Building Learning Communities 2011 Keynote: Dr. Eric Mazur — from November Learning
Excerpt:
Today, we are officially relaunching our opening keynote from BLC11 with Dr. Eric Mazur. Dr. Mazur is the Area Dean of Applied Physics and Balkanski Professor of Physics and Applied Physics at Harvard University in Cambridge, MA.
In his keynote, Dr. Mazur shares his vast research on teaching and learning. Students in Dr. Mazur’s class are moving far away from the traditional stand and deliver lectures given in many k-12 and university classrooms around the world, and they are gaining a much deeper understanding of the material being taught in the process.
As you watch this video, we invite you to take some time and respond to one or more of the following questions…
From DSC:
What I understood the key points to be:
- Teaching and learning should not be about information transfer alone; that is, it’s not about simply having students “parrot back” the information. That doesn’t lead to true learning and long-term retention.
- The more a teacher is an expert in his/her content, the more difficulty this teacher has in understanding how a first time learner in this subject struggles
- Rather we need to guide and use peer instruction/social learning/collaboration amongst students to construct learning and then be able to apply/transfer that learning to a different context
- Lecturing is not an effective way to create a long term retention of information
- Peer instruction/human interaction creates effective learning
- “The plural of anecdotes is not data.”
- Eric is seeking data and feedback to sharpen his theories of how to optimize learning
- Technology serves pedagogy — technology should afford a new mode of learning
- Towards that end, Eric and team working on “Peer instruction 2.0”
- How do I design good questions? Optimize the discussions? Manage time? Insure learning is taking place?
- Eric is working with several other colleagues to create a system for building and using data analytics to give useful information to instructor about who’s “getting it” and who isn’t; about how we learn
- Peer instruction not without issues — how people group themselves and who students choose to collaborate with can be problematical
- Why not have the system do the pairing/grouping?
- System uses algorithms, facial recognition, posture analysis; cameras, microphones
- Surveys also used
- The system is attempting to help Eric and his team learn about learning
- The system being used at Harvard and by invitation only
Eric ended with a summary of the 2 key messages:
- Education is not about lecturing
- We can move way beyond the current technologies and use new methods and technologies to actively manage learning as it happens
From DSC:
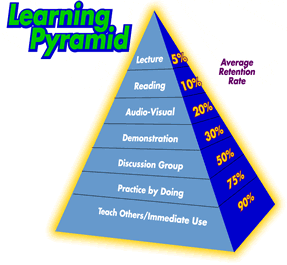
After listening to this lecture, the graphic below captures a bit of what he’s getting at and reflects some of my thinking on this subject as well. That is, we need diagnostic tools — along the lines of those a mechanic might use on our cars to ascertain where the problems/issues are: