Social media as a learning tool: Five suggested sses for the classroom — from frontierinternet.com; with thanks to Laura Tscholl, Communications Specialist | The Gateway for this resource




Social media as a learning tool: Five suggested sses for the classroom — from frontierinternet.com; with thanks to Laura Tscholl, Communications Specialist | The Gateway for this resource
From DSC:
I have often reflected on differentiation or what some call personalized learning and/or customized learning. How does a busy teacher, instructor, professor, or trainer achieve this, realistically?
It’s very difficult and time-consuming to do for sure. But it also requires a team of specialists to achieve such a holy grail of learning — as one person can’t know it all. That is, one educator doesn’t have the necessary time, skills, or knowledge to address so many different learning needs and levels!
Educators and trainers have so many things on their plates that it’s very difficult to come up with _X_ lesson plans/agendas/personalized approaches, etc. On the other side of the table, how do students from a vast array of backgrounds and cognitive skill levels get the main points of a chapter or piece of text? How can they self-select the level of difficulty and/or start at a “basics” level and work one’s way up to harder/more detailed levels if they can cognitively handle that level of detail/complexity? Conversely, how do I as a learner get the boiled down version of a piece of text?
Well… just as with the flipped classroom approach, I’d like to suggest that we flip things a bit and enlist teams of specialists at the publishers to fulfill this need. Move things to the content creation end — not so much at the delivery end of things. Publishers’ teams could play a significant, hugely helpful role in providing customized learning to learners.
Some of the ways that this could happen:
Use an HTML like language when writing a textbook, such as:
<MainPoint> The text for the main point here. </MainPoint>
<SubPoint1>The text for the subpoint 1 here.</SubPoint1>
<DetailsSubPoint1>More detailed information for subpoint 1 here.</DetailsSubPoint1>
<SubPoint2>The text for the subpoint 2 here.</SubPoint2>
<DetailsSubPoint2>More detailed information for subpoint 2 here.</DetailsSubPoint2>
<SubPoint3>The text for the subpoint 3 here.</SubPoint3>
<DetailsSubPoint3>More detailed information for subpoint 3 here.</DetailsSubPoint1>
<SummaryOfMainPoints>A list of the main points that a learner should walk away with.</SummaryOfMainPoints>
<BasicsOfMainPoints>Here is a listing of the main points, but put in alternative words and more basic ways of expressing those main points. </BasicsOfMainPoints>
<Conclusion> The text for the concluding comments here.</Conclusion>
<BasicsOfMainPoints> could be called <AlternativeExplanations>
Bottom line: This tag would be to put things forth using very straightforward terms.
Another tag would be to address how this topic/chapter is relevant:
<RealWorldApplication>This short paragraph should illustrate real world examples
of this particular topic. Why does this topic matter? How is it relevant?</RealWorldApplication>
On the students’ end, they could use an app that works with such tags to allow a learner to quickly see/review the different layers. That is:
It’s like the layers of a Microsoft HoloLens app of the human anatomy:
Or it’s like different layers of a chapter of a “textbook” — so a learner could quickly collapse/expand the text as needed:
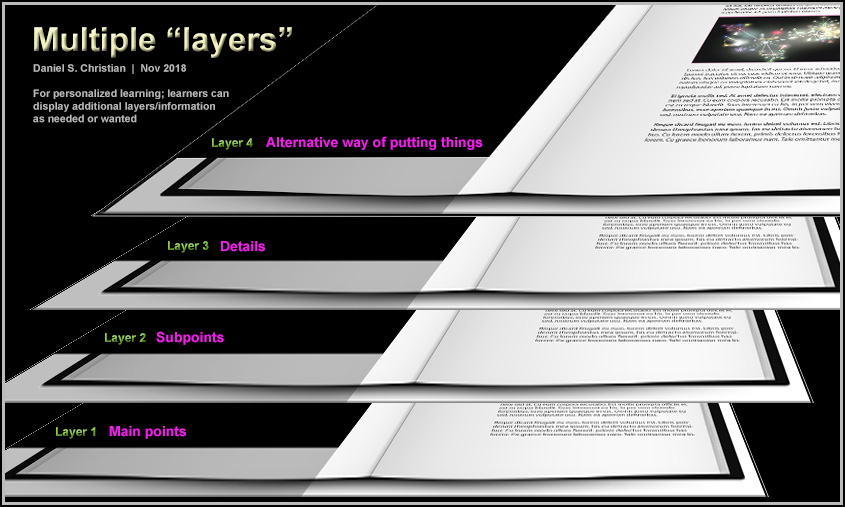
This approach could be helpful at all kinds of learning levels. For example, it could be very helpful for law school students to obtain outlines for cases or for chapters of information. Similarly, it could be helpful for dental or medical school students to get the main points as well as detailed information.
