A second demographic cliff adds to urgency for change — from insidehighered.com by Ray Schroeder
The demographic cliff we have been anticipating since the drop in births with the 2008 recession now has a younger sibling — the COVID-19 cliff is coming with another deep drop in recent births.
Excerpts:
In sum, competition is rapidly growing; the pool of “traditional” students is evaporating; employers are dropping degree requirements; and, with student debt now surpassing $1.7 trillion, we all know that families are looking for more cost-effective paths to the knowledge and skills they seek. “The fundamental business model for delivering education is broken,” said Rick Beyer, a senior fellow and practice area lead for mergers and affiliations at the Association of Governing Boards of Universities and Colleges. “The consolidation era started a few years ago. It will continue. We will see more closures.”
What, then, are the bright spots for postsecondary learning?
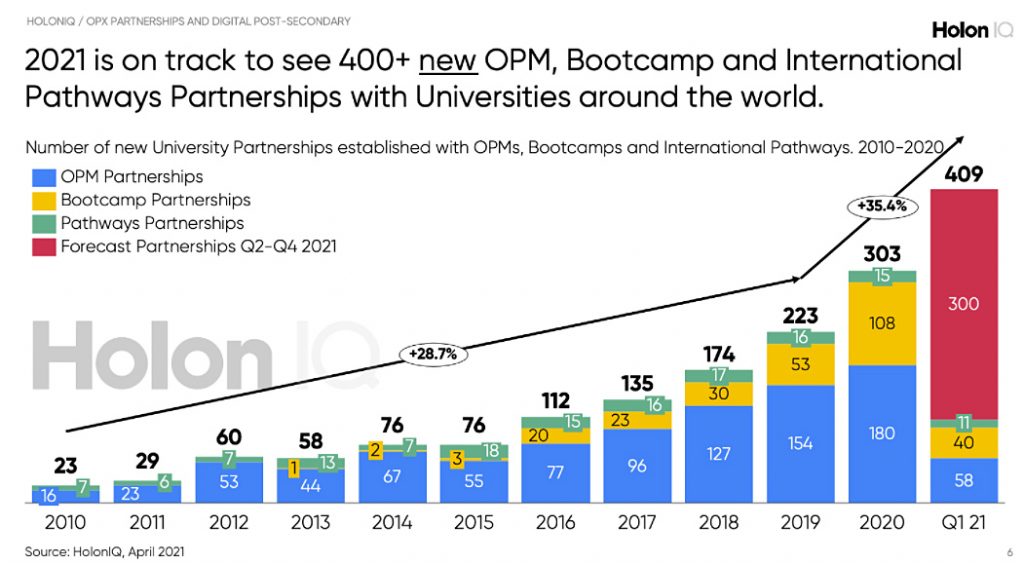
Online learning tops the list despite some bad press for the hastily put-together remote learning of last year. Adult students, in particular, prefer the flexibility and mobility of online. Enrollment in online programs has continued to increase while overall higher ed enrollments have declined each of the past dozen years.