: being kind and trusting students, which builds a culture of mutual respect and care that again diminishes the likelihood that they will cheat.
…
Again, human-centered learning design seems to address so many of the concerns and challenges of the current moment in higher ed. Maybe it’s time to actually practice it more consistently. #aiineducation #higheredteaching #inclusiveteaching