Virtual reality simulates classroom environment for aspiring teachers — from phys.org by Charles Anzalone, University at Buffalo
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
Two University at Buffalo education researchers have teamed up to create an interactive classroom environment in which state-of-the-art virtual reality simulates difficult student behavior, a training method its designers compare to a “flight simulator for teachers.”
The new program, already earning endorsements from teachers and administrators in an inner-city Buffalo school, ties into State University of New York Chancellor Nancy L. Zimpher’s call for innovative teaching experiences and “immersive” clinical experiences and teacher preparation.
…
The training simulator Lamb compared to a teacher flight simulator uses an emerging computer technology known as virtual reality. Becoming more popular and accessible commercially, virtual reality immerses the subject in what Lamb calls “three-dimensional environments in such a way where that environment is continuous around them.” An important characteristic of the best virtual reality environments is a convincing and powerful representation of the imaginary setting.
Also related/see:
- How Virtual Reality Is Helping Train New Teachers — from edweek.org by Liana Loewus
- TeachLive.org
TLE TeachLivE™ is a mixed-reality classroom with simulated students that provides teachers the opportunity to develop their pedagogical practice in a safe environment that doesn’t place real students at risk. This lab is currently the only one in the country using a mixed reality environment to prepare or retrain pre-service and in-service teachers. The use of TLE TeachLivE™ Lab has also been instrumental in developing transition skills for students with significant disabilities, providing immediate feedback through bug-in-ear technology to pre-service teachers, developing discrete trial skills in pre-service and in-service teachers, and preparing teachers in the use of STEM-related instructional strategies.
- Virtual reality lessons can help students become better real-life teachers — from news.psu.edu by Jim Carlson
- 10 amazing virtual museum tours — from virtualiteach.com
This start-up uses virtual reality to get your kids excited about learning chemistry — from Lora Kolodny and Erin Black
- MEL Science raised $2.2 million in venture funding to bring virtual reality chemistry lessons to schools in the U.S.
- Eighty-two percent of science teachers surveyed in the U.S. believe virtual reality content can help their students master their subjects.
This start-up uses virtual reality to get your kids excited about learning chemistry from CNBC.
From DSC:
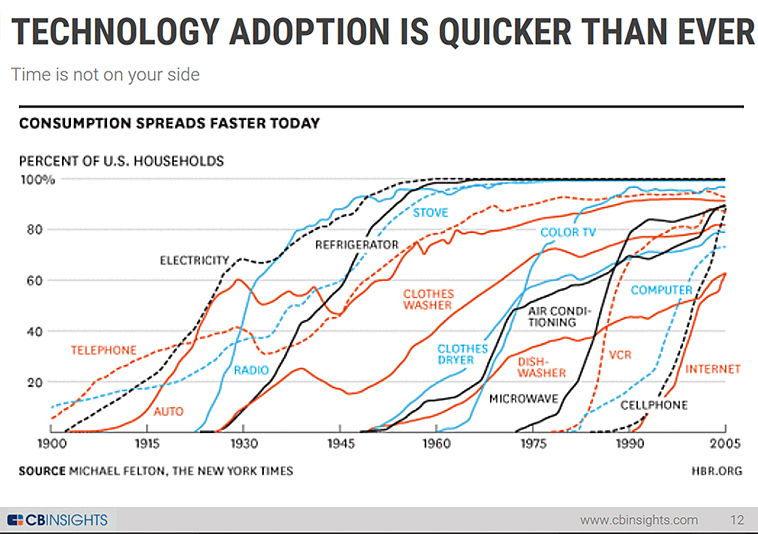
It will be interesting to see all the “places” we will be able to go and interact within — all from the comfort of our living rooms! Next generation simulators should be something else for teaching/learning & training-related purposes!!!
The next gen learning platform will likely offer such virtual reality-enabled learning experiences, along with voice recognition/translation services and a slew of other technologies — such as AI, blockchain*, chatbots, data mining/analytics, web-based learner profiles, an online-based marketplace supported by the work of learning-based free agents, and others — running in the background. All of these elements will work to offer us personalized, up-to-date learning experiences — helping each of us stay relevant in the marketplace as well as simply enabling us to enjoy learning about new things.
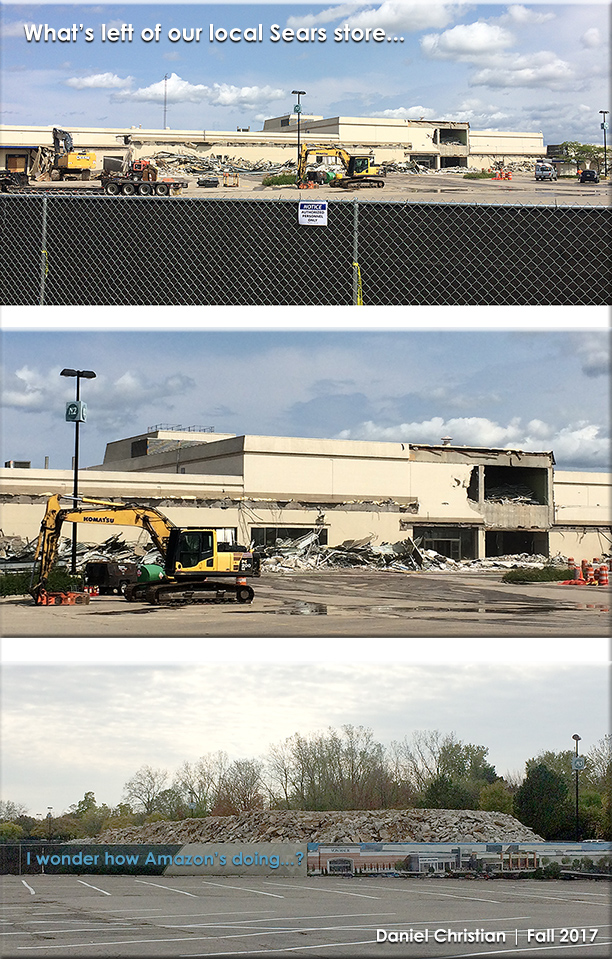
But the potentially disruptive piece of all of this is that this next generation learning platform could create an Amazon.com of what we now refer to as “higher education.” It could just as easily serve as a platform for offering learning experiences for learners in K-12 as well as the corporate learning & development space.
I’m tracking these developments at:
http://danielschristian.com/thelivingclassroom/
* Also see:
Blockchain, Bitcoin and the Tokenization of Learning — from edsurge.com by Sydney Johnson
Excerpt:
In 2014, Kings College in New York became the first university in the U.S. to accept Bitcoin for tuition payments, a move that seemed more of a PR stunt than the start of some new movement. Much has changed since then, including the value of Bitcoin itself, which skyrocketed to more than $19,000 earlier this month, catapulting cryptocurrencies into the mainstream.
A handful of other universities (and even preschools) now accept Bitcoin for tuition, but that’s hardly the extent of how blockchains and tokens are weaving their way into education: Educators and edtech entrepreneurs are now testing out everything from issuing degrees on the blockchain to paying people in cryptocurrency for their teaching.










![The Living [Class] Room -- by Daniel Christian -- July 2012 -- a second device used in conjunction with a Smart/Connected TV](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian-July-2012.jpg)