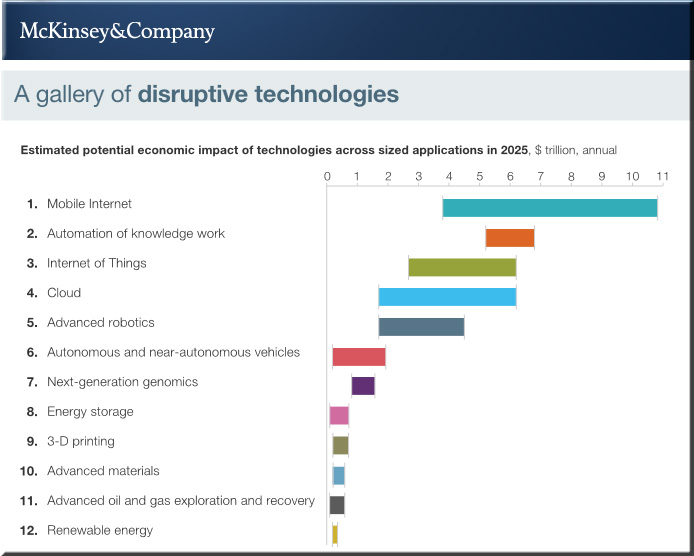
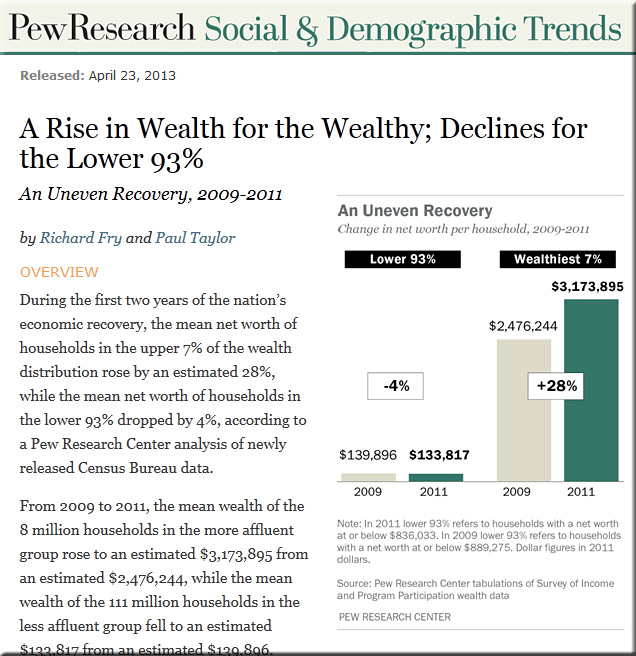
No surprise: Accrediting agency opts to stunt innovation — from disruptingclass.mhprofessional.com by Clayton Christensen
Excerpts:
Several years ago I offered words of praise when Tiffin College partnered with Altius Education to create Ivy Bridge College, a two-year online institution dedicated to providing an affordable higher education option that boosted the transfer rate of two-year students to four-year institutions.
The Higher Learning Commission (HLC), the accrediting body for the North Central region and thus this partnership because Tiffin College is located in an Ohio city that was once populated with industry, agreed strongly, as in 2010 it approved continuing accreditation for Tiffin University and Ivy Bridge College through 2020. At the time, the HLC lauded the partnership.
In the last few weeks, everything changed.
From DSC:
What needs to be done to force accreditation bodies to change who can be on these accreditation teams? Why is it that the people that institutions of higher education claim to serve can’t be on such boards? i.e. one must be an “insider” to the higher education industry, but not an “outsider?”
