From DSC:
One of my sisters shared this piece with me. She is very concerned about our society’s use of technology — whether it relates to our youth’s use of social media or the relentless pressure to be first in all things AI. As she was a teacher (at the middle school level) for 37 years, I greatly appreciate her viewpoints. She keeps me grounded in some of the negatives of technology. It’s important for us to listen to each other.
The new legal intelligence — from jordanfurlong.substack.com by Jordan Furlong
We’ve built machines that can reason like lawyers. Artificial legal intelligence is becoming scalable, portable and accessible in ways lawyers are not. We need to think hard about the implications.
Much of the legal tech world is still talking about Clio CEO Jack Newton’s keynote at last week’s ClioCon, where he announced two major new features: the “Intelligent Legal Work Platform,” which combines legal research, drafting and workflow into a single legal workspace; and “Clio for Enterprise,” a suite of legal work offerings aimed at BigLaw.
Both these features build on Clio’s out-of-nowhere $1B acquisition of vLex (and its legally grounded LLM Vincent) back in June.
A new source of legal intelligence has entered the legal sector.
…
Legal intelligence, once confined uniquely to lawyers, is now available from machines. That’s going to transform the legal sector.
Where the real action is: enterprise AI’s quiet revolution in legal tech and beyond — from canadianlawyermag.com by Tim Wilbur
Harvey, Clio, and Cohere signal that organizational solutions will lead the next wave of change
The public conversation about artificial intelligence is dominated by the spectacular and the controversial: deepfake videos, AI-induced psychosis, and the privacy risks posed by consumer-facing chatbots like ChatGPT. But while these stories grab headlines, a quieter – and arguably more transformative – revolution is underway in enterprise software. In legal technology, in particular, AI is rapidly reshaping how law firms and legal departments operate and compete. This shift is just one example of how enterprise AI, not just consumer AI, is where real action is happening.
Both Harvey and Clio illustrate a crucial point: the future of legal tech is not about disruption for its own sake, but partnership and integration. Harvey’s collaborations with LexisNexis and others are about creating a cohesive experience for law firms, not rendering them obsolete. As Pereira put it, “We don’t see it so much as disruption. Law firms actually already do this… We see it as ‘how do we help you build infrastructure that supercharges this?’”
…
The rapid evolution in legal tech is just one example of a broader trend: the real action in AI is happening in enterprise software, not just in consumer-facing products. While ChatGPT and Google’s Gemini dominate the headlines, companies like Cohere are quietly transforming how organizations across industries leverage AI.
Also from canadianlawyermag.com, see:
- Harvey’s $5 billion bet: Why the hottest company in legal tech is eyeing Canada
Co-founder Gabe Pereyra says their new Toronto office will have both tech expertise and customer support
The AI company’s plan to open an office in Toronto isn’t just about expanding territory – it’s a strategic push to tap into top technical talent and capture a market known for legal innovation.
Unseeable prompt injections in screenshots: more vulnerabilities in Comet and other AI browsers — from brave.com by Artem Chaikin and Shivan Kaul Sahib
Building on our previous disclosure of the Perplexity Comet vulnerability, we’ve continued our security research across the agentic browser landscape. What we’ve found confirms our initial concerns: indirect prompt injection is not an isolated issue, but a systemic challenge facing the entire category of AI-powered browsers. This post examines additional attack vectors we’ve identified and tested across different implementations.
As we’ve written before, AI-powered browsers that can take actions on your behalf are powerful yet extremely risky. If you’re signed into sensitive accounts like your bank or your email provider in your browser, simplysummarizing a Reddit postcould result in an attacker being able to steal money or your private data.
The above item was mentioned by Grant Harvey out at The Neuron in the following posting:
- AI browser risks and the “AI trust tax” you’re already paying — from theneurondaily.com by Grant Harvey
PLUS: OpenAI’s new music maker + China’s 90% power?cut AI server.
Robin AI’s Big Bet on Legal Tech Meets Market Reality — from lawfuel.com
Robin’s Legal Tech Backfire
Robin AI, the poster child for the “AI meets law” revolution, is learning the hard way that venture capital fairy dust doesn’t guarantee happily-ever-after. The London-based legal tech firm, once proudly waving its genAI-plus-human-experts flag, is now cutting staff after growth dreams collided with the brick wall of economic reality.
The company confirmed that redundancies are under way following a failed major funding push. Earlier promises of explosive revenue have fizzled. Despite around $50 million in venture cash over the past two years, Robin’s 2025 numbers have fallen short of investor expectations. The team that once ballooned to 200 is now shrinking.
The field is now swarming with contenders: CLM platforms stuffing genAI into every feature, corporate legal teams bypassing vendors entirely by prodding ChatGPT directly, and new entrants like Harvey and Legora guzzling capital to bulldoze into the market. Even Workday is muscling in.
Meanwhile, ALSPs and AI-powered pseudo-law firms like Crosby and Eudia are eating market share like it’s free pizza. The number of inhouse teams actually buying these tools at scale is still frustratingly small. And investors don’t have much patience for slow burns anymore.
Why Being ‘Rude’ to AI Could Win Your Next Case or Deal — from thebrainyacts.beehiiv.com by Josh Kubicki
TL;DR: AI no longer rewards politeness—new research shows direct, assertive prompts yield better, more detailed responses. Learn why this shift matters for legal precision, test real-world examples (polite vs. blunt), and set up custom instructions in OpenAI (plus tips for other models) to make your AI a concise analytical tool, not a chatty one. Actionable steps inside to upgrade your workflow immediately.