Also, as Artificial Intelligence (AI) grows, the system could check a learner’s cloud-based learner profile to see their reading level or prior knowledge, any IEP’s on file, their learning preferences (audio, video, animations, etc.), etc. to further provide a personalized/customized learning experience.
To recap:
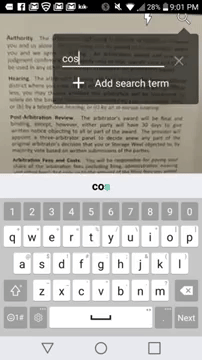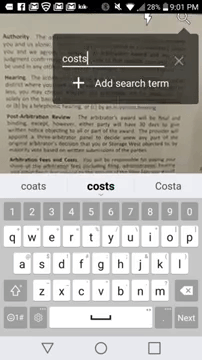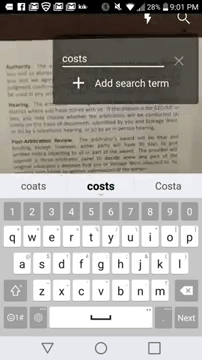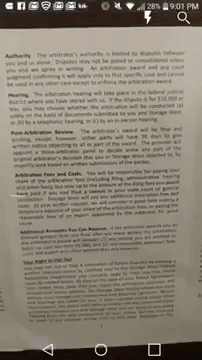
This Android app lets you search for specific words in books & documents via augmented reality — from mobile-ar.reality.news by Tommy Palladino
Excerpt:
One of the neatest tricks available in Google Lens, an app that can identify and interpret real world information, is the ability to copy text from the app’s camera view and paste it into a digital document.
And while the computer vision assistance of Google Lens takes care of the copy and paste function in augmented reality, a new mobile app from Find It Software fulfills the find function directly on printed documents in real time.

Production Values for Audio Podcasts, Part I — from learningsolutionsmag.com by Jeff D’Anza
Excerpts:
There are a number of production values that narrative podcasters find effective for grabbing listener attention and keeping their audiences engaged in the story; you could think of these as technical elements of professional audio quality. They range from techniques for improving content when applied to script writing to methods applied to audio recording and editing. The most successful professional podcasters use these elements to create immersion in the audio environment and to eliminate audio distraction. The result is the creation of a kind of audio theater. Here are four basic practices to embrace while creating your narrative podcasts.
Production Values for Audio Podcasts, Part II — from learningsolutionsmag.com by Jeff D’Anza
Excerpts:
In this article, I will continue with more production tricks that can substantially increase the quality of your narrative podcasts.
Use music to reset scenes
It’s not revolutionary to suggest that learners tend to have short attention spans, and the case is no different when it comes to narrative podcasts. Every so often you need to reset your learners’ brains in order to keep their attention level high.
One excellent way to accomplish this is through the use of musical breaks. Music breaks can function as a type of auditory palate cleanser, allowing the brain a few moments to stop focusing on information that is being presented and prepare the learner to be ready for the next section of content.
Also:
From DSC:
Seems to me there’s some wisdom here for instructional designers as well as professors, teachers, and trainers who are creating learning/training related content and/or who are flipping their classrooms.
100 things students can create to demonstrate what they know — from teachthought.com
Excerpt:
[Here] is a diverse list adapted from resources found at fortheteachers.org of potential student products or activities learners can use to demonstrate their mastery of lesson content. The list also offers several digital tools for students to consider using in a technology-enriched learning environment.
Delaying the grade: How to get students to read feedback — from cultofpedagogy.com by Kristy Louden
Excerpt:
This meant that I could return papers with comments but without grades.
And from this a whole new system was born: Return papers to students with only feedback. Delay the delivery of the actual grade so student focus moves from the grade to the feedback.
The simple act of delaying the grade meant that students had to think about their writing. They had to read their own writing—after a few weeks away from it—and digest my comments, which allowed them to better recognize what they did well or not so well. The response from students was extremely positive; they understood the benefit of rereading their essays and paying attention to feedback. One boy said, “Mrs. Louden, you’re a genius. I’ve never read what a teacher writes on my essay before, and now I have to.”