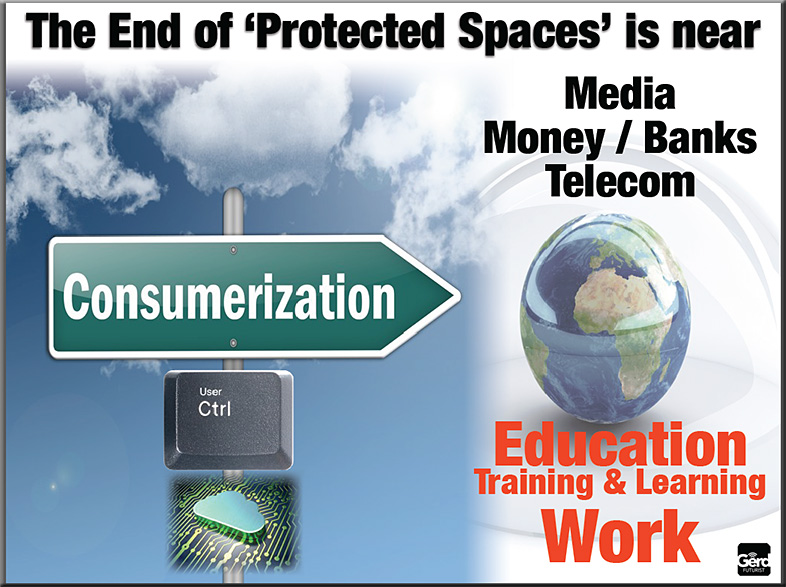
Pursuing the current status quo may have a serious backfiring effect when alternatives present themselves. In fact, taking steps to insure the status quo only serves to put more energy behind MOOCs and puts yet more heat in higher ed’s kitchen. I would hope that folks inside higher ed would take the steps to allow for more experimentation and innovation and to take some heat out of the kitchen.
