From 70/20/10 to 90/10 — from drphilippahardman.substack.com by Dr Philippa Hardman
A new L&D operating system for the AI Era?
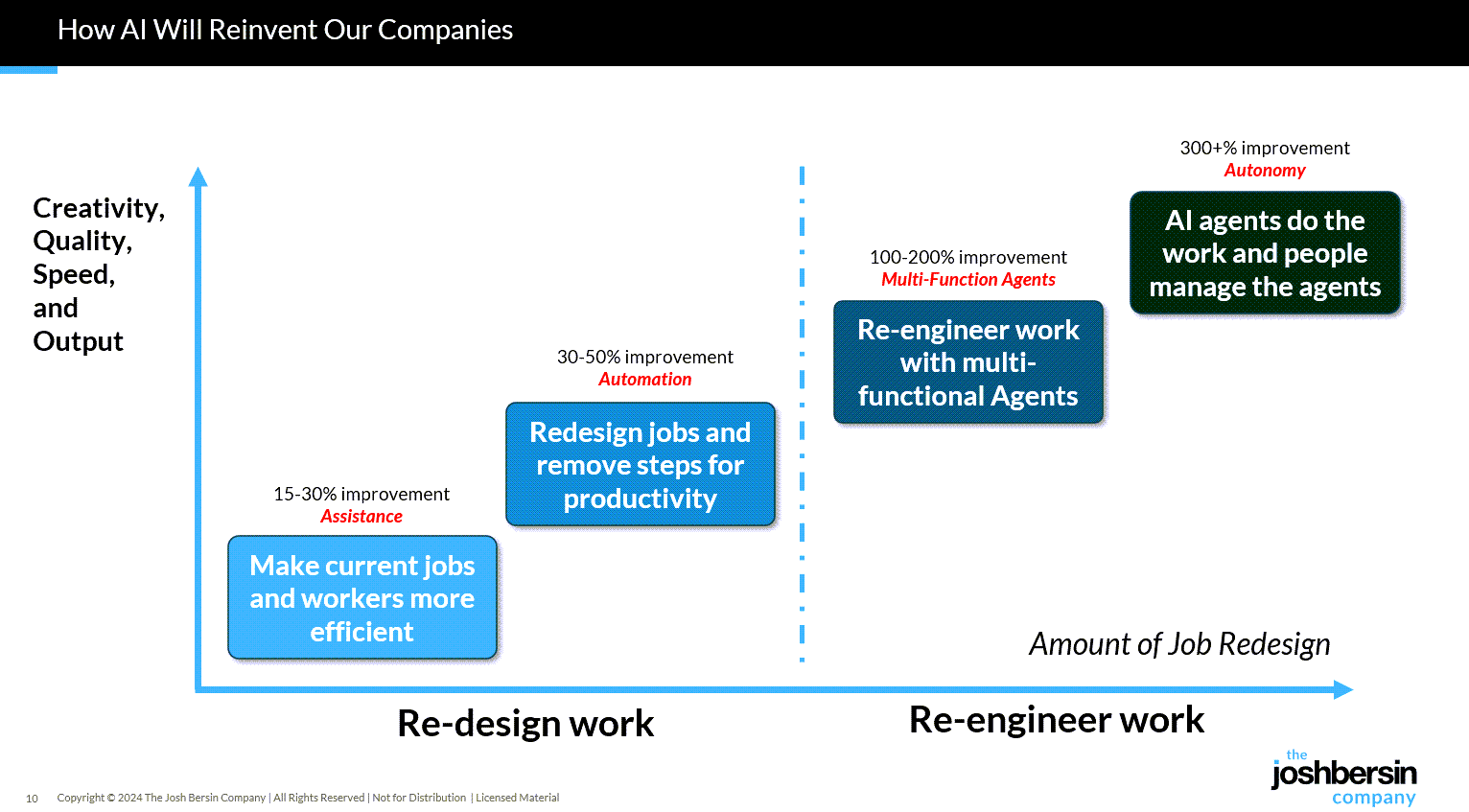
This week I want to share a hypothesis I’m increasingly convinced of: that we are entering an age of the 90/10 model of L&D.
90/10 is a model where roughly 90% of “training” is delivered by AI coaches as daily performance support, and 10% of training is dedicated to developing complex and critical skills via high-touch, human-led learning experiences.
Proponents of 90/10 argue that the model isn’t about learning less, but about learning smarter by defining all jobs to be done as one of the following:
- Delegate (the dead skills): Tasks that can be offloaded to AI.
- Co-Create (the 90%): Tasks which well-defined AI agents can augment and help humans to perform optimally.
- Facilitate (the 10%): Tasks which require high-touch, human-led learning to develop.
So if AI at work is now both real and material, the natural question for L&D is: how do we design for it? The short answer is to stop treating learning as an event and start treating it as a system.
My daughter’s generation expects to learn with AI, not pretend it doesn’t exist, because they know employers expect AI fluency and because AI will be ever-present in their adult lives.
— Jenny Maxell
The above quote was taken from this posting.
Unlocking Young Minds: How Gamified AI Learning Tools Inspire Fun, Personalized, and Powerful Education for Children in 2025 — from techgenyz.com by Sreyashi Bhattacharya
Highlight
- Gamified AI Learning Tools personalize education by adapting the difficulty and content to each child’s pace, fostering confidence and mastery.
- Engaging & Fun: Gamified elements like quests, badges, and stories keep children motivated and enthusiastic.
- Safe & Inclusive: Attention to equity, privacy, and cultural context ensures responsible and accessible learning.
