An Opinionated Guide to Which AI to Use: ChatGPT Anniversary Edition — from oneusefulthing.org by Ethan Mollick
A simple answer, and then a less simple one.
If you are at all interested in generative AI and understanding what it can do and why it matters, you should just get access to OpenAI’s GPT-4 in as unadulterated and direct way as possible. Everything else comes after that.
…
Now, to be clear, this is not the free ChatGPT, which uses GPT-3.5.

1. America’s Next Top Model LLMs in Educational Settings
- PDF
Topics Discussed:
Need for a Comprehensive Student-Centric Approach
Collaboration between EdTech Companies and Educators
Personalized Learning Orchestration
Innovation and Agility of Startups vs. Resources of Big Tech
The Essential Role of AI in Transforming Education
- Video recording from Edtech Insiders
2. Hello, Mr. Chips: AI Teaching Assistants, Tutors, Coaches and Characters
- PDF
Topics discussed:
Engagement and Co-Creation
Educator Skills and AI Implementation
Teacher Empowerment and Student Creativity
Efficacy and Ethical Concerns
- Video recording from Edtech Insiders
He Was Falsely Accused of Using AI. Here’s What He Wishes His Professor Did Instead | Tech & Learning — from techlearning.com by Erik Ofgang
When William Quarterman was accused of submitting an AI-generated midterm essay, he started having panic attacks. He says his professor should have handled the situation differently.
Teaching: Practical AI strategies for the classroom — from chronicle.com by Beckie Supiano and Luna Laliberte
Here are several strategies you can try.
- Quick Hits: Several presenters suggested exercises that can be quick, easy, and fun for students. Invite your class to complete a Mad Libs using ChatGPT. It’s a playful way to leverage ChatGPT’s ability to predict the next word, giving students insight into how generative AI works on a fundamental level. You can also have your students use ChatGPT to rewrite their own writing in the tone and style of their favorite writers. This exercise demonstrates AI’s ability to mimic style and teaches students about adopting different tones in writing.
- Vetting Sources
- Grade ChatGPT
- Lead by Example
Embracing Artificial Intelligence in the Classroom — from gse.harvard.edu; via Alex Webb at Bloomberg
Generative AI tools can reflect our failure of imagination and that is when the real learning starts
Class Disrupted S5 E3: The Possibilities & Challenges of Artificial Intelligence in the Classroom — from the74million.org by Michael B. Horn & Diane Tavenner
AI expert and Minerva University senior Irhum Shafkat joins Michael and Diane to discuss where the technology is going.
Schools urged to teach children how to use AI from age of 11 — from news.sky.com by Tom Acres
Artificial intelligence tools such as ChatGPT are being used by children to help with homework and studying – and there are calls for it to become a central part of the school curriculum.
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
Schools have been urged to teach children how to use AI from the age of 11 as the technology threatens to upend the jobs market.
Rather than wait for pupils to take up computer science at GCSE, the British Computer Society (BCS, The Chartered institute for IT) said all youngsters need to learn to work with tools like ChatGPT.
The professional body for computing wants a digital literary qualification to be introduced, with a strong focus on artificial intelligence and its practical applications.
An understanding of AI should also become a key part of teacher training and headteacher qualifications, it added.
Improving Your Teaching With an AI Coach — from edutopia.org by Stephen Noonoo
New tools are leveraging artificial intelligence to help teachers glean insights into how they interact with students.
COMMENTARY
Embracing artificial intelligence in the workforce starts with higher education — from nebraskaexaminer.com by Jaci Lindburg and Cassie Mallette
When students can understand the benefit of using it effectively, and learn how to use AI to brainstorm, problem solve, and think through decision making scenarios, they can work more efficiently, make difficult decisions faster and improve a company’s production output.
It is through embracing the power and potential of AI that we can equip our students with future-ready skills. Through intentional teaching strategies that guide students to think creatively about how to use AI in their work, higher education can ensure that students are on the cutting edge in terms of using advancing technologies and being workforce ready upon graduation.
Also see:
The ChatGPT/AI Prompt Book is a resource for the UNO community that demonstrates how students can use AI in their studies and how faculty can incorporate it into their courses and daily work. The goal: to teach individuals how to be better prompt engineers and develop the skills needed to utilize this emerging technology as one of the many tools available to them in the workforce.
Two Ideas for Teaching with AI: Course-Level GPTs and AI-Enhanced Polling — from derekbruff.org by Derek Bruff
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
Might we see course-level GPTs, where the chatbot is familiar with the content in a particular course and can help students navigate and maybe even learn that material? The answer is, yes and they’re already here. Top Hat recently launched Ace, an AI-powered learning assistant embedded in its courseware platform. An instructor can activate Ace, which then trains itself on all the learning materials in the course. Students can then use Ace as a personal tutor of sorts, asking it questions about course material.
Reflections On AI Policies in Higher Education — from jeppestricker.substack.com by Jeppe Klitgaard Stricker
And Why First-Hand Generative AI Experience is Crucial for Leadership
AI is already showing far-reaching consequences for societies and educational institutions around the world. It is my contention that it is impossible to set strategic direction for AI in higher education if you haven’t yet tried working with the technology yourself. The first wave of overwhelming, profound surprise simply cannot be outsourced to other parts of the organization.
I mention this because the need for both strategic and operational guidance for generative AI is growing rapidly in higher education institutions. Without the necessary – and quite basic – personal generative AI experience, however, it becomes difficult for leadership to meaningfully direct and anchor AI in the organization.
And without clear guidance in place, uncertainty arises for all internal stakeholders about expectations and appropriate uses of AI. This makes developing an institutional AI policy not just sensible, but necessary.
A free report for educational leaders and policymakers who want to understand the AI World — from stefanbauschard.substack.com by Stefan Bauschard
And the immediate need for AI literacy

Beyond synthesizing many ideas from educational theory and AI deep learning, the report provides a comprehensive overview of developments in the field of AI, including current “exponential advances.” It’s updated through the release of Gemini and Meta’s new “Seamless” translation technology that arguably eliminates the need for most translators, and probably even the need to learn to speak another language for most purposes.
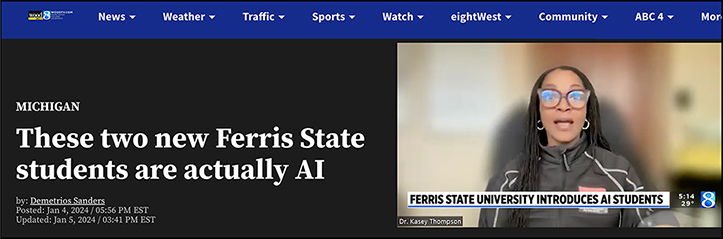
We were a mere 18 hours too late from covering an entire newscast (and news channel) that is produced with AI in a way that creates representations that are indistinguishable from what is “real” (see below) though it super-charges our comprehensive case and immediate AI literacy.
We also provide several suggestions and a potential roadmap for schools to help students prepare for an AI World where computers are substantialy smarter than them in many ways.