The University in Ruins — from chronicle.com by Johann N. Neem
The “innovations” that promise to save higher ed are a farce.
From DSC:
First of all, I appreciated Johann Neem mentioning and/or discussing several books in one posting:
- Ronald G. Musto’s The Attack on Higher Education (2021)
- Arthur Levine’s and Scott J. Van Pelt’s The Great Upheaval (2021)
- Bill Readings’ The University in Ruins (1996)
- Ronald J. Daniels’ What Universities Owe Democracy (2021)
And as a disclosure here, I have not read those books.
Below are excerpts with some of my comments:
It’s already happening. Today, we walk among the ruins of an institution that once had a larger purpose. It’s not clear what role universities should play in society, and to what or to whom they are accountable, other than their corporate interests.
To some, that’s not a problem, at least according to Arthur Levine and Scott J. Van Pelt in The Great Upheaval (2021). They see higher education undergoing the same transformation that reshaped the music, film, and newspaper industries. Rather than place-based education overseen by tenured professors, they anticipate “the rise of anytime, anyplace, consumer-driven content and source agnostic, unbundled, personalized education paid for by subscription.”
Between Musto’s existential fears of disruption and Levine and Van Pelt’s embrace of it lies a third path. It takes the form of a wager — outlined by Ronald J. Daniels in What Universities Owe Democracy (2021) — that universities can and should continue to matter because of their importance in civic democratic life.
The article covers how the learning ecosystems within higher education have morphed from their religious roots to being an apparatus of the nation-state to then becoming a relatively independent bureaucratic system to other things and to where we are today.
Along the journey discussing these things, one of the things that caught my eye was this statement:
Hopkins, in this sense, lived up to its founding president Daniel Coit Gilman’s 19th-century aspiration that universities be places that acquire, conserve, refine, and distribute knowledge.
From DSC:
While I completely agree with that aspiration, I think more institutions of higher education could follow what John Hopkins University did with their efforts concerning the Covid-19 situation, as Neem mentioned. Generally speaking, institutions of higher education are not distributing knowledge to the levels that Gilman envisioned years ago.
In fact, these days those working within K12 are doing a whole lot better at sharing information with society than those who work within higher education are. For example, when I search Twitter for K12 educators who share content on Twitter, they are out there all over the place — and many with tens of thousands of followers. They share information with parents, families, fellow educators, students, school boards, and others. Yet this is not the case for those working in higher education. Faculty members normally:
- aren’t out on Twitter
- don’t blog
- don’t have a podcast
- don’t write for society at large. Instead, their expertise is often locked up — existing behind paywalls in academic journals. In other words, they talk to each other.
Later on…
As Daniels intuits, without a larger purpose to hold them fast, there is nothing to prevent universities from being buffeted by winds until they have lost direction. That is what Readings foresaw: Globalization liberates universities from national fetters, but at the risk of ruin.
From DSC:
While globalization may have something to do with universities becoming unanchored from their original purposes, globalization isn’t at the top of my mind when I reflect upon what’s been happening with colleges and universities these last few decades.
To see but one area of massive change, let’s take a brief look at college sports. There are now multimillion-dollar stadium projects, enormous coaches’ salaries, and numerous situations where tax-paying citizens can’t even watch sporting events without tons of advertisements being thrown into their faces every few seconds. Personally speaking, on numerous occasions, I couldn’t even access the games at all — as I wasn’t paying for the subscriptions to the appropriate providers.
Also, as another example of becoming anchored — and going back to the 1980’s — I attended Northwestern University for my undergraduate degree in Economics. While I have several wonderful lifelong friends from that experience for whom I’m deeply grateful, even back then NU had already moved far away from its motto which is based on Philippians 4:8.
Instead, please allow me to tell you what that learning community taught me and strongly encouraged me to think about:
- You are only successful if you have the corner office, drive the higher numbered BMW’s, and have many people reporting to you.
- If you make a lot of money.
- You are supposed to compete against others vs. being in relationships with others. As but one example here, our test scores were published — by our Social Security numbers — outside our professors’ offices for all to see how we measured up to our classmates.
In fact, I’m not even sure that I would use the word “community” at all when I reflect upon my years at Northwestern. Instead, a WIIFM approach was encouraged (i.e., What’s In It For Me? where you are supposed to look out for #1). It took me years to unlearn some of those “lessons” and “learnings.”
But I realize that that’s not the case with all learning communities.
As Neem alluded to, I love the idea that an institution of higher education can — and often does — impact students’ hearts as well as minds. That was the focus at Calvin College (now Calvin University). Our oldest daughter went there and she was profoundly and positively influenced by her experiences there. In that context, students were encouraged to be in relationships with one another. There was plenty of hugging, praying for one another, etc. going on in that setting. There truly was community there.
