Accenture announces jaw-dropping $3 billion investment in AI — from venturebeat.com by Carl Franzen; via Superhuman
Excerpt:
The generative AI announcements are coming fast and furious these days, but among the biggest in terms of sheer dollar commitments just landed: Accenture, the global professional services and consulting giant, today announced it will invest $3 billion (with a “b”!) in AI over the next three years in building out its team of AI professionals and AI-focused solutions for its clients.
“There is unprecedented interest in all areas of AI, and the substantial investment we are making in our Data & AI practice will help our clients move from interest to action to value, and in a responsible way with clear business cases,” said Julie Sweet, Accenture’s chairwoman and CEO.
Also related/see:
Artificial intelligence creates 40,000 new roles at Accenture — from computerweekly.com by Karl Flinders
Accenture is planning to add thousands of AI experts to its workforce as part of a $3bn investment in its data and artificial intelligence practice
Why leaders need to evolve alongside generative AI — from fastcompany.com by Kelsey Behringer
Even if you’re not an educator, you should not be sitting on the sidelines watching the generative AI conversation being had around you—hop in.
Excerpts (emphasis DSC):
Leaders should be careful to watch and support education right now. At the end of the day, the students sitting in K-12 and college classrooms are going to be future CPAs, lawyers, writers, and teachers. If you are parenting a child, you have skin in the game. If you use professional services, you have skin in the game. When it comes to education, we all have skin in the game.
…
Students need to master fundamental skills like editing, questioning, researching, and verifying claims before they can use generative AI exceptionally well.
GenAI & Education: Enhancement, not Replacement — from drphilippahardman.substack.com by Dr. Philipa Hardman
How to co-exist in the age of automation
Excerpts (emphasis DSC):
[On 6/15/23, I joined] colleagues from OpenAI, Google, Microsoft, Stanford, Harvard and other others at the first meeting of the GenAI Summit. Our shared goal [was] to help to educate universities & schools in Europe about the impact of Generative AI on their work.
…how can we effectively communicate to education professionals that generative AI will enhance their work rather than replace them?
A recent controlled study found that ChatGPT can help professionals increase their efficiency in routine tasks by ~35%. If we keep in mind that the productivity gains brought by the steam engine in the nineteenth century was ~25%, this is huge.
As educators, we should embrace the power of ChatGPT to automate the repetitive tasks which we’ve been distracted by for decades. Lesson planning, content creation, assessment design, grading and feedback – generative AI can help us to do all of these things faster than ever before, freeing us up to focus on where we bring most value for our students.
Google, one of AI’s biggest backers, warns own staff about chatbots — from reuters.com by Jeffrey Dastin and Anna Tong
Excerpt:
SAN FRANCISCO, June 15 (Reuters) – Alphabet Inc (GOOGL.O) is cautioning employees about how they use chatbots, including its own Bard, at the same time as it markets the program around the world, four people familiar with the matter told Reuters.
The Google parent has advised employees not to enter its confidential materials into AI chatbots, the people said and the company confirmed, citing long-standing policy on safeguarding information.
The economic potential of generative AI: The next productivity frontier — from mckinsey.com
Generative AI’s impact on productivity could add trillions of dollars in value to the global economy—and the era is just beginning.
Preparing for the Classrooms and Workplaces of the Future: Generative AI in edX — from campustechnology.com by Mary Grush
A Q&A with Anant Agarwal
Adobe Firefly for the Enterprise — Dream Bigger with Adobe Firefly.
Dream it, type it, see it with Firefly, our creative generative AI engine. Now in Photoshop (beta), Illustrator, Adobe Express, and on the web.
Apple Vision Pro, Higher Education and the Next 10 Years — from insidehighered.com by Joshua Kim
How this technology will play out in our world over the next decade.
