Yahoo! and Samsung form multi-year partnership to deliver Interactive TV — from dailyfinance.com by Business Wirevia The Motley Fool
Partnership to provide real-time, enhanced entertainment and advertising to homes across the United States
Excerpt:
SUNNYVALE, Calif. & RIDGEFIELD PARK, N.J.–(BUSINESS WIRE)– Yahoo! (NAS: YHOO) and Samsung today announced an expanded multi-year partnership to integrate Yahoo!’s Broadcast Interactivity platform into Samsung 2012 Smart TVs. Yahoo! Broadcast Interactivity, powered by its automatic content recognition (ACR) technology, SoundPrintTM, will be deployed in Samsung’s SyncPlus platform, enabling new opportunities for intelligent content discovery, advertising and engagement, bringing an unprecedented level of interactivity in the living room.
.
From DSC:
Another steps towards:
![The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian---July-2012 The Living [Class] Room -- by Daniel Christian -- July 2012 -- a second device used in conjunction with a Smart/Connected TV](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian-July-2012.jpg)
.
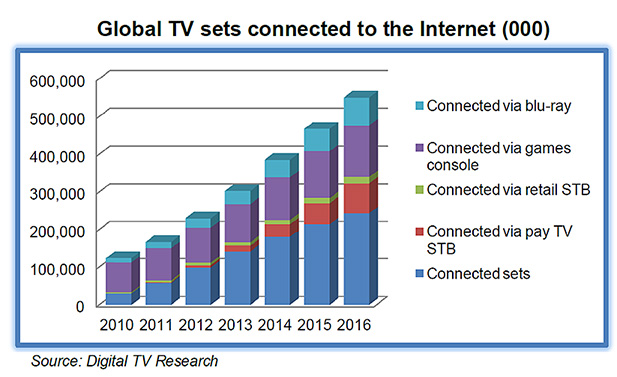
A fifth of TV sets connected to the Internet by 2016 — from digitaltvresearch.com
.
.
Welcome to Star Scholar U., where a personal brand is the credential — from The Chronicle by By Jeffrey R. Young
.

Keri Rasmussen for The Chronicle
Tyler Cowen, an economics professor at George Mason U., helped build an online-education site, Marginal Revolution U, based on a blog he runs with Alex Tabarrok. “In part we did it just to show it could be done—that you can have a Web site which looks nice and works,” Mr. Cowen said.
Excerpt:
A new kind of university has begun to emerge: Call it Star Scholar U.
Professors with large followings and technical prowess are breaking off to start their own online institutions, delivering courses with little or no backing from traditional campuses.
Founding a university may sound dramatic, but in an era of easy-to-use online tools it can be done as a side project—akin to blogging or writing a textbook. Soon there could be hundreds of Star Scholar U’s.
.
5 perspectives on the future of the human interface — from techcrunch.com by Alex Williams
Excerpt:
The next generation of apps will require developers to think more of the human as the user interface. It will become more about the need to know how an app works while a person stands up or with their arms in the air more so than if they’re sitting down and pressing keys with their fingers.
Also see:

.
Rethinking carrots: A new method for measuring what players find most rewarding and motivating about your game — from gamasutra.com by Scott Rigby, Richard Ryan
Excerpt:
The Player Experience of Need Satisfaction model (PENS) outlines three basic psychological needs, those of competence, autonomy, and relatedness, that we have demonstrated lie at the heart of the player’s fun, enjoyment, and valuing of games. By collecting players’ reports of how these needs are being satisfied, the PENS model can strongly and significantly predict positive experiential and commercial outcomes, in many cases much more strongly than more traditional measures of fun and enjoyment. And despite the simplicity of the model conceptually, it shows promise as a “unified theory” of the player experience by demonstrating predictive value regardless of genre, platform, or even the individual preferences of players.
.
Pearson project will let professors mix free and paid content in e-textbooks — from The Chronicle by Alisha Azevedo
Excerpt:
Pearson, a major textbook publisher, continued its push into digital education on Monday by introducing a service that allows instructors to create e-textbooks using open-access content and Pearson material.
.
A river of data — from educationnext.org by Bror Saxberg
Making the learning experience more effective
.
How should teaching change in the age of Siri? –– from MindShift
Excerpt:
Short of banning smartphones (a short-term solution, at best), the evolution of artificial intelligence services like Siri means that there will be a shift from a focus on finding the answer as the endpoint to a greater focus on analysis. You have the answer, but so what? What does that answer mean in a real-life situation?
.
Degreed launches crowdfunding campaign for reimagined ‘digital diploma’ — from gigaom.com by Ki Mae Heussner
San Francisco startup Degreed is challenging the traditional college diploma with an online service that tracks and scores educational achievements from established institutions as well as new online learning platforms. Ahead of a public launch in 2013, Degreed this week began a crowd funding campaign.
.
A capitalist’s dilemma, whoever wins on Tuesday — from the New York Times by Clayton Christensen
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
In a way, this mirrors the microeconomic paradox explored in my book “The Innovator’s Dilemma,” which shows how successful companies can fail by making the “right” decisions in the wrong situations. America today is in a macroeconomic paradox that we might call the capitalist’s dilemma. Executives, investors and analysts are doing what is right, from their perspective and according to what they’ve been taught. Those doctrines were appropriate to the circumstances when first articulated — when capital[From DSC: or from an educational perspective, we could use the word information] was scarce.
But we’ve never taught our apprentices that when capital is abundant and certain new skills are scarce, the same rules are the wrong rules. Continuing to measure the efficiency of capital prevents investment in empowering innovations that would create the new growth we need because it would drive down their RONA, ROCE and I.R.R.
.
Gartner sees 821M unit smart device mkt in 2012; 1.2B 2013 — from forbes.com by Eric Savitz
.













![The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian---July-2012 The Living [Class] Room -- by Daniel Christian -- July 2012 -- a second device used in conjunction with a Smart/Connected TV](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian-July-2012.jpg)