Custom AI Development: Evolving from Static AI Systems to Dynamic Learning Agents in 2025 — community.nasscom.in
This blog explores how custom AI development accelerates the evolution from static AI to dynamic learning agents and why this transformation is critical for driving innovation, efficiency, and competitive advantage.
…
Dynamic Learning Agents: The Next Generation
Dynamic learning agents, sometimes referred to as adaptive or agentic AI, represent a leap forward. They combine continuous learning, autonomous action, and context-aware adaptability.
Custom AI development plays a crucial role here: it ensures that these agents are designed specifically for an enterprise’s unique needs rather than relying on generic, one-size-fits-all AI platforms. Tailored dynamic agents can:
- Continuously learn from incoming data streams
- Make autonomous, goal-directed decisions aligned with business objectives
- Adapt behavior in real time based on context and feedback
- Collaborate with other AI agents and human teams to solve complex challenges
The result is an AI ecosystem that evolves with the business, providing sustained competitive advantage.
Also from community.nasscom.in, see:
Building AI Agents with Multimodal Models: From Perception to Action
Perception: The Foundation of Intelligent Agents
Perception is the first step in building AI agents. It involves capturing and interpreting data from multiple modalities, including text, images, audio, and structured inputs. A multimodal AI agent relies on this comprehensive understanding to make informed decisions.
For example, in healthcare, an AI agent may process electronic health records (text), MRI scans (vision), and patient audio consultations (speech) to build a complete understanding of a patient’s condition. Similarly, in retail, AI agents can analyze purchase histories (structured data), product images (vision), and customer reviews (text) to inform recommendations and marketing strategies.
Effective perception ensures that AI agents have contextual awareness, which is essential for accurate reasoning and appropriate action.
From 70-20-10 to 90-10: a new operating system for L&D in the age of AI? — from linkedin.com by Dr. Philippa Hardman
Also from Philippa, see:
- Defining & Navigating the Jagged Frontier in Instructional Design (October, 2025)
What we know about where AI helps (and where it hinders) Instructional Design, and how to manage it
Your New ChatGPT Guide — from wondertools.substack.com by Jeremy Caplan and The PyCoach
25 AI Tips & Tricks from a guest expert
- ChatGPT can make you more productive or dumber. An MIT study found that while AI can significantly boost productivity, it may also weaken your critical thinking. Use it as an assistant, not a substitute for your brain.
- If you’re a student, use study mode in ChatGPT, Gemini, or Claude. When this feature is enabled, the chatbots will guide you through problems rather than just giving full answers, so you’ll be doing the critical thinking.
- ChatGPT and other chatbots can confidently make stuff up (aka AI hallucinations). If you suspect something isn’t right, double-check its answers.
- NotebookLM hallucinates less than most AI tools, but it requires you to upload sources (PDFs, audio, video) and won’t answer questions beyond those materials. That said, it’s great for students and anyone with materials to upload.
- Probably the most underrated AI feature is deep research. It automates web searching for you and returns a fully cited report with minimal hallucinations in five to 30 minutes. It’s available in ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Gemini, so give it a try.
Adobe Reinvents its Entire Creative Suite with AI Co-Pilots, Custom Models, and a New Open Platform — from theneuron.ai by Grant Harvey
Adobe just put an AI co-pilot in every one of its apps, letting you chat with Photoshop, train models on your own style, and generate entire videos with a single subscription that now includes top models from Google, Runway, and Pika.
Adobe came to play, y’all.
At Adobe MAX 2025 in Los Angeles, the company dropped an entire creative AI ecosystem that touches every single part of the creative workflow. In our opinion, all these new features aren’t about replacing creators; it’s about empowering them with superpowers they can actually control.
Adobe’s new plan is to put an AI co-pilot in every single app.
- For professionals, the game-changer is Firefly Custom Models. Start training one now to create a consistent, on-brand look for all your assets.
- For everyday creators, the AI Assistants in Photoshop and Express will drastically speed up your workflow.
- The best place to start is the Photoshop AI Assistant (currently in private beta), which offers a powerful glimpse into the future of creative software—a future where you’re less of a button-pusher and more of a creative director.
Adobe MAX Day 2: The Storyteller Is Still King, But AI Is Their New Superpower — from theneuron.ai by Grant Harvey
Adobe’s Day 2 keynote showcased a suite of AI-powered creative tools designed to accelerate workflows, but the real message from creators like Mark Rober and James Gunn was clear: technology serves the story, not the other way around.
On the second day of its annual MAX conference, Adobe drove home a message that has been echoing through the creative industry for the past year: AI is not a replacement, but a partner. The keynote stage featured a powerful trio of modern storytellers—YouTube creator Brandon Baum, science educator and viral video wizard Mark Rober, and Hollywood director James Gunn—who each offered a unique perspective on a shared theme: technology is a powerful tool, but human instinct, hard work, and the timeless art of storytelling remain paramount.
From DSC:
As Grant mentioned, the demos dealt with ideation, image generation, video generation, audio generation, and editing.
Adobe Max 2025: all the latest creative tools and AI announcements — from theverge.com by Jess Weatherbed
The creative software giant is launching new generative AI tools that make digital voiceovers and custom soundtracks for videos, and adding AI assistants to Express and Photoshop for web that edit entire projects using descriptive prompts. And that’s just the start, because Adobe is planning to eventually bring AI assistants to all of its design apps.