How to test GenAI’s impact on learning — from timeshighereducation.com by Thibault Schrepel
Rather than speculate on GenAI’s promise or peril, Thibault Schrepel suggests simple teaching experiments to uncover its actual effects
Generative AI in higher education is a source of both fear and hype. Some predict the end of memory, others a revolution in personalised learning. My two-year classroom experiment points to a more modest reality: Artificial intelligence (AI) changes some skills, leaves others untouched and forces us to rethink the balance.
This indicates that the way forward is to test, not speculate. My results may not match yours, and that is precisely the point. Here are simple activities any teacher can use to see what AI really does in their own classroom.
4. Turn AI into a Socratic partner
Instead of being the sole interrogator, let AI play the role of tutor, client or judge. Have students use AI to question them, simulate cross-examination or push back on weak arguments. New “study modes” now built into several foundation models make this kind of tutoring easy to set up. Professors with more technical skills can go further, design their own GPTs or fine-tuned models trained on course content and let students interact directly with them. The point is the practice it creates. Students learn that questioning a machine is part of learning to think like a professional.
Assessment tasks that support human skills — from timeshighereducation.com by Amir Ghapanchi and Afrooz Purarjomandlangrudi
Assignments that focus on exploration, analysis and authenticity offer a road map for university assessment that incorporates AI while retaining its rigour and human elements
Rethinking traditional formats
1. From essay to exploration
When ChatGPT can generate competent academic essays in seconds, the traditional format’s dominance looks less secure as an assessment task. The future lies in moving from essays as knowledge reproduction to assessments that emphasise exploration and curation. Instead of asking students to write about a topic, challenge them to use artificial intelligence to explore multiple perspectives, compare outputs and critically evaluate what emerges.
Example: A management student asks an AI tool to generate several risk plans, then critiques the AI’s assumptions and identifies missing risks.
What your students are thinking about artificial intelligence — from timeshighereducation.com by Florencia Moore and Agostina Arbia
GenAI has been quickly adopted by students, but the consequences of using it as a shortcut could be grave. A study into how students think about and use GenAI offers insights into how teaching might adapt
However, when asked how AI negatively impacts their academic development, 29 per cent noted a “weakening or deterioration of intellectual abilities due to AI overuse”. The main concern cited was the loss of “mental exercise” and soft skills such as writing, creativity and reasoning.
The boundary between the human and the artificial does not seem so easy to draw, but as the poet Antonio Machado once said: “Traveller, there is no path; the path is made by walking.”
Jelly Beans for Grapes: How AI Can Erode Students’ Creativity — from edsurge.com by Thomas David Moore
There is nothing new about students trying to get one over on their teachers — there are probably cuneiform tablets about it — but when students use AI to generate what Shannon Vallor, philosopher of technology at the University of Edinburgh, calls a “truth-shaped word collage,” they are not only gaslighting the people trying to teach them, they are gaslighting themselves. In the words of Tulane professor Stan Oklobdzija, asking a computer to write an essay for you is the equivalent of “going to the gym and having robots lift the weights for you.”
Deloitte will make Claude available to 470,000 people across its global network — from anthropic.com
As part of the collaboration, Deloitte will establish a Claude Center of Excellence with trained specialists who will develop implementation frameworks, share leading practices across deployments, and provide ongoing technical support to create the systems needed to move AI pilots to production at scale. The collaboration represents Anthropic’s largest enterprise AI deployment to date, available to more than 470,000 Deloitte people.
Deloitte and Anthropic are co-creating a formal certification program to train and certify 15,000 of its professionals on Claude. These practitioners will help support Claude implementations across Deloitte’s network and Deloitte’s internal AI transformation efforts.
How AI Agents are finally delivering on the promise of Everboarding: driving retention when it counts most — from premierconstructionnews.com
Everboarding flips this model. Rather than ending after orientation, everboarding provides ongoing, role-specific training and support throughout the employee journey. It adapts to evolving responsibilities, reinforces standards, and helps workers grow into new roles. For high-turnover, high-pressure environments like retail, it’s a practical solution to a persistent challenge.
AI agents will be instrumental in the success of everboarding initiatives; they can provide a much more tailored training and development process for each individual employee, keeping track of which training modules may need to be completed, or where staff members need or want to develop further. This personalisation helps staff to feel not only more satisfied with their current role, but also guides them on the right path to progress in their individual careers.
Digital frontline apps are also ideal for everboarding. They offer bite-sized training that staff can complete anytime, whether during quiet moments on shift or in real time on the job, all accessible from their mobile devices.
TeachLM: insights from a new LLM fine-tuned for teaching & learning — from drphilippahardman.substack.com by Dr Philippa Hardman
Six key takeaways, including what the research tells us about how well AI performs as an instructional designer
As I and many others have pointed out in recent months, LLMs are great assistants but very ineffective teachers. Despite the rise of “educational LLMs” with specialised modes (e.g. Anthropic’s Learning Mode, OpenAI’s Study Mode, Google’s Guided Learning) AI typically eliminates the productive struggle, open exploration and natural dialogue that are fundamental to learning.
This week, Polygence, in collaboration with Stanford University researcher Prof Dora Demszky. published a first-of-its-kind research on a new model — TeachLM — built to address this gap.
In this week’s blog post, I deep dive what the research found and share the six key findings — including reflections on how well TeachLM performs on instructional design.
The Dangers of using AI to Grade — from marcwatkins.substack.com by Marc Watkins
Nobody Learns, Nobody Gains
AI as an assessment tool represents an existential threat to education because no matter how you try and establish guardrails or best practices around how it is employed, using the technology in place of an educator ultimately cedes human judgment to a machine-based process. It also devalues the entire enterprise of education and creates a situation where the only way universities can add value to education is by further eliminating costly human labor.
For me, the purpose of higher education is about human development, critical thinking, and the transformative experience of having your ideas taken seriously by another human being. That’s not something we should be in a rush to outsource to a machine.