How to Use Logic Pro X: The Ultimate Guide for Beginners — from soundswow.com by Donovan Sharpe; with thanks to Yana Mogyla for this resource. Yana is the content manager at SoundsWow — “a resource blog dedicated to helping individual musicians build home recording studios.”
Excerpts:
Logic Pro X is one of the best DAWs for music creation and production. It’s an extremely capable tool that provides you with everything you need to make music professionally in any way you can dream up.
With all this power at your fingertips, getting started with Logic Pro X can be challenging if you don’t have any experience. This guide was written with beginners in mind and will direct you through all the first steps to using the app.
.
Which trends are on your radar? Fantastic resource for #HigherEducation about the changing ecology: Higher Learning Commission’s Annual Trends Report. https://t.co/Lzgph6u3lP
— Melanie Booth, Ed.D. (@boothmelanie) March 25, 2023
Designing Virtual Edtech Faculty Development Workshops That Stick: 10 Guiding Principles — from er.educause.edu by Tolulope (Tolu) Noah
These ten principles offer guidance on ways to design and facilitate effective and engaging virtual workshops that leave faculty feeling better equipped to implement new edtech tools.
Excerpt:
I share here ten guiding principles that have shaped my design and facilitation of virtual synchronous edtech workshops. These guiding principles are based on lessons learned in both my previous role as a professional learning specialist at a major technology company and my current role as a faculty developer at a university. In the spirit of James M. Lang’s book Small Teaching, my hope is that the principles shared here may prompt reflection on the small yet impactful moves academic technology specialists, instructional designers, and educational developers can make to create virtual learning experiences whereby faculty leave feeling better equipped to implement the edtech tools they have learned.
Somewhat relevant/see:
Evidence-Based Learning Design 101 — by Dr. Philippa Hardman
A practical guide on how to bake the science of learning into the art of course design
Excerpt:
As I reflect on the experience and what I’ve learned so far, I thought I’d share a response to the question I probably get asked most: what process do you use to go from an idea to a designed learning experience?
So, let’s do a rapid review of the four step process I and my bootcamp alumni use – aka the DOMS™? process – to go from zero to a designed learning experience.
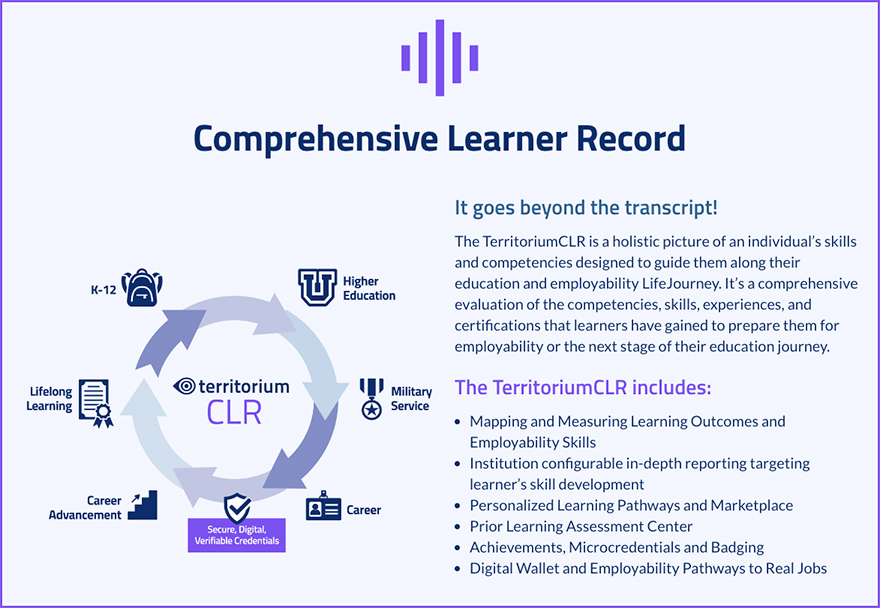
Territorium Introduces AI-Powered System to Track Skills and Competencies from K–12 to Career — from campustechnology.com by Kate Lucariello
Excerpt:
Global ed tech provider Territorium has launched LifeJourney, a suite of AI-powered tools for users to keep track of education, job skills, and career readiness capabilities. With the LifeJourney toolkit’s comprehensive individual records all in one place, students can provide quick and easily accessible information to prospective employers, according to the company. The suite of tools keeps track of progress and achievements from K–12 through higher education and career readiness.
From DSC:
This type of comprehensive learner record is a piece of the vision that I’ve been tracking at “Learning from the Living [Class] Room” — where I call it a Cloud-Based Learner Profile.
Also relevant/see:
College Accreditation 101: How It Works & Why It Matters — from business-essay.com; with thanks to Lili North for this resource
Excerpt:
Entering a prestigious college and getting a quality education is one of the top priorities for high school graduates. But how do you know if the college you are considering is really worth it?
Well, luckily, there is accreditation: a process of evaluating educational institutions. Accreditation is an important factor to consider when selecting a college: after all, unaccredited schools don’t provide you with widely recognized diplomas and can leave you with insufficient knowledge and skills.
Want to know more? You’re in the right place! This article covers the essential information every college applicant should know about accreditation.
Also relevant/see:
- Building a Microcredential Program Framework to Meet the Needs of a Changing Academic Landscape — from campustechnology.com by Justin Louder
From curriculum to technology concerns, consider these essentials for creating alternative education opportunities at your institution. - Lessons Learned from Communities Accelerating Pathways to Credentials — from accelerate-ed.org with thanks to Tom Vander Ark from GettingSmart.com for this resource
Addendum on 3/18/23:
Credentialing Everything: A Primer on Learning and Employment Records and Digital Wallets — from gettingsmart.com by Nate McClennen and Rachelle Dené Poth
Key Points
- Credentials and learner records are accelerating the shift to competency-based learning.
- They help learners manage unbundled learning by collecting evidence from multiple providers and provide quicker and more personalized onramps to high-wage employment.
Measuring Learning Growth: Competencies and Standards — from gettingsmart.com by Nate McClennen and Rebecca Midles
Key Points
- The role of competencies has become increasingly important as employers, students and educators realize the impact of transferable skill deficit in young people.
- The challenge, however, becomes implementation.