Also see Adobe Delivers New AI Innovations, Assistants and Models Across Creative Cloud to Empower Creative Professionals plus other items from the News section from Adobe
OpenAI’s Atlas: the End of Online Learning—or Just the Beginning? — from drphilippahardman.substack.com by Dr. Philippa Hardman
My take is this: in all of the anxiety lies a crucial and long-overdue opportunity to deliver better learning experiences. Precisely because Atlas perceives the same context in the same moment as you, it can transform learning into a process aligned with core neuro-scientific principles—including active retrieval, guided attention, adaptive feedback and context-dependent memory formation.
Perhaps in Atlas we have a browser that for the first time isn’t just a portal to information, but one which can become a co-participant in active cognitive engagement—enabling iterative practice, reflective thinking, and real-time scaffolding as you move through challenges and ideas online.
With this in mind, I put together 10 use cases for Atlas for you to try for yourself.
…
6. Retrieval Practice
What: Pulling information from memory drives retention better than re-reading.
Why: Practice testing delivers medium-to-large effects (Adesope et al., 2017).
Try: Open a document with your previous notes. Ask Atlas for a mixed activity set: “Quiz me on the Krebs cycle—give me a near-miss, high-stretch MCQ, then a fill-in-the-blank, then ask me to explain it to a teen.”
Atlas uses its browser memory to generate targeted questions from your actual study materials, supporting spaced, varied retrieval.
From DSC:
A quick comment. I appreciate these ideas and approaches from Katarzyna and Rita. I do think that someone is going to want to be sure that the AI models/platforms/tools are given up-to-date information and updated instructions — i.e., any new procedures, steps to take, etc. Perhaps I’m missing the boat here, but an internal AI platform is going to need to have access to up-to-date information and instructions.
Chegg CEO steps down amid major AI-driven restructure — from linkedin.com by Megan McDonough
Edtech firm Chegg confirmed Monday it is reducing its workforce by 45%, or 388 employees globally, and its chief executive officer is stepping down. Current CEO Nathan Schultz will be replaced effective immediately by executive chairman (and former CEO) Dan Rosensweig. The rise of AI-powered tools has dealt a massive blow to the online homework helper and led to “substantial” declines in revenue and traffic. Company shares have slipped over 10% this year. Chegg recently explored a possible sale, but ultimately decided to keep the company intact.
At the most recent NVIDIA GTC conference, held in Washington, D.C. in October 2025, CEO Jensen Huang announced major developments emphasizing the use of AI to “reindustrialize America”. This included new partnerships, expansion of the Blackwell architecture, and advancements in AI factories for robotics and science. The spring 2024 GTC conference, meanwhile, was headlined by the launch of the Blackwell GPU and significant updates to the Omniverse and robotics platforms.
During the keynote in D.C., Jensen Huang focused on American AI leadership and announced several key initiatives.
- Massive Blackwell GPU deployments: The company announced an expansion of its Blackwell GPU architecture, which first launched in March 2024. Reportedly, the company has already shipped 6 million Blackwell chips, with orders for 14 million more by the end of 2025.
- AI supercomputers for science: In partnership with the Department of Energy and Oracle, NVIDIA is building new AI supercomputers at Argonne National Laboratory. The largest, named “Solstice,” will deploy 100,000 Blackwell GPUs.
- 6G infrastructure: NVIDIA announced a partnership with Nokia to develop a U.S.-based, AI-native 6G technology stack.
- AI factories for robotics: A new AI Factory Research Center in Virginia will use NVIDIA’s technology for building massive-scale data centers for AI.
- Autonomous robotaxis: The company’s self-driving technology, already adopted by several carmakers, will be used by Uber for an autonomous fleet of 100,000 robotaxis starting in 2027.
Nvidia and Uber team up to develop network of self-driving cars — from finance.yahoo.com by Daniel Howley
Nvidia (NVDA) and Uber (UBER) on Tuesday revealed that they’re working to put together what they say will be the world’s largest network of Level 4-ready autonomous cars.
The duo will build out 100,000 vehicles beginning in 2027 using Nvidia’s Drive AGX Hyperion 10 platform and Drive AV software.
Nvidia stock hits all-time high, nears $5 trillion market cap after slew of updates at GTC event — from finance.yahoo.com by Daniel Howley
Nvidia (NVDA) stock on Tuesday rose 5% to close at a record high after the company announced a slew of product updates, partnerships, and investment initiatives at its GTC event in Washington, D.C., putting it on the doorstep of becoming the first company in history with a market value above $5 trillion.
The AI chip giant is approaching the threshold — settling at a market cap of $4.89 trillion on Tuesday — just months after becoming the first to close above $4 trillion in July.
There is no God Tier video model — from downes.ca by Stephen Downes
From DSC:
Stephen has some solid reflections and asks some excellent questions in this posting, including:
The question is: how do we optimize an AI to support learning? Will one model be enough? Or do we need different models for different learners in different scenarios?
A More Human University: The Role of AI in Learning — from er.educause.edu by Robert Placido
Far from heralding the collapse of higher education, artificial intelligence offers a transformative opportunity to scale meaningful, individualized learning experiences across diverse classrooms.
The narrative surrounding artificial intelligence (AI) in higher education is often grim. We hear dire predictions of an “impending collapse,” fueled by fears of rampant cheating, the erosion of critical thinking, and the obsolescence of the human educator.Footnote1 This dystopian view, however, is a failure of imagination. It mistakes the death rattle of an outdated pedagogical model for the death of learning itself. The truth is far more hopeful: AI is not an asteroid coming for higher education. It is a catalyst that can finally empower us to solve our oldest, most intractable problem: the inability to scale deep, engaged, and truly personalized learning.
