Time pilot — from ryan2point0.wordpress.com by Ryan Tracey
Elaboration Strategies That Benefit Learning — from theelearningcoach.com by Connie Malamed
Excerpt:
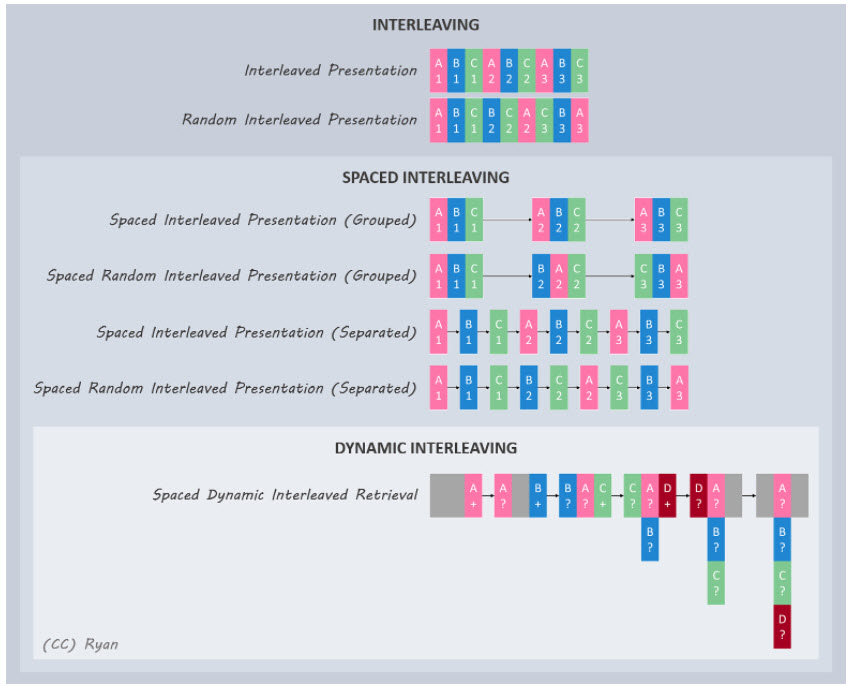
Although retrieval practice and spaced learning may be more well-known, elaboration is an instructional strategy worth our attention. Elaboration strategies refer to the many ways of connecting prior knowledge to what someone has newly learned. This has the potential to make the new material more memorable and meaningful.
We all know that new learning requires a foundation of prior knowledge. Elaboration techniques give people opportunities to make the connections stronger. In the book Make It Stick, the authors write, “The more you can explain about the way your new learning relates to your prior knowledge, the stronger your grasp of the new learning will be, and the more connections you create that will help you remember it later.” (Listen to my conversation with one of the authors of Make It Stick.)
How to Implement Active Learning Strategies and Activities Into Your Classroom — from facultyfocus.com
Excerpt:
Browse the following topics for resources, programs, seminars, free reports, and articles to help guide you in your active learning adventure:
From DSC:
You might be interested in reviewing one or more of the items out at Faculty Focus Live Podcasts.
Some example podcasts:
- Episode 11: Assessing Online Student Learning: How You Can Gauge Activities and Writing Through Online Assessment
- Episode 9: Live with Wendy Trevor: Overcoming Student Distaste for Collaborative Group Work Online
- Episode 8: Establishing and Revisiting Our Teaching Philosophies and Teaching Personas
- Episode 7: Finding the Missing Piece: How to Help Your Students Who Are Struggling with Online Learning