Growing Enrollment, Shrinking Future — from insidehighered.com by Liam Knox
Undergraduate enrollment rose for the first time since 2020, stoking hopes for a long-awaited recovery. But surprising areas of decline may dampen that optimism.
There is good news and bad news in the National Student Clearinghouse Research Center’s latest enrollment report.
First, the good news: undergraduate enrollment climbed by 2.1 percent this fall, its first total increase since 2020. Enrollment increases for Black, Latino and Asian students—by 2.2 percent, 4.4 percent and 4 percent, respectively—were especially notable after last year’s declines.
The bad news is that freshman enrollment declined by 3.6 percent, nearly undoing last year’s gain of 4.6 percent and leaving first-year enrollment less than a percentage point higher than it was in fall 2021, during the thick of the pandemic. Those declines were most pronounced for white students—and, perhaps most surprisingly, at four-year institutions with lower acceptance rates, reversing years of growth trends for the most selective colleges and universities.
An Army of Temps: AFT Contingent Faculty Quality of Work/Life Report 2022 — from aft.org (American Federation of Teachers) by Randi Weingarten, Fedrick C. Ingram, and Evelyn DeJesus

This recent survey adds to our understanding of how contingency plays out in the lives of millions of college and university faculty.
- More than one-quarter of respondents earn less than $26,500 annually. The percentage of faculty respondents earning below the federal poverty line has remained unchanged through all three reports, which is not surprising with real wages falling behind inflation throughout the academy.2
- Only 22.5 percent of respondents report having a contract that provides them with continuing employment, even assuming adequate enrollment and satisfactory job performance.
- For 3 out of 4 respondents, employment is only guaranteed for a term or semester at a time.
- Two-thirds of part-time respondents want to work full time but are offered only part-time work.
- Twenty-two percent of those responding report having anxiety about accessing adequate food, with another 6 percent reporting reduced food intake due to lack of resources.
- Only 45 percent of respondents have access to employer-provided health insurance, and nearly 19 percent rely on Medicare/Medicaid.
- Nearly half of faculty members surveyed have put off getting needed healthcare, including mental health services, and 68 percent have forgone dental care.
- Fewer than half of faculty surveyed have received the training they need to help students in crisis.
- Only 45 percent of respondents believe that their college administration guarantees academic freedom in the classroom at a time when right-wing legislators are passing laws removing control of the curriculum from educators.
From DSC:
A college or university’s adjunct faculty members — if they are out there practicing what they are teaching about — are some of the most valuable people within higher education. They have real-life, current experience. They know which skills are necessary to thrive in their fields. They know their sections of the marketplace.
Some parts of rural America are changing fast. Can higher education keep up? — from usatoday.com by Nick Fouriezos (Open Campus)
More states have started directly tying academic programming to in-demand careers.
Across rural America, both income inequality and a lack of affordable housing are on the rise. Remote communities like the Tetons are facing not just an economic challenge, but also an educational one, as changing workforce needs meet a critical skills and training gap.
…
Earlier this month, Montana announced that 12 of its colleges would establish more than a dozen “micro-pathways” – stackable credential programs that can be completed in less than a year – to put people on a path to either earning an associate degree or immediately getting hired in industries such as health, construction, manufacturing and agriculture.
“Despite unemployment hitting record lows in Montana, rural communities continue to struggle economically, and many low-income families lack the time and resources to invest in full-time education and training,” the Montana University System announced in a statement with its partner on the project, the national nonprofit Education Design Lab.
Colleges Must Respond to America’s Skill-Based Economy — from edsurge.com by Mordecai I. Brownlee (Columnist)
To address our children’s hunger and our communities’ poverty, our educational system must be redesigned to remove the boundaries between high school, college and careers so that more Americans can train for and secure employment that will sustain them.
In 2021, Jobs for the Future outlined a pathway toward realizing such a revolution in The Big Blur report, which argues for a radical restructuring of education for grades 11 through 14 by erasing the arbitrary dividing line between high school and college. Ideas for accomplishing this include courses and work experiences for students designed for career preparation.
