But how do you move forward with such an innovation, when there isn’t definitive proof that it will work? That is the key question educators and policymakers are grappling with.
Under the education priorities of President George W. Bush’s administration, the catchphrase “research base” was drilled into educators” heads when it came to new programs and initiatives. If it wasn’t research-based, it wasn’t worth adopting.
But technology innovations occur so rapidly that it’s often impossible to do scientifically based trials proving effectiveness before schools embrace new approaches. Think of social-networking tools, iPads, and e-readers. And what other new digital-learning tools might also emerge well before scientifically based research can justify their use in classrooms?
Also see:
- ‘Hybrid’ Charter Schools on the Rise — from Education Week’s Digital Directions by Michelle Davis
New charter school models are combining online-only learning and face-to-face instruction
From DSC:
From my 20+ years of experience with working with a variety of technologies, while there is an element of risk taking to implementing technologies, there are also enormous payoffs if organizations implement the appropriate technologies.
But how can we select and implement the most effective technologies? This is where we need to rely on our technologists out there and keep them growing in the knowledge of “the business”, not just the technologies. Tell them what you are trying to achieve, and they can greatly assist. No one can hit 100% — but good technologists can get you into the right game and into the right ballpark (if not exactly lining up the exact right players, which may change or take some tweaking).
NOTE:
Don’t rely on technologists who only see their jobs as keeping the systems running. Though we need technologists who keep the infrastructures up and running, at this juncture what organizations really need are visionaries who are knowledgeable about the needs of the business (as well as the technologies), and those who are willing to explore, experiment, and take some risks…i.e. to lead….to be instrumental in forming strategies and visions. The areas outside IT need to be aware of how critical technologies are becoming in their core strategies and plans. It’s not the same ball-game as it was. Those who use technologies strategically will survive and thrive.
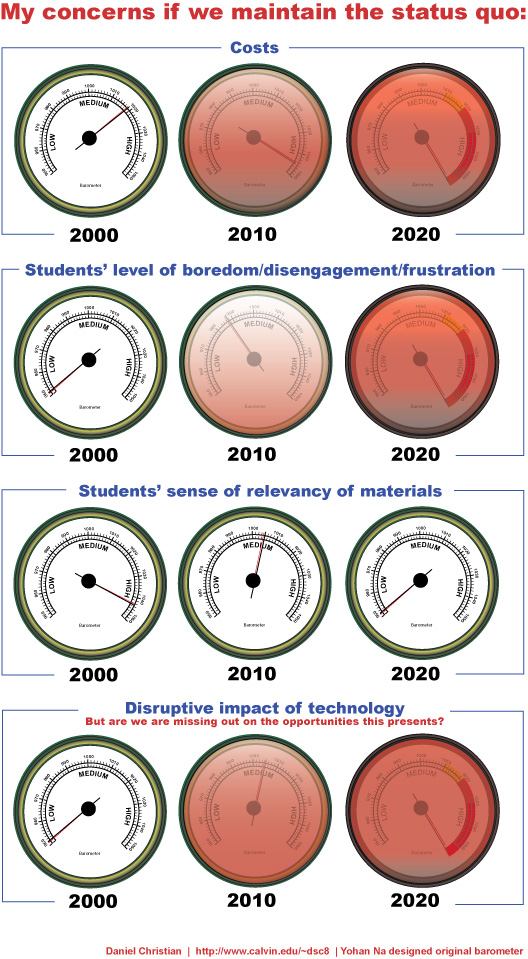
It should be noted that there have been risks inherent in maintaining the status quo — a 20%-30% dropout rate (in K-12) across the United States is pretty risky too, at least in my mind.