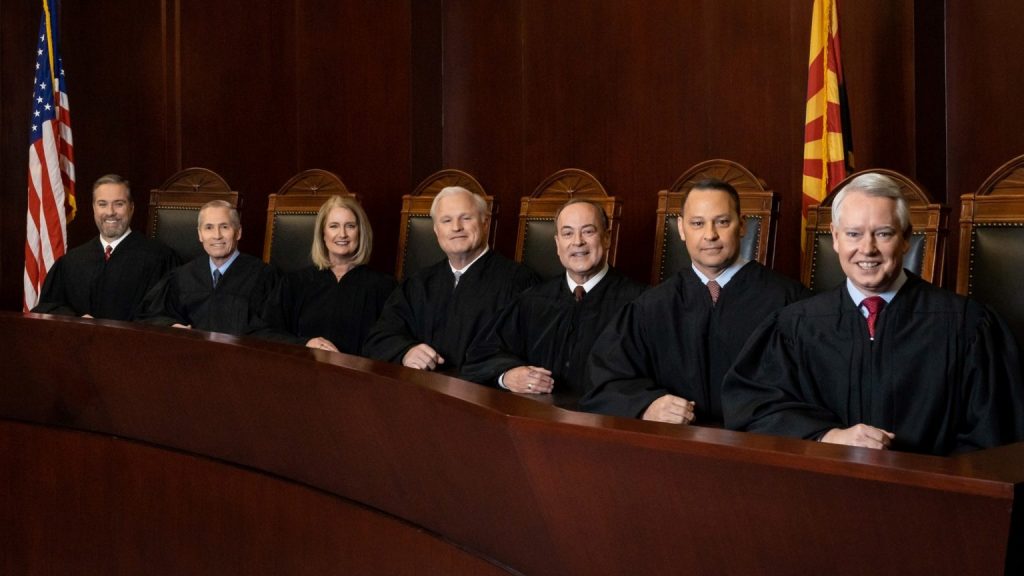
Arizona is first state to eliminate ban on nonlawyer ownership of law firms — from lawsitesblog.com by Bob Ambrogi
The future of the academic work force — from chronicle.com
How will the pandemic change the way higher education works?
Excerpt:
Heading into a fall in which the pandemic shows no signs of abating, we asked administrators, professors, grad students, and university staff to peer around the corner and speculate about how the coronavirus will change the academic work force. What has the pandemic revealed about the campus workplace — and how will that change it going forward? What jobs will be most in demand? Which roles are most imperiled? What sort of shared governance will survive the pandemic? When this is all over, what should the composition of university work forces look like?
Big 4 as the next legal disruptor: Is it game over? — from legaltechmonitor.com by Stephen Embry
Excerpt:
One of the more fascinating keynotes at this week’s ILTA virtual conference was a panel discussion among three representatives of the big four accounting firms: Peter Krakaur, Managing Director of EY Law, Mark Ross, Principal, Deloitte, and Juan Crosby, PWC NewLaw Services Leader. The title of the talk was Legal’s Next Disruptor? Demystifying the Big 4. Or as I put it before, is the Big 4 the proverbial big bad wolf?
Also see:
Friday happenings at the ILTA-ON* Virtual Conference: eDiscovery Trends — from
Excerpt:
As I discussed last week (and have discussed all this week as well), the International Legal Technology Association’s (ILTA) annual conference has gone virtual this year and ILTA>ON has been running throughout the week.
The Great Online Migration and Curricular Materials Product-Market Fit — from eliterate.us by Michael Feldstein
Excerpts:
Third, COVID-19 will accelerate the need of colleges and universities to find ways of continuing to serve their graduates for 20 or 40 years rather than for two or four. Quite simply, they will need revenue at a time when the pace and breadth of reskilling needs in the workplace is accelerating. These students will need online or blended educational experience, which will mean that more instructors will be called upon to teach using new modalities.
…
Major changes in the market
This shift online will drastically shift approaches to curricular materials at both the individual instructor and the institutional levels.
…
Meanwhile, institutions will face two pedagogy-related challenges. First, they will have to work very hard to retain students who are under increased financial stress and may struggle in an online environment more than they would in a residential program. Since the colleges will also be under financial stress, they will need to retain every student possible. They will no longer have the luxury of simply letting faculty teach however they like and accepting that some of them are not good at helping their students to succeed.