Claude for Life Sciences — from anthropic.com
Increasing the rate of scientific progress is a core part of Anthropic’s public benefit mission.
We are focused on building the tools to allow researchers to make new discoveries – and eventually, to allow AI models to make these discoveries autonomously.
Until recently, scientists typically used Claude for individual tasks, like writing code for statistical analysis or summarizing papers. Pharmaceutical companies and others in industry also use it for tasks across the rest of their business, like sales, to fund new research. Now, our goal is to make Claude capable of supporting the entire process, from early discovery through to translation and commercialization.
To do this, we’re rolling out several improvements that aim to make Claude a better partner for those who work in the life sciences, including researchers, clinical coordinators, and regulatory affairs managers.
AI as an access tool for neurodiverse and international staff — from timeshighereducation.com by Vanessa Mar-Molinero
Used transparently and ethically, GenAI can level the playing field and lower the cognitive load of repetitive tasks for admin staff, student support and teachers
Where AI helps without cutting academic corners
When framed as accessibility and quality enhancement, AI can support staff to complete standard tasks with less friction. However, while it supports clarity, consistency and inclusion, generative AI (GenAI) does not replace disciplinary expertise, ethical judgement or the teacher–student relationship. These are ways it can be put to effective use:
- Drafting and tone calibration: …
- Language scaffolding: …
- Structure and templates: ..
- Summarise and prioritise: …
- Accessibility by default: …
- Idea generation for pedagogy: …
- Translation and cultural mediation: …
Beyond learning design: supporting pedagogical innovation in response to AI — from timeshighereducation.com by Charlotte von Essen
To avoid an unwinnable game of catch-up with technology, universities must rethink pedagogical improvement that goes beyond scaling online learning
The Sleep of Liberal Arts Produces AI — from aiedusimplified.substack.com by Lance Eaton, Ph.D.
A keynote at the AI and the Liberal Arts Symposium Conference
This past weekend, I had the honor to be the keynote speaker at a really fantstistic conferece, AI and the Liberal Arts Symposium at Connecticut College. I had shared a bit about this before with my interview with Lori Looney. It was an incredible conference, thoughtfully composed with a lot of things to chew on and think about.
It was also an entirely brand new talk in a slightly different context from many of my other talks and workshops. It was something I had to build entirely from the ground up. It reminded me in some ways of last year’s “What If GenAI Is a Nothingburger”.
It was a real challenge and one I’ve been working on and off for months, trying to figure out the right balance. It’s a work I feel proud of because of the balancing act I try to navigate. So, as always, it’s here for others to read and engage with. And, of course, here is the slide deck as well (with CC license).
2. Concern and excitement about AI — from pewresearch.org by Jacob Poushter,Moira Faganand Manolo Corichi
Key findings
- A median of 34% of adults across 25 countries are more concerned than excited about the increased use of artificial intelligence in daily life. A median of 42% are equally concerned and excited, and 16% are more excited than concerned.
- Older adults, women, people with less education and those who use the internet less often are particularly likely to be more concerned than excited.
Also relevant here:
- The U.S. Public Wants Regulation (or Prohibition) of Expert-Level and Superhuman AI — from futureoflife.org
Three?quarters of U.S. adults want strong regulations on AI development, preferring oversight akin to pharmaceuticals rather than industry “self?regulation.”
AI Video Wars include Veo 3.1, Sora 2, Ray3, Kling 2.5 + Wan 2.5 — from heatherbcooper.substack.com by Heather Cooper
House of David Season 2 is here!
In today’s edition:
- Veo 3.1 brings richer audio and object-level editing to Google Flow
- Sora 2 is here with Cameo self-insertion and collaborative Remix features
- Ray3 brings world-first reasoning and HDR to video generation
- Kling 2.5 Turbo delivers faster, cheaper, more consistent results
- WAN 2.5 revolutionizes talking head creation with perfect audio sync
- House of David Season 2 Trailer
- HeyGen Agent, Hailuo Agent, Topaz Astra, and Lovable Cloud updates
- Image & Video Prompts
From DSC:
By the way, the House of David (which Heather referred to) is very well done! I enjoyed watching Season 1. Like The Chosen, it brings the Bible to life in excellent, impactful ways! Both series convey the context and cultural tensions at the time. Both series are an answer to prayer for me and many others — as they are professionally-done. Both series match anything that comes out of Hollywood in terms of the acting, script writing, music, the sets, etc. Both are very well done.
.
An item re: Sora:
- Association of Talent Agents, United Talent Agency, Creative Artists Agency also Join to Protect Performers. — from sagaftra.org
Other items re: Open AI’s new Atlas browser:
Introducing ChatGPT Atlas — from openai.com
The browser with ChatGPT built in.
[On 10/21/25] we’re introducing ChatGPT Atlas, a new web browser built with ChatGPT at its core.
AI gives us a rare moment to rethink what it means to use the web. Last year, we added search in ChatGPT so you could instantly find timely information from across the internet—and it quickly became one of our most-used features. But your browser is where all of your work, tools, and context come together. A browser built with ChatGPT takes us closer to a true super-assistant that understands your world and helps you achieve your goals.
With Atlas, ChatGPT can come with you anywhere across the web—helping you in the window right where you are, understanding what you’re trying to do, and completing tasks for you, all without copying and pasting or leaving the page. Your ChatGPT memory is built in, so conversations can draw on past chats and details to help you get new things done.
