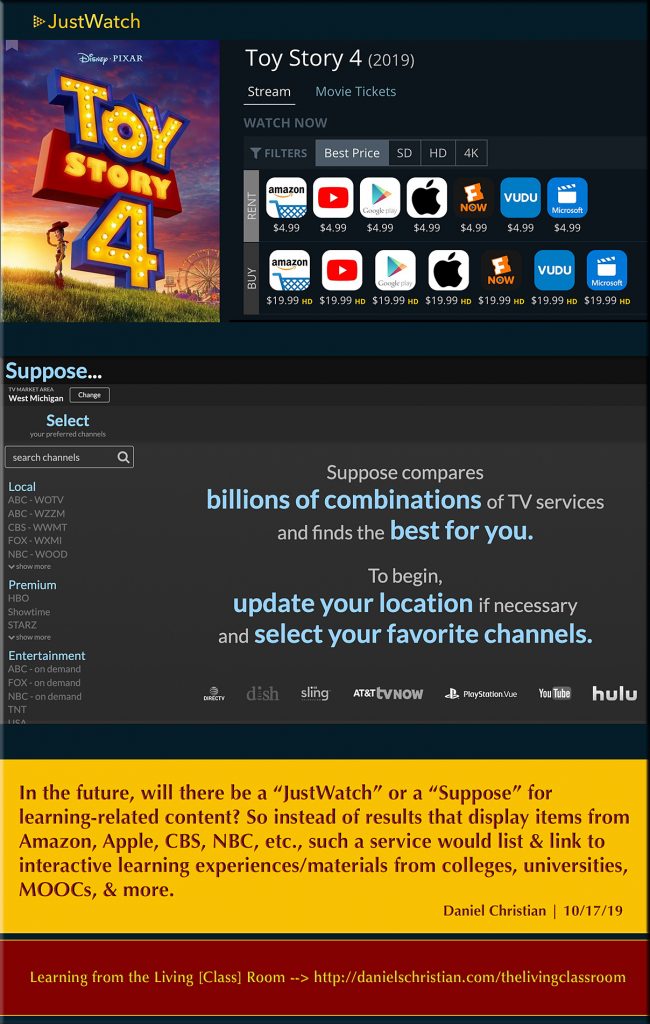
The next age of the internet could suck power away from Big Tech while living on the same backbone as cryptocurrencies. Here’s what to know about Web3. — from businessinsider.com by Katie Canales
Excerpts (emphasis DSC):
- Web3 is the next generation of the internet and will exist on the blockchain.
- It will be decentralized, meaning it won’t be controlled entities like Facebook or Google.
- Twitter, GameStop, Reddit, and VC firm a16z are all putting resources into building Web3.
…
One aspect of the metaverse is that users will hopefully be able to go virtually from platform to platform with one single account — just like we will in Web3.
And NFTs, one-of-a-kind tokens representing your ownership of a virtual good, could be more easily bought and sold with cryptocurrencies within a space like Web3.
From DSC:
How might “Web3” translate into the future of lifelong learning? Here’s one vision/possibility:

Each person would have a learner profile/account that could seamlessly log into multiple education/training providers’ platforms and services. The results of that learning could be stored in one’s cloud-based learner profile. This type of next-generation learning platform would still need subject matter experts, instructional designers, programmers, and other team members. But the focus would be on building skills — skills that an artificial intelligence-backed interface would demonstrate are currently being requested by the modern workplace. This constantly-being-updated list of skills could then link to the learning-related experiences and resources that people could choose from in order to develop those skills.
The following vision/graphic also comes to my mind: