EdX Expands xConsortium to Asia and doubles in size with addition of 15 new global institutions — from prnewswire.com
From MOOC platform edX announces 15 new university partners (from educationdive.com)
These are the new partner institutions:
- The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong (HKUx)
- Hong Kong University of Science & Technology, Hong Kong (HKUSTx)
- Kyoto University, Japan (KyotoUx)
- Peking University, Beijing, China (PekingX)
- Seoul National University, South Korea (SNUx)
- Tsinghua University, Beijing, China (TsinghuaX)
- The University of Queensland in Australia (UQx)
- Karolinska Institutet, Sweden (KIx)
- Universite catholique de Louvain, Louvain-la-Neuve, Belgium (LouvainX)
- Technische Universitat Munchen, Germany (TUMx)
- Berklee College of Music, Boston, Mass. (BerkleeX)
- Boston University, Boston, Mass. (BUx)
- Cornell University, Ithaca, N.Y. (CornellX)
- Davidson College, Davidson, N.C. (DavidsonX)
- University of Washington, Seattle (UWashingtonX)
The graphic below is from:
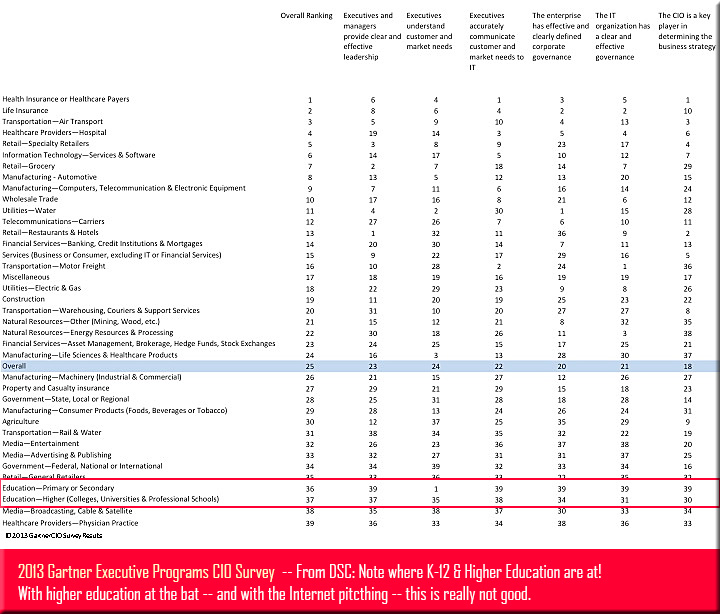
How strong is the business/IT relationship in your industry? — from Gartner.com by Mark P. McDonald; with thanks to Mr. Stephen Landry for putting this resource out on LinkedIn.
.

The IT conversation we should be having — from HBR.org by Jim Stikeleather
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
It is a conversation about the increasing importance of information technology and the role it must assume in every enterprise, regardless of size, industry or geography.
…
Our observations:
- CEOs are demanding more visible value from their CIOs, in terms of generating revenue, gaining new customers, and increasing customer satisfaction.
- Increasingly, the CIO and IT must be seen less as developing and deploying technology, and more as a source of innovation and transformation that delivers business value, leveraging technology instead of directly delivering it.
- The CIO must be responsible and accountable if technology enables, facilitates or accelerates competition that the C-suite didn’t see coming, or allows the enterprise to miss opportunities because the C-suite did not understand the possibilities technology offered.
- CIOs today must adapt or risk being marginalized.
From DSC:
This is critical in the higher ed space as well!
The majority of the higher education industry still isn’t getting it — we are operating in a brand new ball game where technology must be used strategically. It’s not just about building and maintaining the infrastructure/plumbing anymore (though that is extremely important as well). It’s about the strategic, innovative use of IT that counts from here on out.
Innovation U — from Southern New Hampshire University by Michelle E. Dunn, Editor
Excerpt:
Blowing Up the Business Model
SNHU has a history of innovation that includes establishing satellite campuses and launching a groundbreaking three-year Honors Program in Business. But more recent initiatives have placed SNHU at the forefront of a movement to fundamentally change American higher education and earned it acclaim from the noted business magazine Fast Company, which placed SNHU 12th on its recent World’s 50 Most Innovative Companies list. Ranked alongside business giants such as Apple, Google, Facebook and Starbucks, SNHU was the only university on the list.
In the Fast Company article highlighting SNHU’s forward thinking, President Paul LeBlanc acknowledged that innovation is imperative to survival in a rapidly changing higher education landscape.
“We want to create the business model that blows up our current business model,” he told the magazine, “because if we don’t, someone else will.”
…
The Innovation Lab
Imagine a new education model that would enable students to earn an SNHU associate degree for less than $3,000 per year.
Making that model a reality is the goal of the SNHU Innovation Lab, an educational incubator that is working to reduce costs, increase access and provide transformational experiences for students who have been marginalized by traditional higher education.
Established last November and staffed by four SNHU academic and technology experts, the Innovation Lab is spearheading the Pathways Project, an initiative that will seek to educate 5,000 disadvantaged students in the next five years. Slated to launch this fall, the project’s pilot degree program will apply a competency-based approach that leverages technology, community support, social networking and strong assessment.
Also see:
- Competency-based education advances with U.S. approval of program — from thechronicle.com by Marc Parry
40 years coming, the revolution is here — from gettingsmart.com by Tom Vander Ark
Excerpt:
Moe sees learners creating a “personalized knowledge portfolio,” an unbundled sequence of learning experiences from multiple providers.