ChatGPT Atlas: the AI browser test — from getsuperintel.com by Kim “Chubby” Isenberg
Chat GPT Atlas aims to transform web browsing into a conversational, AI-native experience, but early reviews are mixed
OpenAI’s new ChatGPT Atlas promises to merge web browsing, search, and automation into a single interface — an “AI-native browser” meant to make the web conversational. After testing it myself, though, I’m still trying to see the real breakthrough. It feels familiar: summaries, follow-ups, and even the Agent’s task handling all mirror what I already do inside ChatGPT.
OpenAI’s new Atlas browser remembers everything — from theneurondaily.com by Grant Harvey
PLUS: Our AIs are getting brain rot?!
Here’s how it works: Atlas can see what you’re looking at on any webpage and instantly help without you needing to copy/paste or switch tabs. Researching hotels? Ask ChatGPT to compare prices right there. Reading a dense article? Get a summary on the spot. The AI lives in the browser itself.
OpenAI’s new product — from bensbites.com
The latest entry in AI browsers is Atlas – A new browser from OpenAI. Atlas would feel similar to Dia or Comet if you’ve used them. It has an “Ask ChatGPT” sidebar that has the context of your page, and choose “Agent” to work on that tab. Right now, Agent is limited to a single tab, and it is way too slow to delegate anything for real to it. Click accuracy for Agent is alright on normal web pages, but it will definitely trip up if you ask it to use something like Google Sheets.
One ambient feature that I think many people will like is “select to rewrite” – You can select any text in Atlas, hover/click on the blue dot in the top right corner to rewrite it using AI.
Your AI Resume Hacks Probably Won’t Fool Hiring Algorithms — from builtin.com by Jeff Rumage
Recruiters say those viral hidden prompt for resumes don’t work — and might cost you interviews.
Summary: Job seekers are using “prompt hacking” — embedding hidden AI commands in white font on resumes — to try to trick applicant tracking systems. While some report success, recruiters warn the tactic could backfire and eliminate the candidate from consideration.
The Job Market Might Be a Mess, But Don’t Blame AI Just Yet — from builtin.com by Matthew Urwin
A new study by Yale University and the Brookings Institution says the panic around artificial intelligence stealing jobs is overblown. But that might not be the case for long.
Summary: A Yale and Brookings study finds generative AI has had little impact on U.S. jobs so far, with tariffs, immigration policies and the number of college grads potentially playing a larger role. Still, AI could disrupt the workforce in the not-so-distant future.
“Future of Professionals Report” analysis: Why AI will flip law firm economics — from thomsonreuters.com by Ragunath Ramanathan
AI forces a reinvention of law firm billing models, the market will reward those firms that price by outcome, guarantee efficiency, and are transparent. The question then isn’t whether to change — it’s whether firms will stand on the sidelines or lead
Key insights:
- Efficiency and cost savings are expected — AI is significantly increasing efficiency and reducing costs in the legal industry, with each lawyer expecting to save 190 work-hours per year by leveraging AI, resulting in approximately $20 billion worth of work-savings in the US alone.
- Challenges to the billable hour model — The traditional billable hour model is being challenged by AI advancements, as lawyers are now able to complete tasks more efficiently and quickly, leading some law firms to explore alternative pricing models that reflect the value delivered rather than the time spent.
- Opportunities for smaller law firms — AI presents unique opportunities for smaller law firms to differentiate themselves and compete with larger firms, as AI solutions allow smaller firms to access advanced technology without significant investment and deliver innovative pricing models.
The legal industry is undergoing a significant transformation that’s being driven by the rapid adoption of AI — a shift that is poised to redefine traditional practices, particularly the billable hour model, a cornerstone of law firm operations.
…
Not surprisingly, AI is anticipated to have the biggest impact on the legal industry over the next five years, with 80% of law firm survey respondents to Thomson Reuters recently published 2025 Future of Professionals report saying that they expect AI to fundamentally alter how they conduct business, especially around how law firms price, staff, and deliver legal work to their clients.
International AI Safety Report — from internationalaisafetyreport.org
About the International AI Safety Report
The International AI Safety Report is the world’s first comprehensive review of the latest science on the capabilities and risks of general-purpose AI systems. Written by over 100 independent experts and led by Turing Award winner Yoshua Bengio, it represents the largest international collaboration on AI safety research to date. The Report gives decision-makers a shared global picture of AI’s risks and impacts, serving as the authoritative reference for governments and organisations developing AI policies worldwide. It is already shaping debates and informing evidence-based decisions across research and policy communities.
From siloed tools to intelligent journeys: Reimagining learning experience in the age of ‘Experience AI’ — from linkedin.com by Lev Gonick
Experience AI: A new architecture of learning
Experience AI represents a new architecture for learning — one that prioritizes continuity, agency and deep personalization. It fuses three dimensions into a new category of co-intelligent systems:
- Agentic AI that evolves with the learner, not just serves them
- Persona-based AI that adapts to individual goals, identities and motivations
- Multimodal AI that engages across text, voice, video, simulation and interaction
Experience AI brings learning into context. It powers personalized, problem-based journeys where students explore ideas, reflect on progress and co-create meaning — with both human and machine collaborators.
The above posting on LinkedIn then links to this document
Designing Microsoft 365 Copilot to empower educators, students, and staff — from microsoft.com by Deirdre Quarnstrom
While over 80% of respondents in the 2025 AI in Education Report have already used AI for school, we believe there are significant opportunities to design AI that can better serve each of their needs and broaden access to the latest innovation.1
That’s why today [10/15/25], we’re announcing AI-powered experiences built for teaching and learning at no additional cost, new integrations in Microsoft 365 apps and Learning Management Systems, and an academic offering for Microsoft 365 Copilot.