From DSC:
I’m including higher ed in the tags here…as this could be effective for college students as well. College students who have long played the game of getting the grade…simply playing the system and putting the ownership and development of their learning much lower on the priority list. Let’s help students stop outsourcing their learning.
Writing Resources from the “State of Writing” — from stateofwriting.com with thanks to Mary Bennett who mentions that this site is an “incredibly useful resource with tips and its own collection of writing and grammar guides.”
Some of the useful sections include resources regarding:
From DSC:
I vote that we change the color that we grade papers — whether on paper (harcopy) or whether via digitally/electronically-based annotations — from red to green. Why? Because here’s how I see the colors:
From DSC:
This application looks to be very well done and thought out! Wow!
Check out the video entitled “Interactive Ink – Enables digital handwriting“ — and you may also wonder whether this could be a great medium/method of having to “write things down” for better information processing in our minds, while also producing digital work for easier distribution and sharing!
Wow! Talk about solid user experience design and interface design! Nicely done.
Below is an excerpt of the information from Bella Pietsch from anthonyBarnum Public Relations
Imagine a world where users interact with their digital devices seamlessly, and don’t suffer from lag and delayed response time. I work with MyScript, a company whose Interactive Ink tech creates that world of seamless handwritten interactivity by combining the flexibility of pen and paper with the power and productivity of digital processing.
According to a recent forecast, the global handwriting recognition market is valued at a trillion-plus dollars and is expected to grow at an almost 16 percent compound annual growth rate by 2025. To add additional context, the new affordable iPad with stylus support was just released, allowing users to work with the $99 Apple Pencil, which was previously only supported by the iPad Pro.
Check out the demo of Interactive Ink using an Apple Pencil, Microsoft Surface Pen, Samsung S Pen or Google Pixelbook Pen here.
Interactive Ink’s proficiencies are the future of writing and equating. Developed by MyScript Labs, Interactive Ink is a form of digital ink technology which allows ink editing via simple gestures and providing device reflow flexibility. Interactive Ink relies on real-time predictive handwriting recognition, driven by artificial intelligence and neural network architectures.
Apple Special Event. March 27, 2018.
From Lane Tech College Prep High School, Chicago.
From DSC:
While it was great to see more Augmented Reality (AR) apps in education and to see Apple putting more emphasis again on educational-related endeavors, I’m doubtful that the iPad is going to be able to dethrone the Chromebooks. Apple might have better results with a system that can be both a tablet device and a laptop and let students decide which device to use and when.
Also see:
Here are the biggest announcements from Apple’s education event — from engadget.com by Chris Velazco
The new iPad was only the beginning.
Apple’s Education-Focused iPad Event Pushes Augmented Reality Further into the Classroom — from next.reality.news by Tommy Palladino
Excerpt:
At Apple’s education event in Chicago on Tuesday, augmented reality stood at the head of the class among the tech giant’s new offerings for the classroom.
The company showcased a number of ARKit-enabled apps that promise to make learning more immersive. For example, the AR mode for Froggipedia, expected to launch on March 30 for $3.99 on the App Store, will allow students to view and dissect a virtual frog’s anatomy. And a new update to the GeoGebra app brings ARKit support to math lessons.
Meanwhile, the Free Rivers app from the World Wildlife Federation enables students to explore miniature landscapes and learn about various ecosystems around the world.
In addition, as part of its Everyone Can Code program, Apple has also updated its Swift Playgrounds coding app with ARKit support, enabling students to begin learning to code via an ARKit module, according to a report from The Verge.
Apple’s Education Page…which covers what was announced (at least as of 3/30/18)
Comparing Apple, Google and Microsoft’s education plays — from techcrunch.com by Brian Heater
Excerpt:
[The 3/27/18] Apple event in Chicago was about more than just showing off new hardware and software in the classroom — the company was reasserting itself as a major player in education. The category has long been a lynchpin in Apple’s strategy — something that Steve Jobs held near and dear.
Any ’80s kid will tell you that Apple was a force to be reckoned with — Apple computers were mainstays in computer labs across the country. It’s always been a good fit for a company focused on serving creators, bringing that extra bit of pizzazz to the classroom. In recent years, however, there’s been a major shift. The Chromebook has become the king of the classroom, thanks in no small part to the inexpensive hardware and limited spec requirements.
