Augmented Reality
Augmented reality app brings art history to life — from creativebloq.com
Excerpt:
Dazzle It is a cool new augmented reality app that lets you remix artwork from artists including the Sir Peter Blake, Godfather of Pop Art – best known for designing the 1967 Beatles’ Sgt Pepper’s Lonely Hearts Club Band album cover.
Developed by digital design agency, Corporation Pop, it combines the latest augmented reality techniques with design to bring history to life. And notably, unlike most augmented reality apps, you don’t need a pre-supplied marker to view what you create in a real-world scene.
7 Great Augmented Reality Apps for Your Classroom — from teachercast.net
Apps Discussed on the Show:
- Aurasma
- Anatomy 4D
- ColAR
- Spacecraft 3D
- AR Flash Cards
- Elements 3D
- Google Translate
Angus park to host augmented reality performance — from scotsman.com with thanks to Woontack Woo for his posting on this
Excerpt:
A FOREST park in Angus is to host the UK’s first live theatrical performance featuring augmented reality (AR) technology.
By downloading an app, audiences will be able to spot magical creatures through their smartphones and capture them on camera, before sharing the images with friends and family on social media.
DragonQuest, which will be performed in Monikie Country Park, allows visitors to wander around a forest using their smartphone to create images of fantastical creatures in addition to real-life characters and events on the set.
Here are the signs that point to Apple’s next big innovation in computing, according to one analyst — from businessinsider.com
Check Out How These Teachers and Students are Using Augmented Reality — from emergingedtech.com
Using Augmented Reality for Learning and Teaching — from edtechreview.in by Prasanna Bharti
Excerpt:
Various Application of Augmented Reality in Learning Different Subjects
Astronomy: AR can be used to make student understand about the relationship between the Sun and the Earth. Here AR technology can be used with 3D rendered sun and earth shapes.
Chemistry: Teachers can demonstrate what a molecule and atoms consist of using AR technology.
Biology: Teachers can use Augmented Reality to showcase their student’s body structure or anatomy. Teachers can show their students different types of organ and how they look in a 3D atmosphere. Students can even study human body structure on their own by using devices with AR embedded technology in it.
Physics: Physics is one of the subjects where AR technology can be used perfectly. Various kinematics properties can be easily understood by using AR technology.
Virtual Reality
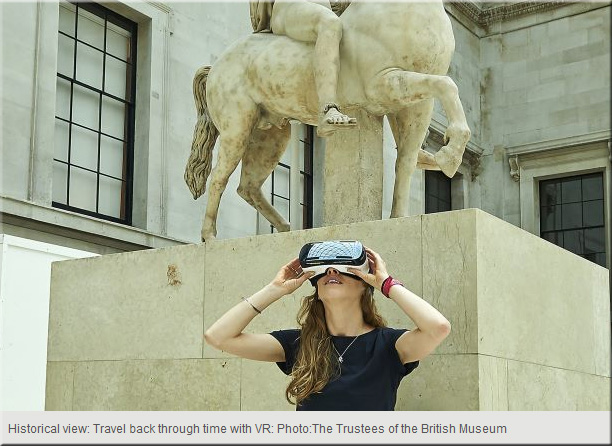
Virtual reality can take us to the world’s greatest museums — from venturebeat.com by Mike Minotti

