The Growing Profile of Non-Degree Credentials: Diving Deeper into ‘Education Credentials Come of Age’ — from evolllution.com by Sean Gallagher
Higher education is entering a “golden age” of lifelong learning and that will mean a spike in demand for credentials. If postsecondary institutions want to compete in a crowded market, they need to change fast.
Excerpts (emphasis DSC):
One of the first levels of opportunity is simply embedding the skills that are demanded in the job market into educational programs. Education certainly has its own merits independent of professional outcomes. But critics of higher education who suggest graduates aren’t prepared for the workforce have a point in terms of the opportunity for greater job market alignment, and less of an “ivory tower” mentality at many institutions. Importantly, this does not mean that there isn’t value in the liberal arts and in broader ways of thinking—problem solving, leadership, critical thinking, analysis, and writing are among the very top skills demanded by employers across all educational levels. These are foundational and independent of technical skills.
The second opportunity is building an ecosystem for better documentation and sharing of skills—in a sense what investor Ryan Craig has termed a “competency marketplace.” Employers’ reliance on college degrees as relatively blunt signals of skill and ability is partly driven by the fact that there aren’t many strong alternatives. Technology—and the growth of platforms like LinkedIn, ePortfolios and online assessments—is changing the game. One example is digital badges, which were originally often positioned as substitutes to degrees or certificates.
Instead, I believe digital badges are a supplement to degrees and we’re increasingly seeing badges—short microcredentials that discretely and digitally document competency—woven into degree programs, from the community college to the graduate degree level.
However, it is becoming increasingly clear that the market is demanding more “agile” and shorter-form approaches to education. Many institutions are making this a strategic priority, especially as we read the evolution of trends in the global job market and soon enter the 2020s.
Online education—which in all its forms continues to slowly and steadily grow its market share in terms of all higher ed instruction—is certainly an enabler of this vision, given what we know about pedagogy and the ability to digitally document outcomes.
In addition, 64 percent of the HR leaders we surveyed said that the need for ongoing lifelong learning will demand higher levels of education and more credentials in the future.
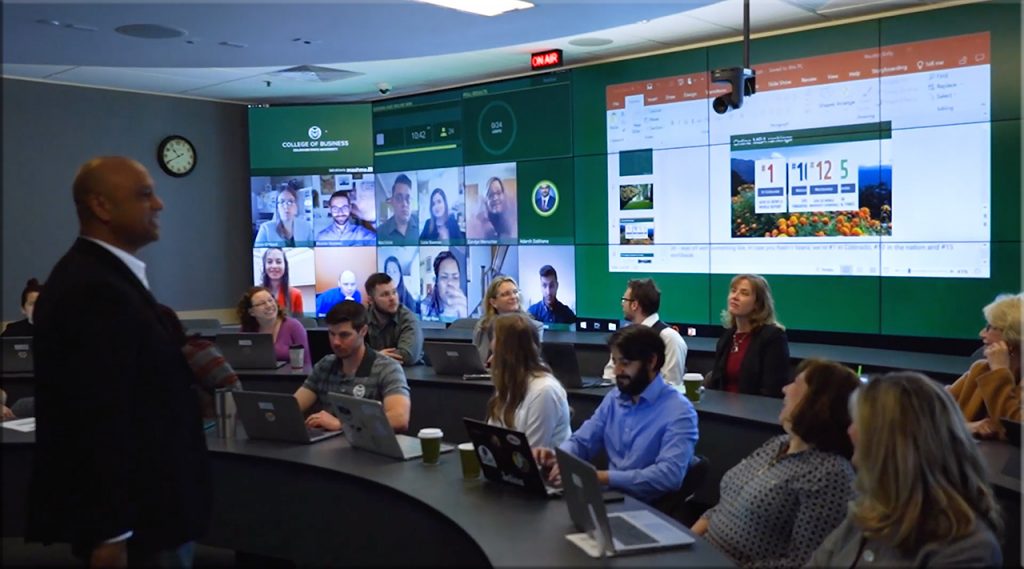
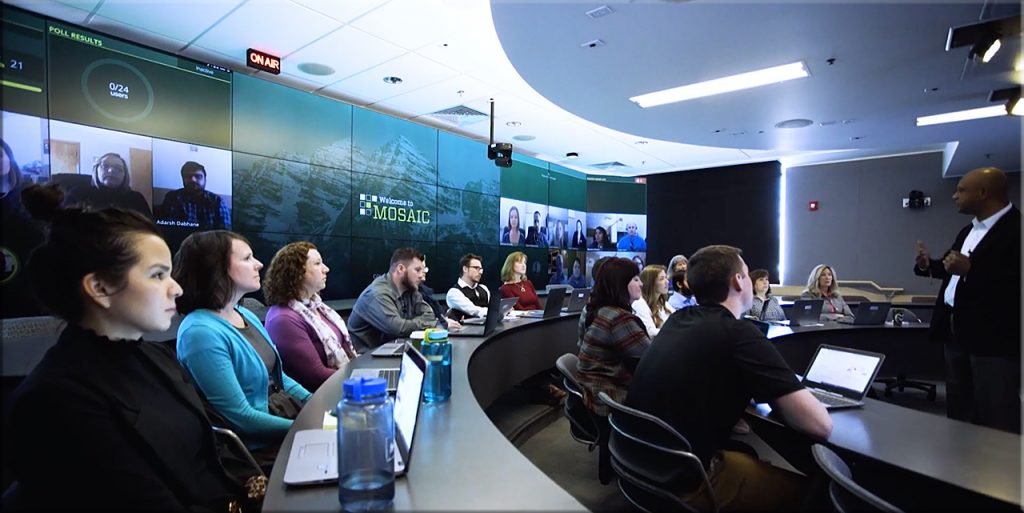
Along these lines of online-based collaboration and learning,
go to the 34 minute mark of this video:
From DSC:
The various pieces are coming together to build the next generation learning platform. Although no one has all of the pieces yet, the needs/trends/signals are definitely there.

Addendums on 4/20/19: