From DSC:
When the race track is going 180mph, you can’t walk or jog onto the track. What do I mean by that?
Consider this quote from an article that Jeanne Meister wrote out at Forbes entitled, “The Future of Work: Three New HR Roles in the Age of Artificial Intelligence:”*
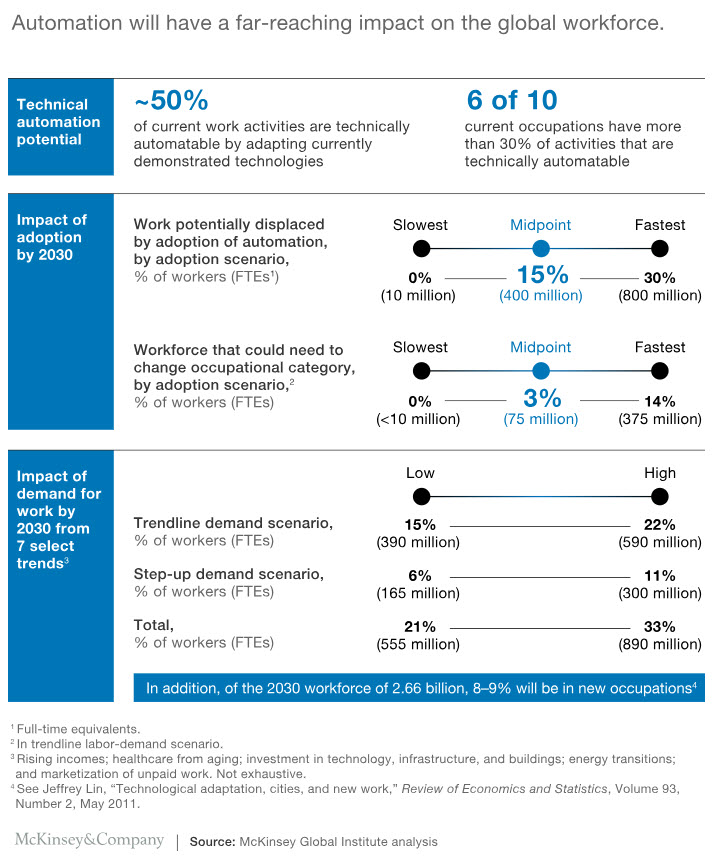
This emphasis on learning new skills in the age of AI is reinforced by the most recent report on the future of work from McKinsey which suggests that as many as 375 million workers around the world may need to switch occupational categories and learn new skills because approximately 60% of jobs will have least one-third of their work activities able to be automated.
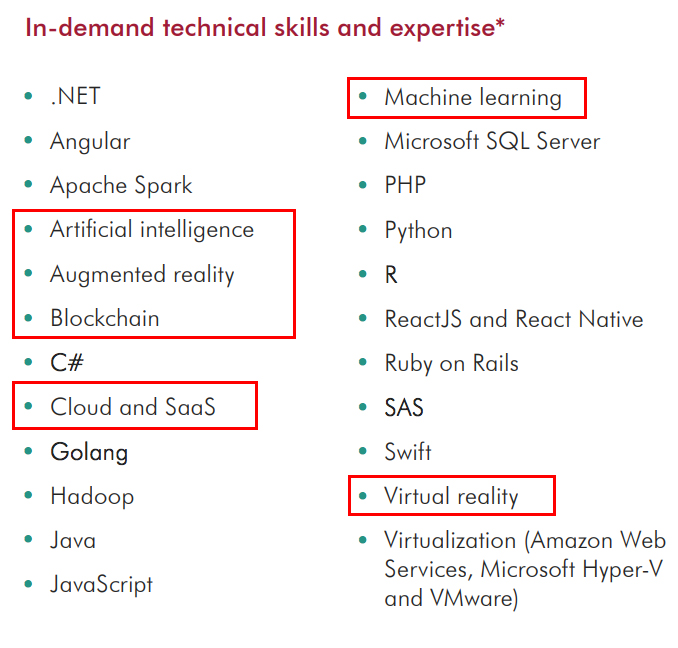
Go scan the job openings and you will likely see many that have to do with technology, and increasingly, with emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, deep learning, machine learning, virtual reality, augmented reality, mixed reality, big data, cloud-based services, robotics, automation, bots, algorithm development, blockchain, and more.
From Robert Half’s 2019 Technology Salary Guide
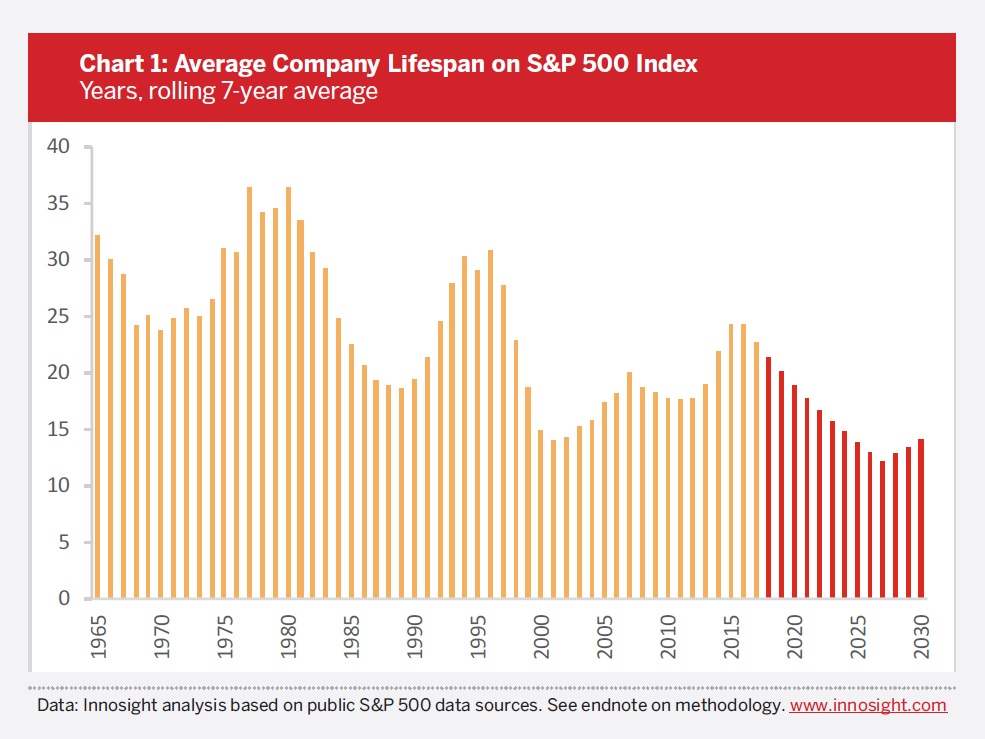
How many of us have those kinds of skills? Did we get that training in the community colleges, colleges, and universities that we went to? Highly unlikely — even if you graduated from one of those institutions only 5-10 years ago. And many of those institutions are often moving at the pace of a nice leisurely walk, with some moving at a jog, even fewer are sprinting. But all of them are now being asked to enter a race track that’s moving at 180mph. Higher ed — and society at large — are not used to moving at this pace.
This is why I think that higher education and its regional accrediting organizations are going to either need to up their game hugely — and go through a paradigm shift in the required thinking/programming/curricula/level of responsiveness — or watch while alternatives to institutions of traditional higher education increasingly attract their learners away from them.
This is also, why I think we’ll see an online-based, next generation learning platform take place. It will be much more nimble — able to offer up-to-the minute, in-demand skills and competencies.
The below graphic is from:
Jobs lost, jobs gained: What the future of work will mean for jobs, skills, and wages
* Three New HR Roles To Create Compelling Employee Experiences
These new HR roles include:
- IBM: Vice President, Data, AI & Offering Strategy, HR
- Kraft Heinz Senior Vice President Global HR, Performance and IT
- SunTrust Senior Vice President Employee Wellbeing & Benefits
What do these three roles have in common? All have been created in the last three years and acknowledge the growing importance of a company’s commitment to create a compelling employee experience by using data, research, and predictive analytics to better serve the needs of employees. In each case, the employee assuming the new role also brought a new set of skills and capabilities into HR. And importantly, the new roles created in HR address a common vision: create a compelling employee experience that mirrors a company’s customer experience.
An excerpt from McKinsey Global Institute | Notes from the Frontier | Modeling the Impact of AI on the World Economy
Workers.
A widening gap may also unfold at the level of individual workers. Demand for jobs could shift away from repetitive tasks toward those that are socially and cognitively driven and others that involve activities that are hard to automate and require more digital skills.12 Job profiles characterized by repetitive tasks and activities that require low digital skills may experience the largest decline as a share of total employment, from some 40 percent to near 30 percent by 2030. The largest gain in share may be in nonrepetitive activities and those that require high digital skills, rising from some 40 percent to more than 50 percent. These shifts in employment would have an impact on wages. We simulate that around 13 percent of the total wage bill could shift to categories requiring nonrepetitive and high digital skills, where incomes could rise, while workers in the repetitive and low digital skills categories may potentially experience stagnation or even a cut in their wages. The share of the total wage bill of the latter group could decline from 33 to 20 percent.13 Direct consequences of this widening gap in employment and wages would be an intensifying war for people, particularly those skilled in developing and utilizing AI tools, and structural excess supply for a still relatively high portion of people lacking the digital and cognitive skills necessary to work with machines.












![The Living [Class] Room -- by Daniel Christian -- July 2012 -- a second device used in conjunction with a Smart/Connected TV](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian-July-2012.jpg)