The key, he added, was to try to avoid mistakes like those made by the music industry on its road to iTunes. “This is a Napster moment for education,” he said. “It’s a big opportunity and an existential threat.”











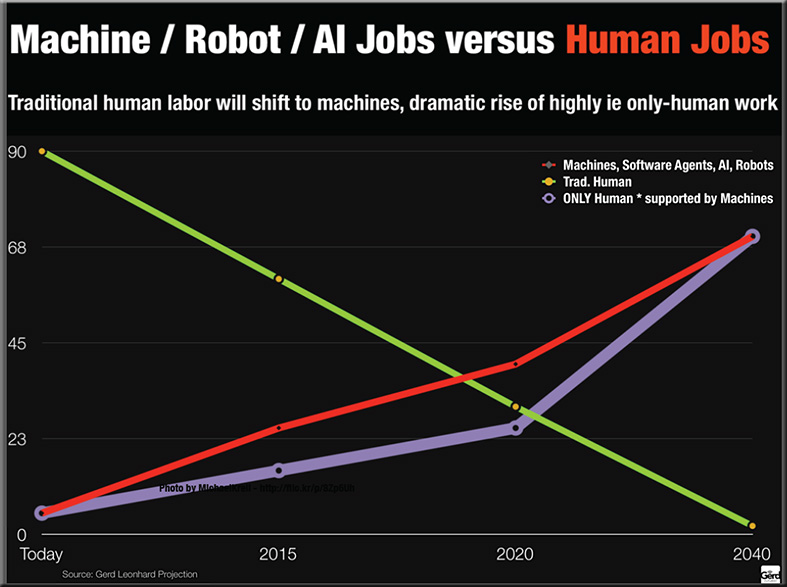
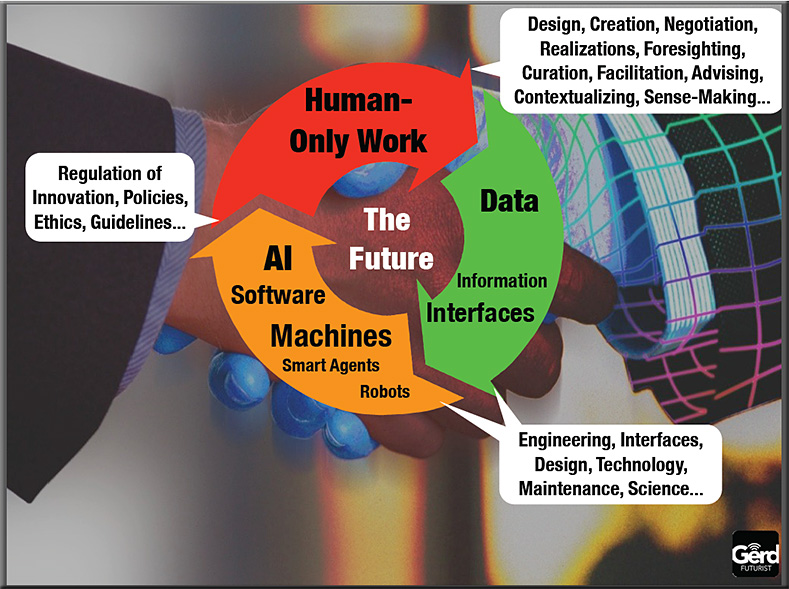
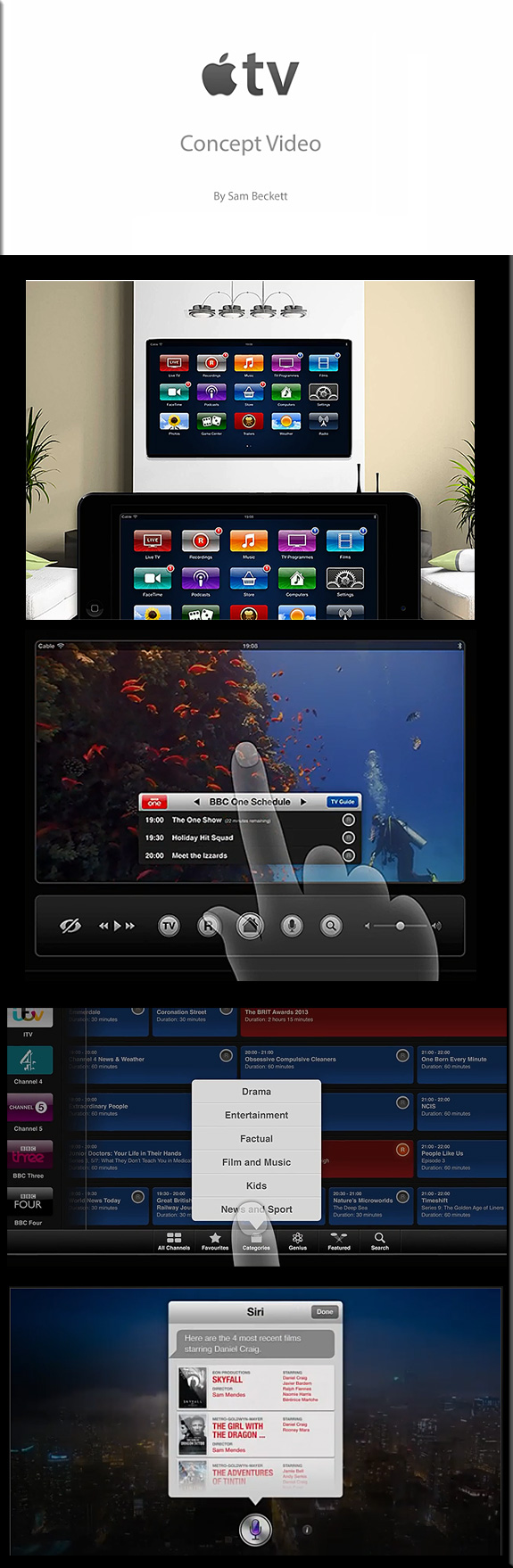
![The Living [Class] Room -- by Daniel Christian -- July 2012 -- a second device used in conjunction with a Smart/Connected TV](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian-July-2012.jpg)