Microsoft teams with Khan Academy to make its AI tutor free for K-12 educators and will develop a Phi-3 math model — from venturebeat.com by Ken Yeung
Microsoft is partnering with Khan Academy in a multifaceted deal to demonstrate how AI can transform the way we learn. The cornerstone of today’s announcement centers on Khan Academy’s Khanmigo AI agent. Microsoft says it will migrate the bot to its Azure OpenAI Service, enabling the nonprofit educational organization to provide all U.S. K-12 educators free access to Khanmigo.
In addition, Microsoft plans to use its Phi-3 model to help Khan Academy improve math tutoring and collaborate to generate more high-quality learning content while making more courses available within Microsoft Copilot and Microsoft Teams for Education.
One-Third of Teachers Have Already Tried AI, Survey Finds — from the74million.org by Kevin Mahnken
A RAND poll released last month finds English and social studies teachers embracing tools like ChatGPT.
One in three American teachers have used artificial intelligence tools in their teaching at least once, with English and social studies teachers leading the way, according to a RAND Corporation survey released last month. While the new technology isn’t yet transforming how kids learn, both teachers and district leaders expect that it will become an increasingly common feature of school life.
Professors Try ‘Restrained AI’ Approach to Help Teach Writing — from edsurge.com by Jeffrey R. Young
Can ChatGPT make human writing more efficient, or is writing an inherently time-consuming process best handled without AI tools?
This article is part of the guide: For Education, ChatGPT Holds Promise — and Creates Problems.
When ChatGPT emerged a year and half ago, many professors immediately worried that their students would use it as a substitute for doing their own written assignments — that they’d click a button on a chatbot instead of doing the thinking involved in responding to an essay prompt themselves.
But two English professors at Carnegie Mellon University had a different first reaction: They saw in this new technology a way to show students how to improve their writing skills.
“They start really polishing way too early,” Kaufer says. “And so what we’re trying to do is with AI, now you have a tool to rapidly prototype your language when you are prototyping the quality of your thinking.”
He says the concept is based on writing research from the 1980s that shows that experienced writers spend about 80 percent of their early writing time thinking about whole-text plans and organization and not about sentences.
On Building AI Models for Education — from aieducation.substack.com by Claire Zau
Google’s LearnLM, Khan Academy/MSFT’s Phi-3 Models, and OpenAI’s ChatGPT Edu
This piece primarily breaks down how Google’s LearnLM was built, and takes a quick look at Microsoft/Khan Academy’s Phi-3 and OpenAI’s ChatGPT Edu as alternative approaches to building an “education model” (not necessarily a new model in the latter case, but we’ll explain). Thanks to the public release of their 86-page research paper, we have the most comprehensive view into LearnLM. Our understanding of Microsoft/Khan Academy small language models and ChatGPT Edu is limited to the information provided through announcements, leaving us with less “under the hood” visibility into their development.
AI tutors are quietly changing how kids in the US study, and the leading apps are from China — from techcrunch.com by Rita Liao
Answer AI is among a handful of popular apps that are leveraging the advent of ChatGPT and other large language models to help students with everything from writing history papers to solving physics problems. Of the top 20 education apps in the U.S. App Store, five are AI agents that help students with their school assignments, including Answer AI, according to data from Data.ai on May 21.
Is your school behind on AI? If so, there are practical steps you can take for the next 12 months — from stefanbauschard.substack.com by Stefan Bauschard
If your school (district) or university has not yet made significant efforts to think about how you will prepare your students for a World of AI, I suggest the following steps:
July 24 – Administrator PD & AI Guidance
In July, administrators should receive professional development on AI, if they haven’t already. This should include…
August 24 –Professional Development for Teachers and Staff…
Fall 24 — Parents; Co-curricular; Classroom experiments…
December 24 — Revision to Policy…
New ChatGPT Version Aiming at Higher Ed — from insidehighered.com by Lauren Coffey
ChatGPT Edu, emerging after initial partnerships with several universities, is prompting both cautious optimism and worries.
OpenAI unveiled a new version of ChatGPT focused on universities on Thursday, building on work with a handful of higher education institutions that partnered with the tech giant.
The ChatGPT Edu product, expected to start rolling out this summer, is a platform for institutions intended to give students free access. OpenAI said the artificial intelligence (AI) toolset could be used for an array of education applications, including tutoring, writing grant applications and reviewing résumés.











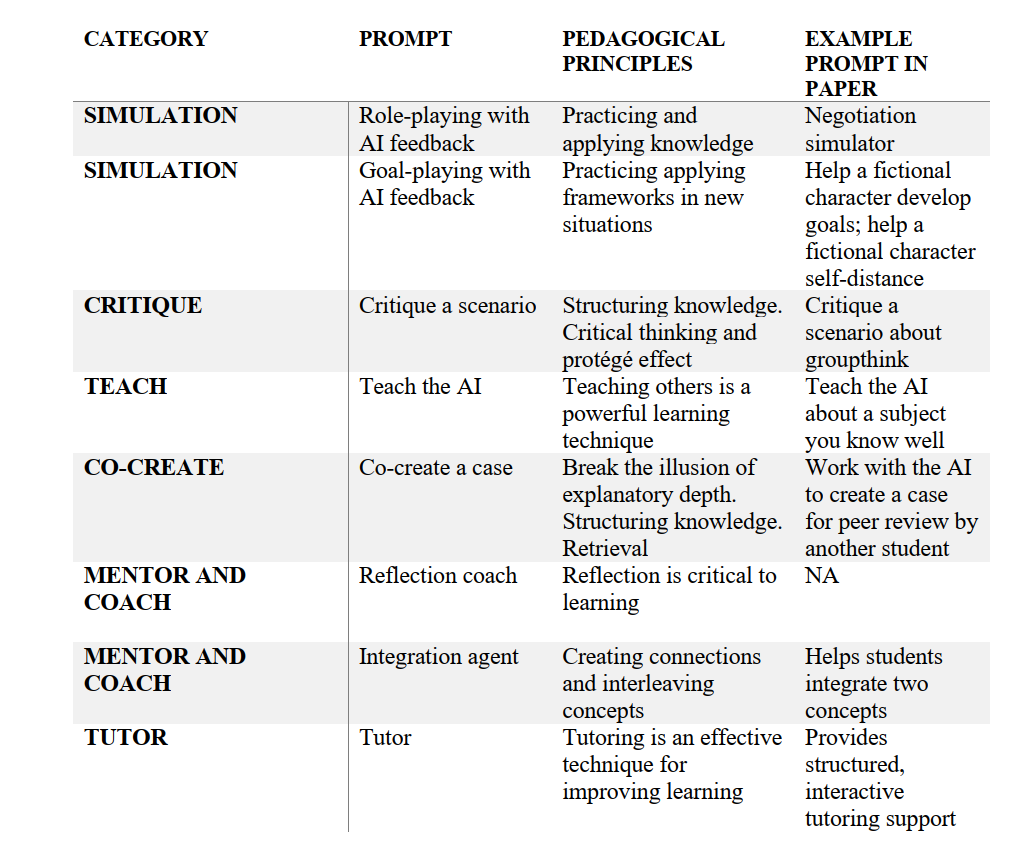

.jpg)