Based on Google’s early positioning of the category, it appears that the Chromebook’s classroom success even managed to catch its creators off-guard. The company has since happily embraced that success — while Microsoft appears to have shifted its own approach in response to Chrome OS’s success.
Apple’s own responses have been less direct, and today’s event was a reconfirmation of the company’s commitment to the iPad as the centerpiece of its educational play. If Apple can be seen as reacting, it’s in the price of the product. Gone are the days that schools’ entire digital strategy revolved around a bunch of stationary desktops in a dusty old computer lab.
Apple Should Have Cut iPad Price Further For Schools, Say Analysts
Apple announced another affordable iPad and some cool new educational software today, but it might be too pricey to unseat Chromebooks in many classrooms.
Apple’s New Low-End iPad For Students Looks To Thwart Google, Microsoft
What educators think about Apple’s new iPad
Can a bunch of new apps make up for the high price?
Apple needs more than apps to win over educators
Apple used to be in a lot of classrooms, but are new iPads enough to woo educators?
Work From Home 2018: The Top 100 Companies For Remote Jobs — from forbes.com by Laura Shin
Excerpt:
The top sectors offering such work are health care, computer/IT, education/training, sales, customer service, finance and travel/hospitality of the 19 industries represented on the list. Five of the fastest-growing remote career categories are therapy, virtual administration, client services, tutoring, and state and local government. The 20 most common telecommuting job titles include teacher, writer, developer, analyst, sales representative, nurse, accountant and program manager. Five companies are fully remote, and 30 are newcomers to the list.
Also see:
20 Most Common Work-from-Home Job Titles — from by Jessica Howington
From DSC:
I have been trying to blog more about learning how to learn — and to provide some more resources on metacognition and the like.
Along these lines — and with permission from the author — the following excerpt is from Quentin Schultze’s solid book, Communicate like a True Leader (pages 35 & 36). I asked Quin if I could share this excerpt because I think it could be a great strategy to share with students (at least for them to experiment with, and try it out to see if it helps them). Whether they know it or not, learning how to learn is THEE key skill these days.
Quin would also emphasize some other items such as listening, attending to reality, communicating effectively with others, and more…but my focus here is on learning strategies. So I share it in the hope that it will help some of you students out there just as it helped Quin.
During the beginning of my sophomore year, I started reviewing each day’s class notes after classes were over. I soon realized how little I recalled even of that day’s lectures and discussions. It dawned on me that normal note-taking merely gave me the impression that I was learning. I implemented a strategy that revolutionized my learning, launched me successfully into graduate school, helped me become a solid teacher, equipped me to be a productive researcher-writer, and made it possible for me to be an engaging speaker.
I not only reviewed my notes daily. I rewrote them from scratch within a couple of hours of each class meeting. I used my actual course notes as prompts to recall more of the lecture and to help me organize my own reactions to the material. My notes expanded. My retention swelled.
My revised notes became a kind of journal of my dialogue with the instructor and the readings. I integrated into my revised course notes my daily reading notes, reworking them into language that was meaningful to me and preparing to ask the instructor at the next class anything that I was uncertain about. From then on I earned nearly straight A’s with far less cramming for exams.
Moreover, I had begun journaling about my learning — one of the most important communication skills. I became a real learner by discovering how to pay attention to others and myself.
In a broad sense, I learned how to listen.
From DSC:
While I haven’t gone through all of these videos/modules/practice problems, I find the idea of using music to teach math very intriguing. So I wanted to pass this information along in case it helps some students (and teachers) out there!
You might find some (or all) of this a bit corny, but some kids out there might find this style much more interesting and engaging. It might better help get and maintain their attentions. It might help them better remember some of these concepts.
I’m posting these resources/links on my blog here because of such students. If such an approach helps them connect with the material, I say, “Good deal!” Such an approach might suit their preferences quite well.
In fact, perhaps teachers could have their students design and produce these sorts of videos themselves! Talk about active learning/project based learning! Such a cross-disciplinary, team-based approach would involve students with interests and developing skills involving:
Per Matt Wolf, Managing Director at Tylerbarnettpr.com:
Singing math tutor, Huzefa Kapedia, has launched a new musically-based SAT Math Video Course that is sure to bring a smile to faces.
From crooning about the quadratic formula to rapping about slope intercept form, Huzefa introduces the only math SAT course to teach difficult concepts through the power of song.