Introducing AI-powered teaching and learning
Empowering educators with Teach
We’re introducing Teach to help streamline class prep and adapt AI to support educators’ teaching expertise with intuitive and customizable features. In one place, educators can easily access AI-powered teaching tools to create lesson plans, draft materials like quizzes and rubrics, and quickly make modifications to language, reading level, length, difficulty, alignment to relevant standards, and more.
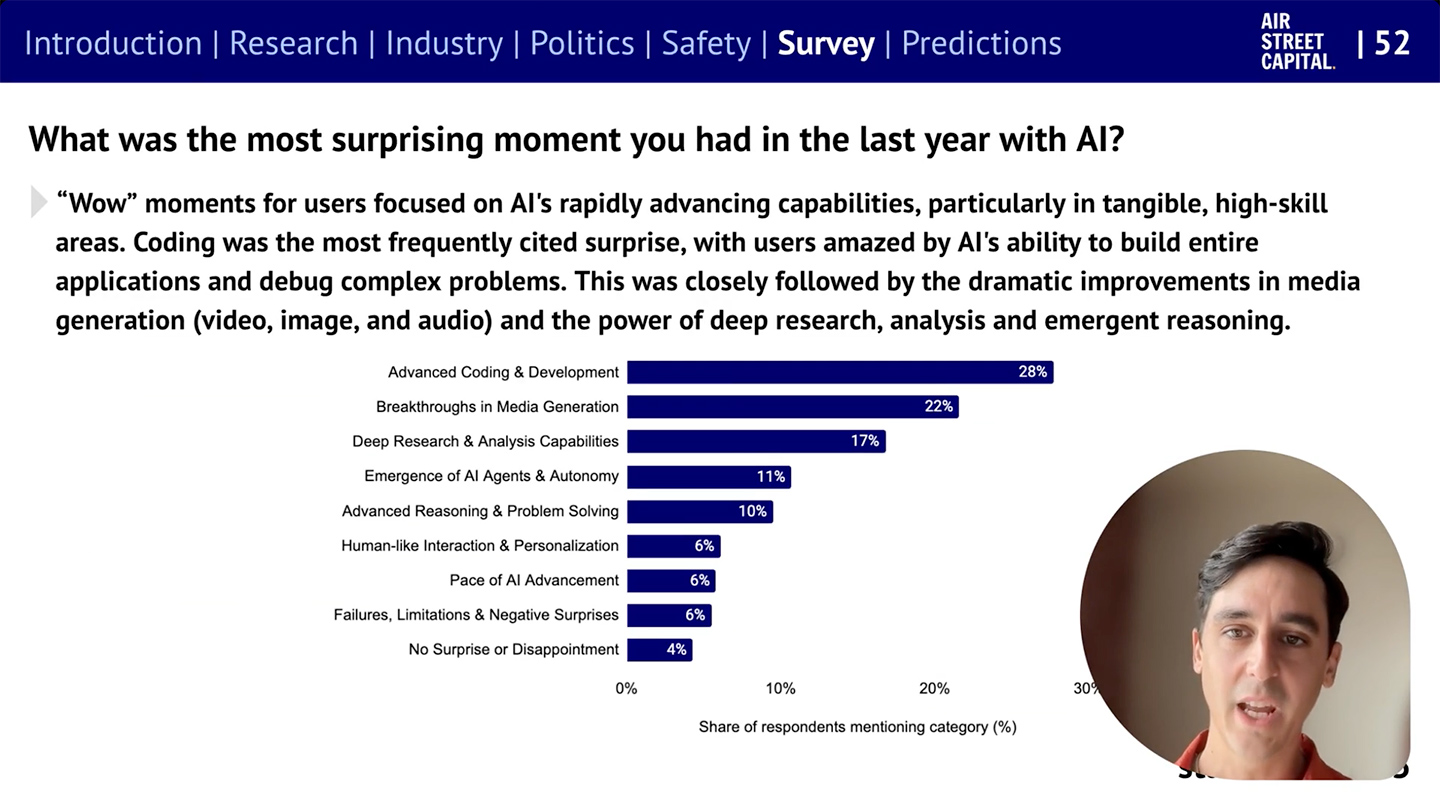
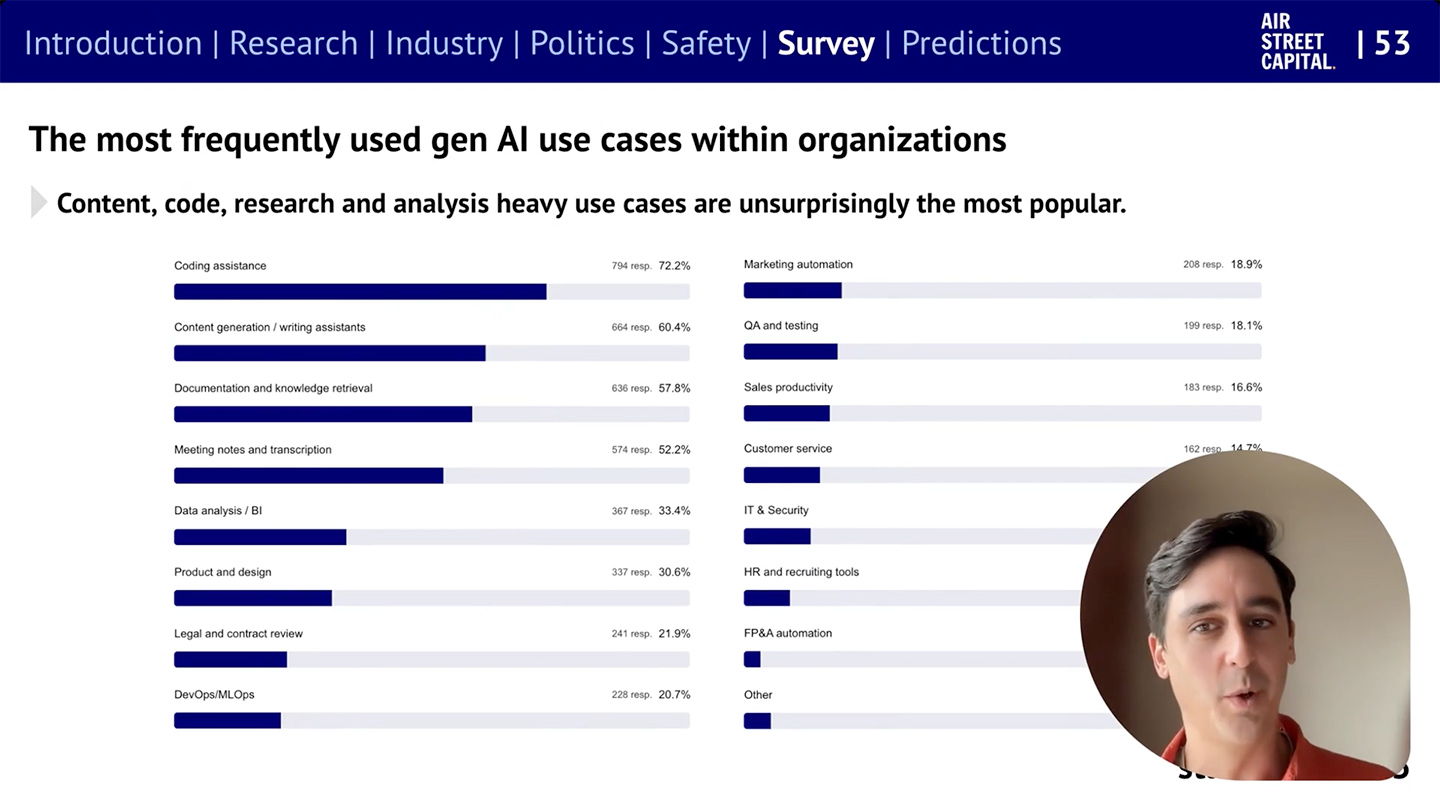
The State of AI Report 2025 — from nathanbenaich.substack.com by Nathan Benaich
In short, it’s been a monumental 12 months for AI. Our eighth annual report is the most comprehensive it’s ever been, covering what you need to know about research, industry, politics, and safety – along with our first State of AI Usage Survey of 1,200 practitioners.
From 70/20/10 to 90/10 — from drphilippahardman.substack.com by Dr Philippa Hardman
A new L&D operating system for the AI Era?
This week I want to share a hypothesis I’m increasingly convinced of: that we are entering an age of the 90/10 model of L&D.
90/10 is a model where roughly 90% of “training” is delivered by AI coaches as daily performance support, and 10% of training is dedicated to developing complex and critical skills via high-touch, human-led learning experiences.
Proponents of 90/10 argue that the model isn’t about learning less, but about learning smarter by defining all jobs to be done as one of the following:
- Delegate (the dead skills): Tasks that can be offloaded to AI.
- Co-Create (the 90%): Tasks which well-defined AI agents can augment and help humans to perform optimally.
- Facilitate (the 10%): Tasks which require high-touch, human-led learning to develop.