First They Came for Adjuncts, Now They’ll Come for Tenure: And who will be left to stop them? — from chronicle.com by Ed Burmila
Excerpts:
If, by their own accord or by caving to outside political pressures, university administrators take the current crisis as an opportunity to eliminate tenure once and for all, who’s going to stop them?
Put another way: Are there enough academic workers with a stake in the tenure system left to defend it?
…
As go the adjuncts and the nonacademic staff today, so go the tenured faculty tomorrow.
It is in the interest of tenured faculty to fight for their non-tenure-track colleagues. But the key question, as The Chronicle’s Emma Pettit asks, is: Will it be too little too late? When contingent labor protested for years about poor working conditions, it did not find many allies willing to fight alongside it. Now the roles are reversed: Tenured faculty will soon need the rest of the profession to help fight attempts to erode tenure.
Addendum on 8/20/20:
Higher ed group offers ideas for supporting contingent faculty — from educationdive.com by Hallie Busta
Dive Brief:
- Support for non-tenure-track faculty members continues to be a concern amid pandemic-related cutbacks and pushback over how some campuses plan to reopen.
- A faculty industry group this week put out a list of principles and recommendations for institutions to protect those instructors, calling for them to get paid sick leave, unemployment benefits, and extended access to rehire or promotion opportunities.
- The ideas come as calls for greater shared governance grow across the sector in light of the ongoing health crisis.
Joining host @DanLinna, @MISupremeCourt Chief Justice @BridgetMaryMC details the “unexpected upsides” of the global pandemic, like opportunities for greater access to justice, better litigant experiences, and less hassle for lawyers #A2J #legaltech https://t.co/J495CLj3iW
— Legal Talk Network (@LegalTalkNet) August 5, 2020
The Spanish Flu to Covid-19: How this Pandemic is Pushing Courts to Modernize — from legaltalknetwork.com by Bridget Mary McCormack and Daniel Linna
Episode notes:
Even before the global pandemic, Michigan courts were moving more quickly than many others to modernize. Michigan Chief Justice Bridget Mary McCormack talks with host Dan Linna about accelerating the state’s plans to offer online hearings, online dispute resolution, and to continue efforts to establish e-filing statewide.
Not everything is going smoothly, but McCormack notes some judges are almost current on their dockets. And importantly, she believes that many temporary quick fixes will lead to permanent changes that improve access to justice statewide and increase public trust in the judicial branch.
DC: Now there’s a thought/question…
How might increased competition amongst #accreditors impact #innovation within #HigherEducation?!
Is that’s what’s been missing? Hmmm…could easily be an incredible time of change these next few years. https://t.co/5R8Ov8EjiU
— Daniel Christian (@dchristian5) July 15, 2020
Which links to this article:
Another regional accreditor drops geographic limits — from educationdive.com by Hallie Busta
Dive Brief:
- The Middle States Commission on Higher Education (MSCHE) announced Monday that it will accept applications for accreditation from institutions located outside its historical territory, which is primarily the mid-Atlantic states.
- It will also begin taking applications from international institutions seeking accreditation.
- MSCHE is the second of the country’s seven historically regional accreditors to make such a move, the result of new federal regulations removing their geographic boundaries.
We will consider the ways that the Commission engages in its work and whether an alternative structure may be necessary to support the changing nature of accreditation, and its more modern demands. Believe it or not, our requirements and standards are also scheduled for evaluation. We will need to begin to have conversations about the ways we can improve the language of our requirements and standards or our accreditation processes. — source
June 29, 2007: Apple Releases the iPhone, Transforming Much of the Modern World — from by Kevin Levick
Excerpts:
Over the past 10 years, Apple’s iPhone evolved from a mobile device capable of running basic apps to a powerful computer with professional-grade cameras.
…
Today’s app economy is bigger than Hollywood, and WhatsApp, Snapchat, Uber, Tinder, and more are essential parts of modern culture, collectively used by hundreds of millions of people every day.
Now, everything from the way we work, communicate, shop, travel, manage our finances, and experience entertainment can be done through a smartphone.
DC: A lot has happened in just 10 years! Where might we be in another 10 years?! https://t.co/ByZ60S5812
— Daniel Christian (@dchristian5) June 29, 2020