The New Arms Race in Higher Ed — from jeffselingo.com by Jeff Selingo
Bottom line: Given all the discussion about the value of a college education, if you’re looking for “amenities” on campuses these days be sure to find out how faculty are engaging students (both in person and with tools like AR/VR), whether they’re teaching students about using AI, and ways institutions are certifying learning with credentials that have currency in the job market.
In that same newsletter, also see Jeff’s section entitled, “Where Canada leads the U.S. in higher ed.”
College Uncovered — from hechingerreport.org
Thinking of going to college? Sending your kid? You may already be caught up in the needless complexity of the admissions process, with its never-ending stress and that “you’ll-be-lucky-to-get-in” attitude from colleges that nonetheless pretend to have your interests at heart.
What aren’t they telling you? A lot, as it turns out — beginning with how much they actually cost, how long it will take to finish, the likelihood that graduates get jobs and the myriad advantages that wealthy applicants enjoy. They don’t want you to know that transfer credits often aren’t accepted, or that they pay testing companies for the names of prospects to recruit and sketchy advice websites for the contact information of unwitting students. And they don’t reveal tricks such as how to get admitted even if you’re turned down as a freshman.
But we will. In College Uncovered, from The Hechinger Report and GBH News, two experienced higher education journalists pull back the ivy on how colleges and universities really work, providing information students and their parents need to have before they make one of the most expensive decisions in their lives: whether and where to go to college. We expose the problems, pitfalls and risks, with inside information you won’t hear on other podcasts, including disconcerting facts that they’ve sometimes pried from unwilling universities.
.
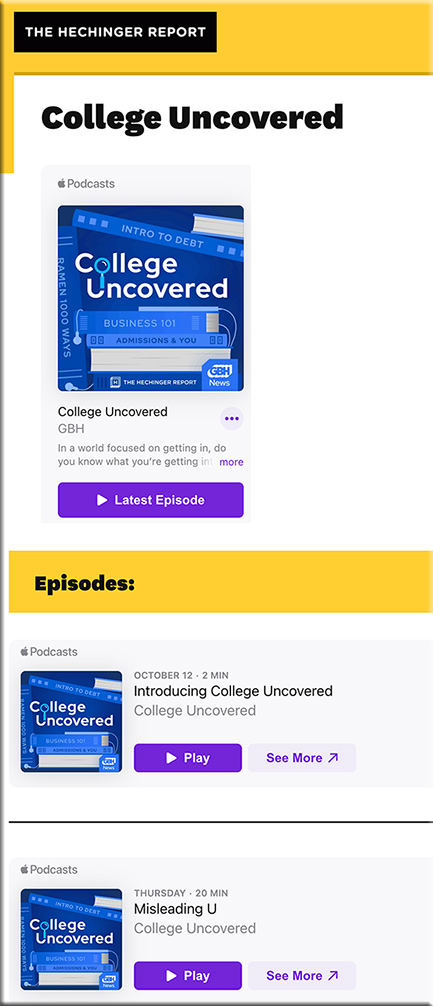
Fall 2023 enrollment trends in 5 charts — from highereddive.com by Natalie Schwartz
We’re breaking down some of the biggest developments this term, based on preliminary figures from the National Student Clearinghouse Research Center.
Short-term credentials continued to prove popular among undergraduate and graduate students. In fall 2023, enrollment in undergraduate certificate programs shot up 9.9% compared to the year before, while graduate certificate enrollment rose 5.7%.
Degree programs didn’t fare as well. Master’s programs saw the smallest enrollment increase, of 0.2%, followed by bachelor’s degree programs, which saw headcounts rise 0.9%.
President Speaks: Colleges need an overhaul to meet the future head on — from highereddive.com by Beth Martin
Higher education faces an existential threat from forces like rapidly changing technology and generational shifts, one university leader argues.
Higher education must increasingly equip students with the skills and mindset to become lifelong learners — to learn how to learn, essentially — so that no matter what the future looks like, they will have the skills, mindset and wherewithal to learn whatever it is that they need and by whatever means. That spans from the commitment of a graduate program or something as quick as a microcredential.
Having survived the pandemic, university administrators, faculty, and staff no longer have their backs against the wall. Now is the time to take on these challenges and meet the future head on.














:format(webp)/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/24976021/Canva_Magic_Studio.png)