From DSC:
The following items made me reflect upon the place of COVID-19 in causing the current ills within higher education — but also thinking about the ills that were present long before Covid hit us.
Key point:
We should be careful not to conveniently use COVID-19 as the scapegoat for all that’s wrong within higher education.
On the faculty/staff side of the house
The Season of Our Professorial Discontent — from chronicle.com by Paul Musgrave
The pandemic irrevocably changed the student-teacher relationship — and not for the better.
Excerpts:
As pandemic slides into endemic, it’s worth asking: Did the pandemic break something fundamental about academe? Was the spring of 2022 the end of pandemic disruptions, or the start of a new normal?
…
This time, as I delivered the lines to an audience of 30 in a course with 200 students enrolled, I was wondering whether I wanted to give a lecture ever again.
From DSC:
Regarding the first quote…several things were broken within academe long before COID-19. Re: the second quote, what should that tell us if only 30 students showed up in a class with 200 students in it?
Faculty autonomy and faculty satisfaction are being whittled away.
From DSC:
From what I can tell, that’s been happening for years within the K-12 learning ecosystem. It seems like this trend is now occurring within the higher ed learning ecosystem. (I could go off on a tangent about why we didn’t help our fellow educators within K-12 — whose “product” directly impacts those working within higher ed — but I better not. This posting is already packed with reflections.)
Below are some relevant quotes from Kevin McClure’s 5/27/22 article out at The Chronicle of Higher Education (emphasis DSC). I agree with much of what Kevin is saying here.
Don’t Blame the Pandemic for Worker Discontent
It hasn’t just been a tough two years. It’s been a tough two decades.
Excerpt:
The pandemic alone didn’t cause the low morale and turnover you might be seeing among your faculty and staff members just as the lack of personal protective equipment didn’t solely give rise to the Amazon Labor Union. Yes, today’s workers are re-evaluating their workplaces, seeking reassignment within their institutions, and in some cases resigning from jobs altogether. But they are doing so for many of the same reasons they did 20 years ago — poor working conditions.
…
So burnout isn’t just about people struggling to cope with stress; it’s about people struggling in workplaces where stress never subsides.
…
In my own interviews on morale, higher-education workers have talked about leaders who aren’t listening, low compensation, and understaffing.
…
We see our workplaces differently, and our tolerance of poor working conditions has evaporated.
On the student side of the house
“It hasn’t just been a tough two years. It’s been a tough two decades.” The same — and likely more — could be said for the student side of the house, especially in regards to the price of education and how relevant/up-to-date the content has been. As the prices of obtaining a degree have skyrocketed over the last several decades, students and parents now HAVE to ask, “What’s the Return On Investment (ROI) here? Am I gaining the skills in college that will get me hired after college?”
Again, the point I’m trying to make here is that we should be careful not to conveniently use COVID-19 as the scapegoat for all that’s wrong within higher education.
Along these lines, the following two quotes seem relevant to me from Beth McMurtrie’s (6/2/22) Teaching e-newsletter (also from The Chronicle):
I asked Walton to tell me more about the setup at his university. He said classes were fully in person but instructors were encouraged to record lectures and be highly flexible with due dates. The result: Most days he had less than 50-percent attendance, and he received a lot of last-minute emails from students who said they woke up that morning with a headache or otherwise not feeling well. A few filed documented absence requests, but not many, suggesting that these were not serious illnesses, like Covid.
…
I’ve never had more incompletes for courses than in the last two years, so signaling to students that their distribution courses are flexible and accommodating has only let them de-emphasize them even more.
There’s likely a variety of causes/possibilities here — and I’m sure that Covid-related reasons are among them. But it makes me really wonder if students don’t think that the content is all that valuable or relevant to begin with these days. Is college even worth it anymore? Why am I here in the first place? Where is the motivation coming from? Is it extrinsic or intrinsic motivation?
Perhaps it’s time to change the curriculum/content as well as the price.
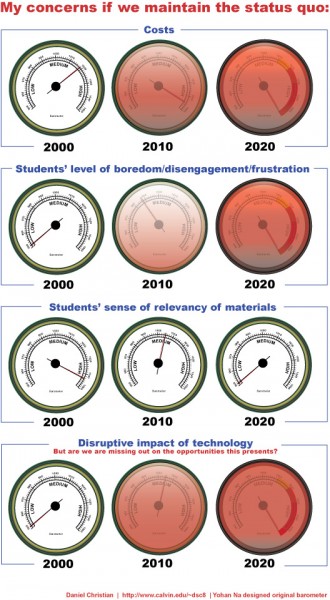
A graphic I created back in 2009, with Yohan Na’s assistance.