Zoom can now give you AI summaries of the meetings you’ve missed — from theverge.com by Emma Roth
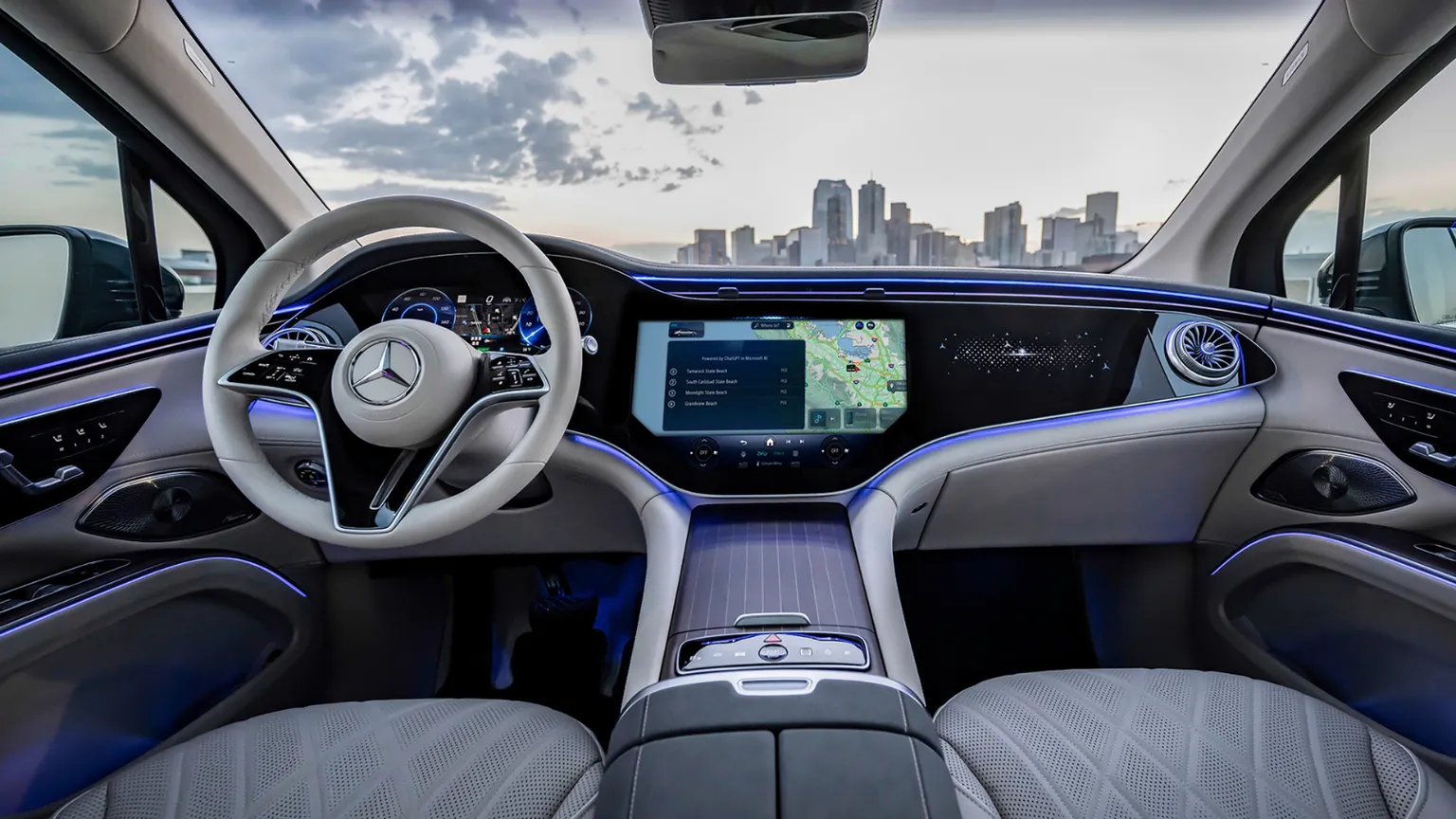
Mercedes-Benz Is Adding ChatGPT to Cars for AI Voice Commands — from decrypt.co by Jason Nelson; via Superhuman
The luxury automaker is set to integrate OpenAI’s ChatGPT chatbot into its Mercedes-Benz User Experience (MBUX) feature in the U.S.



















AI-assisted cheating isn’t a temptation if students have a reason to care about their own learning.
Yesterday I happened to listen to two different podcasts that ended up resonating with one another and with an idea that’s been rattling around inside my head with all of this moral uproar about generative AI:
** If we trust students – and earn their trust in return – then they will be far less motivated to cheat with AI or in any other way. **
First, the question of motivation. On the Intentional Teaching podcast, while interviewing James Lang and Michelle Miller on the impact of generative AI, Derek Bruff points out (drawing on Lang’s Cheating Lessons book) that if students have “real motivation to get some meaning out of [an] activity, then there’s far less motivation to just have ChatGPT write it for them.” Real motivation and real meaning FOR THE STUDENT translates into an investment in doing the work themselves.
…
Then I hopped over to one of my favorite podcasts – Teaching in Higher Ed – where Bonni Stachowiak was interviewing Cate Denial about a “pedagogy of kindness,” which is predicated on trusting students and not seeing them as adversaries in the work we’re doing.
So the second key element: being kind and trusting students, which builds a culture of mutual respect and care that again diminishes the likelihood that they will cheat.
…
Again, human-centered learning design seems to address so many of the concerns and challenges of the current moment in higher ed. Maybe it’s time to actually practice it more consistently. #aiineducation #higheredteaching #inclusiveteaching