So if AI at work is now both real and material, the natural question for L&D is: how do we design for it? The short answer is to stop treating learning as an event and start treating it as a system.
My daughter’s generation expects to learn with AI, not pretend it doesn’t exist, because they know employers expect AI fluency and because AI will be ever-present in their adult lives.
— Jenny Maxell
The above quote was taken from this posting.
Unlocking Young Minds: How Gamified AI Learning Tools Inspire Fun, Personalized, and Powerful Education for Children in 2025 — from techgenyz.com by Sreyashi Bhattacharya
Table of Contents
- Highlight
- Gamified AI Learning Tools: The Future of Fun and Personalized Education
- Key Features of Gamified AI Learning Tools:
- Advantages of Gamified AI in Education
- Challenges and Concerns with Gamified AI Tools
- Emerging Trends in AI + Gamification for Learning
- Real-World Case Study: AI Games for Learning Math
- Conclusion: The Future of Gamified AI in Education
Highlight
- Gamified AI Learning Tools personalize education by adapting the difficulty and content to each child’s pace, fostering confidence and mastery.
- Engaging & Fun: Gamified elements like quests, badges, and stories keep children motivated and enthusiastic.
- Safe & Inclusive: Attention to equity, privacy, and cultural context ensures responsible and accessible learning.
How to test GenAI’s impact on learning — from timeshighereducation.com by Thibault Schrepel
Rather than speculate on GenAI’s promise or peril, Thibault Schrepel suggests simple teaching experiments to uncover its actual effects
Generative AI in higher education is a source of both fear and hype. Some predict the end of memory, others a revolution in personalised learning. My two-year classroom experiment points to a more modest reality: Artificial intelligence (AI) changes some skills, leaves others untouched and forces us to rethink the balance.