***
Neem doesn’t think much of Levine’s and Van Pelt’s perspectives. He claims there’s nothing new in their book. He seems to discard the arguments being made about the cost of higher ed and, like many others, clings to the intellectual roots/purpose of higher ed.
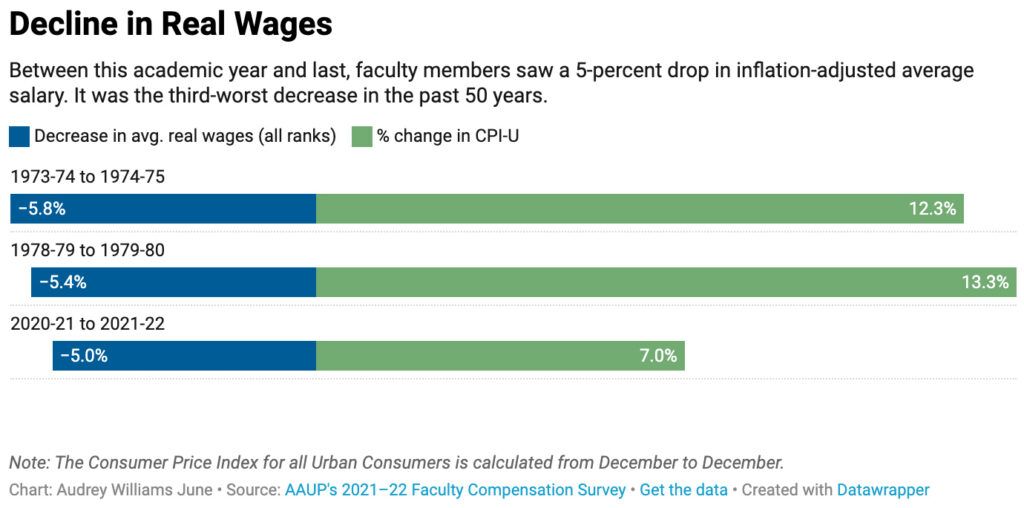
While I’m not against intellect or pursuing knowledge — in fact, I’m all for it — I just have a problem when the price of doing so continues to become out of reach for soooooo many people.
Personally, I’ve tried to lower the cost of obtaining a degree within higher education for many years…but I was/we were only successful in doing so for a few years (and that was during a pilot of online-based learning). Yohan Na and I created the graphic below in 2008 for example — as I was trying to raise awareness of the dangers of the status quo:
.
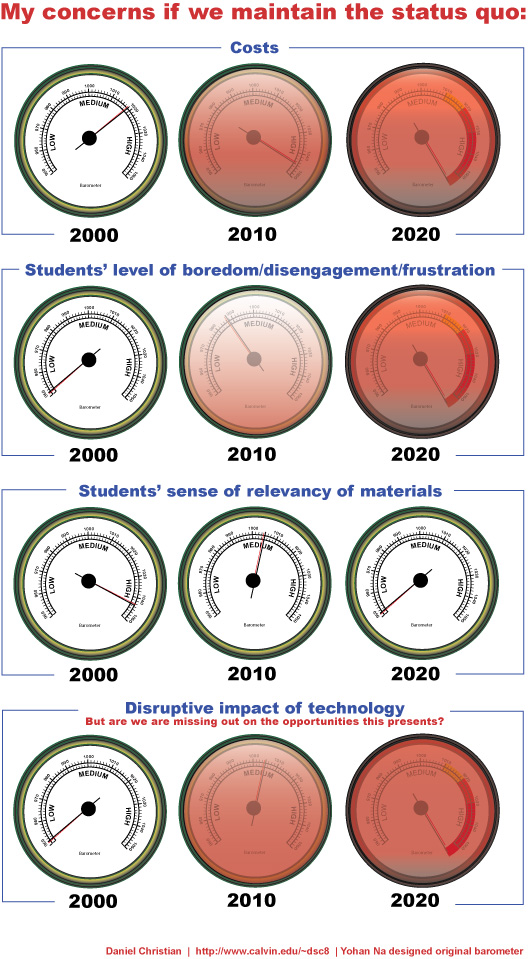
.
So from a cost/access perspective, Levine’s and Van Pelt’s perspectives here sound pretty good to me. It appears to be much more affordable and realistic for the masses. Otherwise, the image/reality of the ivory tower is maintained…allowing “intellectuals” to continue to live and operate within their own sphere/hive/tribe.
Also, we need an AI-backed system of presenting which skills are needed and then how to get them. The ways things are set up today, institutions of traditional higher education have not been able to deal with the current pace of change out there.
As a final comment here…
The changing directions/purposes of institutions of higher education present a good example of why I entitled this blog Learning Ecosystems — as the systems that we use to learn and grow in are constantly morphing:
- People come and go
- Tools and vendors come and go
- Purposes, focuses, and/or mission statements change
- Our sources of information (i.e., our streams of content) come and go
- Etc.