Additionally, he provides 700 practice problems (all frequency-based), each with its own video explanation.
And…it actually works. Huzefa is not only helping kids score big on their SATs; he is also making the whole math studying thing pretty darn enjoyable.
Problem Solved: Scalar Learning Proves Any Person Can Be a Math Person
Online and In-Person Tutoring Platform Introduces Modern Mathematics for Today’s Student
Scalar Learning introduces an innovative online and in-person tutoring platform that enables individuals of all ages and backgrounds with the skills and confidence needed to master mathematics. Founded by software engineer and former patent attorney Huzefa Kapadia, Scalar Learning offers a variety of online courses, private tutoring sessions with specialized educators, and entertaining (and effective) math music videos geared at breathing new life into the outdated tutoring model.
“With Scalar Learning, I wanted to reinvent the tutoring concept for the modern world,” said Kapadia. “Everything I have designed and built is a product of my experience tutoring over 2,500 hours and teaching classrooms of both sixth and second grade math students. By blending vibrant and engaging video tutorials, high quality music videos to convey difficult formulas and concepts, and highly personalized and energetic one-on-one environments, we are able to engage our students on multiple levels. Too many people label themselves as ‘not a math person;’ my goal is to prove to them and the world that there is no such thing. Any person can become a math whiz with the right encouragement and training.”
Scalar Learning offers students a multi-tiered approach to mathematics, designed to engage at every level:
“Mathematics has always been my passion, which is why after years as an attorney, I made the career shift to education,” says Kapadia. “Having worked as a teacher and tutor at both private and public schools, I soon noticed how many students had a mental block when it came to math. They would admit defeat far too early simply because they were intimidated. Scalar Learning was born as a means to dismantle that premature defeat. Our system is proof that there is no such thing as being ‘bad at math.’ With the proper tools, practice, and guidance, any person can not only ‘get it,’ but they can also enjoy it.”
For more information, please visit http://scalarlearning.com.
From DSC:
I know Quentin Schultze from our years working together at Calvin College, in Grand Rapids, Michigan (USA). I have come to greatly appreciate Quin as a person of faith, as an innovative/entrepreneurial professor, as a mentor to his former students, and as an excellent communicator.
Quin has written a very concise, wisdom-packed book that I would like to recommend to those people who are seeking to be better communicators, leaders, and servants. But I would especially like to recommend this book to the leadership at Google, Amazon, Apple, Microsoft, IBM, Facebook, Nvidia, the major companies developing robots, and other high-tech companies. Why do I list these organizations? Because given the exponential pace of technological change, these organizations — and their leaders — have an enormous responsibility to make sure that the technologies that they are developing result in positive changes for societies throughout the globe. They need wisdom, especially as they are working on emerging technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), personal assistants and bots, algorithms, robotics, the Internet of Things, big data, blockchain and more. These technologies continue to exert an increasingly powerful influence on numerous societies throughout the globe today. And we haven’t seen anything yet! Just because we can develop and implement something, doesn’t mean that we should. Again, we need wisdom here.
But as Quin states, it’s not just about knowledge, the mind and our thoughts. It’s about our hearts as well. That is, we need leaders who care about others, who can listen well to others, who can serve others well while avoiding gimmicks, embracing diversity, building trust, fostering compromise and developing/exhibiting many of the other qualities that Quin writes about in his book. Our societies desperately need leaders who care about others and who seek to serve others well.
I highly recommend you pick up a copy of Quin’s book. There are few people who can communicate as much in as few words as Quin can. In fact, I wish that more writing on the web and more articles/research coming out of academia would be as concisely and powerfully written as Quin’s book, Communicate Like a True Leader: 30 Days of Life-Changing Wisdom.
To lead is to accept responsibility and act responsibly.
— Quentin Schultze
For a long, successful career, LinkedIn says nothing beats a liberal arts major — from qz.com by Dan Kopf and Amy Wang
Excerpt:
“There is a real concern that these labor-market-oriented degrees that focus on specific technical skills are not as durable,” says Guy Berger, a LinkedIn economist and one of the researchers who worked on the report. Berger believes that “cross-functional skills” like management and analytical know-how are more adaptable across a range of work environments. As technology changes the nature of work across nearly every industry, it’s important to have a wide range of such talents, rather than a narrow subset applied only to a particular sector that may not look the same in the near future (or, indeed, exist at all).