This indicates that the way forward is to test, not speculate. My results may not match yours, and that is precisely the point. Here are simple activities any teacher can use to see what AI really does in their own classroom.
4. Turn AI into a Socratic partner
Instead of being the sole interrogator, let AI play the role of tutor, client or judge. Have students use AI to question them, simulate cross-examination or push back on weak arguments. New “study modes” now built into several foundation models make this kind of tutoring easy to set up. Professors with more technical skills can go further, design their own GPTs or fine-tuned models trained on course content and let students interact directly with them. The point is the practice it creates. Students learn that questioning a machine is part of learning to think like a professional.
Assessment tasks that support human skills — from timeshighereducation.com by Amir Ghapanchi and Afrooz Purarjomandlangrudi
Assignments that focus on exploration, analysis and authenticity offer a road map for university assessment that incorporates AI while retaining its rigour and human elements
Rethinking traditional formats
1. From essay to exploration
When ChatGPT can generate competent academic essays in seconds, the traditional format’s dominance looks less secure as an assessment task. The future lies in moving from essays as knowledge reproduction to assessments that emphasise exploration and curation. Instead of asking students to write about a topic, challenge them to use artificial intelligence to explore multiple perspectives, compare outputs and critically evaluate what emerges.
Example: A management student asks an AI tool to generate several risk plans, then critiques the AI’s assumptions and identifies missing risks.
What your students are thinking about artificial intelligence — from timeshighereducation.com by Florencia Moore and Agostina Arbia
GenAI has been quickly adopted by students, but the consequences of using it as a shortcut could be grave. A study into how students think about and use GenAI offers insights into how teaching might adapt
However, when asked how AI negatively impacts their academic development, 29 per cent noted a “weakening or deterioration of intellectual abilities due to AI overuse”. The main concern cited was the loss of “mental exercise” and soft skills such as writing, creativity and reasoning.
The boundary between the human and the artificial does not seem so easy to draw, but as the poet Antonio Machado once said: “Traveller, there is no path; the path is made by walking.”
Jelly Beans for Grapes: How AI Can Erode Students’ Creativity — from edsurge.com by Thomas David Moore
There is nothing new about students trying to get one over on their teachers — there are probably cuneiform tablets about it — but when students use AI to generate what Shannon Vallor, philosopher of technology at the University of Edinburgh, calls a “truth-shaped word collage,” they are not only gaslighting the people trying to teach them, they are gaslighting themselves. In the words of Tulane professor Stan Oklobdzija, asking a computer to write an essay for you is the equivalent of “going to the gym and having robots lift the weights for you.”
Deloitte will make Claude available to 470,000 people across its global network — from anthropic.com
As part of the collaboration, Deloitte will establish a Claude Center of Excellence with trained specialists who will develop implementation frameworks, share leading practices across deployments, and provide ongoing technical support to create the systems needed to move AI pilots to production at scale. The collaboration represents Anthropic’s largest enterprise AI deployment to date, available to more than 470,000 Deloitte people.
Deloitte and Anthropic are co-creating a formal certification program to train and certify 15,000 of its professionals on Claude. These practitioners will help support Claude implementations across Deloitte’s network and Deloitte’s internal AI transformation efforts.
How AI Agents are finally delivering on the promise of Everboarding: driving retention when it counts most — from premierconstructionnews.com
Everboarding flips this model. Rather than ending after orientation, everboarding provides ongoing, role-specific training and support throughout the employee journey. It adapts to evolving responsibilities, reinforces standards, and helps workers grow into new roles. For high-turnover, high-pressure environments like retail, it’s a practical solution to a persistent challenge.
AI agents will be instrumental in the success of everboarding initiatives; they can provide a much more tailored training and development process for each individual employee, keeping track of which training modules may need to be completed, or where staff members need or want to develop further. This personalisation helps staff to feel not only more satisfied with their current role, but also guides them on the right path to progress in their individual careers.
Digital frontline apps are also ideal for everboarding. They offer bite-sized training that staff can complete anytime, whether during quiet moments on shift or in real time on the job, all accessible from their mobile devices.
TeachLM: insights from a new LLM fine-tuned for teaching & learning — from drphilippahardman.substack.com by Dr Philippa Hardman
Six key takeaways, including what the research tells us about how well AI performs as an instructional designer
As I and many others have pointed out in recent months, LLMs are great assistants but very ineffective teachers. Despite the rise of “educational LLMs” with specialised modes (e.g. Anthropic’s Learning Mode, OpenAI’s Study Mode, Google’s Guided Learning) AI typically eliminates the productive struggle, open exploration and natural dialogue that are fundamental to learning.
This week, Polygence, in collaboration with Stanford University researcher Prof Dora Demszky. published a first-of-its-kind research on a new model — TeachLM — built to address this gap.
In this week’s blog post, I deep dive what the research found and share the six key findings — including reflections on how well TeachLM performs on instructional design.
The Dangers of using AI to Grade — from marcwatkins.substack.com by Marc Watkins
Nobody Learns, Nobody Gains
AI as an assessment tool represents an existential threat to education because no matter how you try and establish guardrails or best practices around how it is employed, using the technology in place of an educator ultimately cedes human judgment to a machine-based process. It also devalues the entire enterprise of education and creates a situation where the only way universities can add value to education is by further eliminating costly human labor.
For me, the purpose of higher education is about human development, critical thinking, and the transformative experience of having your ideas taken seriously by another human being. That’s not something we should be in a rush to outsource to a machine.