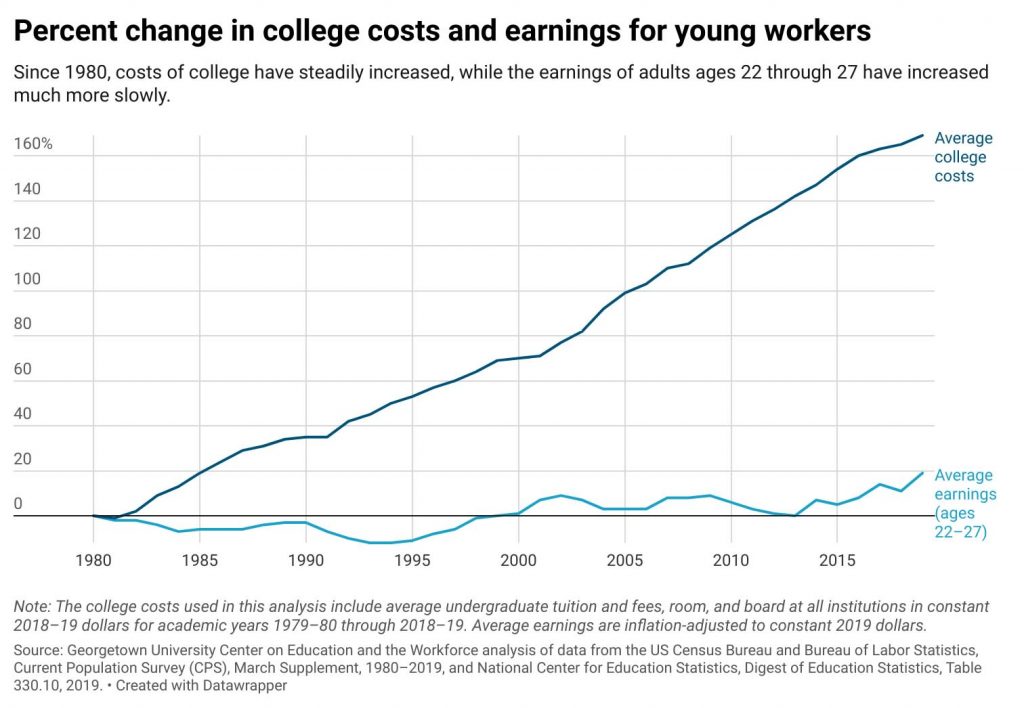
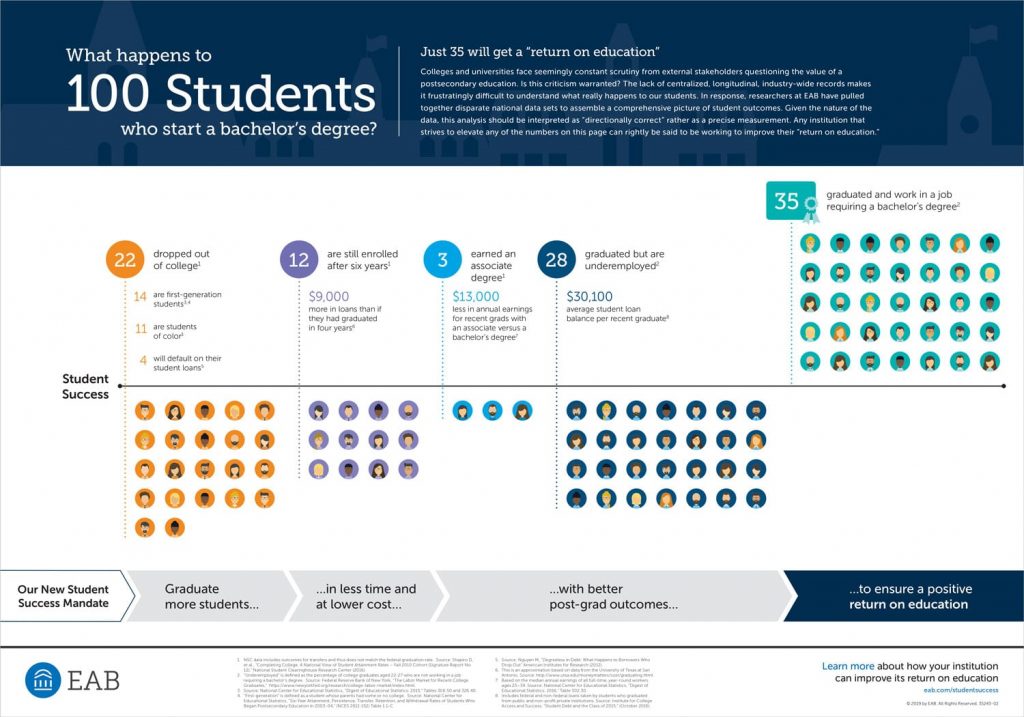
“Unpaid internships should be illegal:” Why colleges should reconsider unpaid internships. — from newamerica.org by Mauriell H. Amechi and Iris Palmer; with thanks to Goldie Blumenstyk for this resource
Excerpts:
College leaders must do more to facilitate access to paid work experience, especially for historically underserved, low-income, and racially minoritized student populations.
- Require all internships offered through career services to be paid. The inequitable practice of not paying interns makes such opportunities impossible to access for many students. Colleges should require that internships they offer be paid for by the employer or through matching funds from the college. Paying interns for their time is the right thing to do and the best way to start creating access for all students.
- Maintain some on-campus internship opportunities to ease transportation and care needs and offer on-campus care.
- Provide shuttles, transit passes, or travel stipends to internship sites.
- Consider working with employers to make internships renewable across semesters.
- Consider student populations that are typically excluded from internships.
- Document what works to create sustainable funding streams.