How Virtual Reality Can Close Learning Gaps in Your Classroom — from edsurge.com
Excerpt:
Virtual Reality (VR) may be the type of educational breakthrough that comes along once in a generation, heralding a tectonic shift toward immersive content for teaching and instruction.
By presenting a complete view of the world in which it is situated, VR offers a new opportunity to close some of the pedagogical gaps that have appeared in 21st century classroom learning. These gaps stem from the fact that curriculum and content in education have not caught up with rapid technology advancements.
Below I introduce three of these gaps and how they might be addressed by virtual reality content soon to be produced and distributed commercially.
Google Cardboard offers virtual trip for Lawrence students — from www2.ljworld.com
Excerpt:
The Lawrence school district recently purchased 20 Google Cardboards, which beginning this school year are available for teachers to check out for use in their classrooms, said Joe Smysor, the district’s technology integration specialist. Cardboard works in conjunction with a smartphone app to deliver a 3-D, 360-degree navigable image. Students can use apps with Cardboard to virtually visit museums, landmarks or cities around the world.
“It’s going to allow teachers to take their class on field trips where school buses couldn’t otherwise go,” Smysor said. “That could be back 100 years in the past, or underwater.”
Virtual college tours with cardboard, a smartphone and YouVisit — from mystatesman.com by Omar L. Gallaga
Excerpt:
While college students are settling into their dorms, it’s already time for next year’s class of high school students to narrow down their potential school choices and schedule campus visits. Or maybe they can just stay home and start the journey virtually.
A site called YouVisit has a surprisingly large set of virtual-reality college tours available. All the major Texas colleges are represented, and one of them, Trinity University, has been making a big push to get cheap sets of cardboard VR goggles out to families at recruiting events such as college fairs. Trinity sent me a pair of the cardboard glasses. The virtual visit to the campus certainly wasn’t the same as being there, but to get at least a visual sense of what the campus looks like and to be generally wowed by the 3-D/360-degree effect, it was worth the trip.
Regis University Creates Remote Campus Tours with Primacy’s Virtual Reality Experience — from businesswire.com
Jesuit university builds on rich tradition of innovation by enabling immersive virtual tours using Oculus Rift technology and virtual reality headsets
Excerpt:
FARMINGTON, Conn. & DENVER–(BUSINESS WIRE)–Regis University today unveiled a unique new way for prospective students to tour and experience the school’s scenic 100-acre campus. Through an interactive, immersive experience created by independent agency Primacy, students are able to put on an Oculus Rift virtual reality (VR) headset and immediately be transformed to the campus where they can get a full, 360-degree tour as if they were on site – including viewing daybreak runs at Red Rocks, being immersed in Regis’ experiential nursing skills lab and visiting the campus pub to watch a live Jenga game.
GoPro is now selling its crazy 16-camera virtual reality rig — from theverge.com by Sean O’Kane
‘Odyssey’ is only available to pros
Excerpt:
Odyssey is the first camera rig built specifically for Google’s Jump platform, which was also announced at this year’s I/O conference. Jump is an entire virtual reality ecosystem that, in theory, will make it easier to both create and consume VR content. With Jump, Google created open plans that companies can use to build their own 16-camera rig (GoPro just happened to be the first), as well as assemble software that can recreate the scene being captured in much higher quality than most existing image stitching software can. Eventually, Jump videos will be hosted in YouTube; think of it as the next logical step following YouTube’s inclusion of 360-degree videos earlier this year.

Behind the Scenes of a Virtual Reality Beethoven Concert — from recode.net by Eric Johnson
Excerpt:
Are you a classical music fan? It’s a question most people would probably say no to, and the Los Angeles Philharmonic knows that.
“People are intimidated by classical music,” said Amy Seidenwurm, the Philharmonic’s director of digital initiatives. “They don’t come to concerts because they feel it might not be for them.”
But to change those minds, the LA Phil is turning to virtual reality. For the next month, it will be driving around the Los Angeles area to parks, festivals and museums, in a van outfitted with real carpeting and seats from the Walt Disney Concert Hall — and six Samsung Gear VR headsets, which have been loaded with a special video performance of Beethoven’s Fifth Symphony. (You know the one: Dun-dun-dun DUNNNN.)
Inside Industrial Light & Magic’s secret Star Wars VR lab — from theverge.com by Bryan Bishop
ILMxLab isn’t just exploring the future of entertainment… they’re already making it
Addendums on 9/10/15:
- The Top 10 Virtual Reality Headsets of 2015 — from avatargeneration.com
5 augmented reality apps to alter your world — from cbronline.com with thanks to Woontack Woo for his posting on this
Learn more about Dazzle It, Streetmuseum, Skyview, Blippar and Colorblind Fix.
Excerpt:
Ever wanted to see the world around you in a different way? These apps will transform your phone into a portal to a world of altered perceptions.




















![The Living [Class] Room -- by Daniel Christian -- July 2012 -- a second device used in conjunction with a Smart/Connected TV](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian-July-2012.jpg)