Moe sees an innovation ecosystem emerging, and calls it KaizenEDU. In this emerging ecosystem, it’s the “return on education” that matters. Moe argues the entrepreneurs that help create great learning gains are the ones that will create great shareholder value.
Healthcare gives us a picture of what that could mean for edtech. In 1970 there were 3 companies worth more than $1 billion. Last year, health care made up 13% of U.S. GDP and there were 398 companies with a market cap of more than $1 billion. Education is about 9% of GDP but there are only 5 public companies worth more than $1 billion. The difference is a result of dramatic under investment in R&D, but that’s changing!
…
The three emerging areas requiring more attention, according to Shelton, are early learning tools and resources, summer and out of school learning, and course redesign in higher education.
Online education for the pros: Udemy launches corporate training tools — from venturebeat.com by Christina Farr
Excerpt:
Online course providers typically target students, but Udemy is going after an underserved group: professionals.
Also, from Learning TRENDS by Elliott Masie – April 18, 2013
#768 – Updates on Learning, Business & Technology
55,949 Readers – www.masie.com – twitter: emasie – The MASIE Center.
Host: TeleWork 2013 – A National Forum – www.telework2013.com
1. MOOC’s & Corporate Learning?
There is a great media interest in MOOC’s – the innovations for Massive Open Online Courses – where one instructor runs a course for thousands or tens of thousands of learners. I have been a student in three MOOC’s and a teacher/facilitator in three. Now, we are hearing from many learning colleagues about the applicability of the MOOC to workplace learning.I would urge TRENDS readers to approach MOOC’s as important beta/lab experiments – where important and cool innovations are emerging in the construction, delivery and economics of educational “packages”. My experience as a MOOC learner has been exciting and mixed. While there were over 70,000 learners in one program – very few made it to the end of the program – and fewer were fully successful from a competency point of view. It was exciting to see how learners could be co-designers of the program and many resources were developed and disseminated from the learners. Finally, there were mixed models of how well the social/collaborative side of the MOOC’s worked.
As a teacher – I struggled with the format shifts reflected by MOOC’s. Were the assignments suggestions or could I predict a level of engagement of the learners. Was the content that was posted by learners legal – some added video that wasn’t within their IP ownership. And, the issue of fees were also interesting. A free MOOC will get high starts but perhaps high drop offs. When fees were added, did that take away the “open” label. It is also interesting to see colleges and universities that have never made a profit on classroom offerings think they will generate good margins by adding MOOC’s to their offerings.
It is early and really too early to predict how MOOC’s might evolve within the corporate world. I have been advocating that we take each of the letters as distinct areas for innovation:
– M: Massive dissemination of content
– O: Open content and content reuse along with curation by learners.
– O: Online resources added to both 1 mode and mixed/blended mode delivery.
– C: Course? Perhaps the MOOC might become a MOOP (Program) or MOOA (Assets)And, is there a Competency check assumed in a MOOC – as well as certification or even college credit?
MOOC’s are important innovations. Now, we need to label them as Lab or Beta tests – and gather evidence as we experiment with the use of all or some of MOOC’s elements in corporate settings. We will be experimenting with the MOOC as a corporate model in an upcoming Learning LAB of our Learning CONSORTIUM. Interested in hearing from TRENDS readers exploring MOOC’s in our world.
The College of 2020
If #HigherEd stays way it is, w/ 19th century style lectures, w/in 10 years Google U. and Walt Disney U. to take it over – Wim Westera
Addendum on 4/19/13:
Bridging the Skills Gap — from trainingmag.com by Lorri Freifeld
Employers want certain skills. Employees don’t have them. Why? And what can organizations and Training, employees, and the educational system do to eliminate the disconnect?
Excerpt:
With the U.S. unemployment rate hovering around 8 percent and millions of people desperately looking for jobs, why are many employers claiming they can’t fill their vacant positions?
The answer: A skills gap that threatens the sustainability of businesses around the world. And while a big part of the skills gap is a shortage of people skilled in the STEM (science, technology, education, and math) industries, there also is a gap in soft skills such as communication and advanced leadership skills.
…
What is causing these skills gaps? What can—and should—employers and their Training departments, employees, and the education system be doing differently? This first article in a five-part series will address these questions. Subsequent articles will explore how corporate partnerships with colleges and universities can help bridge the divide (May/June), how to motivate employees to take advantage of skills gap training and eliminate any sense of promotion entitlement (July/August), how technology can help (September/October), and additional potential solutions and strategies for success (November/December).
.
From DSC:
We had better start talking STEAM not STEM from here on out (i.e. add the ARTS!). You can’t get creative thinkers without fostering some creativity.
About
NovoEd is the only online learning platform that provides a connected, effective and engaging learning environment for students using a combination of techniques in crowd sourcing, design and analysis of reputation systems, and algorithm design.
NovoEd’s philosophy is to advance the online learning experience by making online courses more experiential, interactive, and collaborative. On our platform, students not only have access to lectures by thought leaders and professors from top universities, but they are also able to form teams with people around the world and work on class projects.
NovoEd uses online learning to deliver learning opportunities at massive scale. We offer courses and programs by thought leaders in a wide range of fields and in partnership with universities. By fostering online collaboration, team work and project-based learning, we nurture problem solving, collaboration, and leadership while addressing specific topics and business opportunities.












![The Living [Class] Room -- by Daniel Christian -- July 2012 -- a second device used in conjunction with a Smart/Connected TV](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian-July-2012.jpg)