The Learning and Employment Records (LER) Report for 2026: Building the infrastructure between learning and work — from smartresume.com; with thanks to Paul Fain for this resource
Executive Summary (excerpt)
This report documents a clear transition now underway: LERs are moving from small experiments to systems people and organizations expect to rely on. Adoption remains early and uneven, but the forces reshaping the ecosystem are no longer speculative. Federal policy signals, state planning cycles, standards maturation, and employer behavior are aligning in ways that suggest 2026 will mark a shift from exploration to execution.
Across interviews with federal leaders, state CIOs, standards bodies, and ecosystem builders, a consistent theme emerged: the traditional model—where institutions control learning and employment records—no longer fits how people move through education and work. In its place, a new model is being actively designed—one in which individuals hold portable, verifiable records that systems can trust without centralizing control.
Most states are not yet operating this way. But planning timelines, RFP language, and federal signals indicate that many will begin building toward this model in early 2026.
As the ecosystem matures, another insight becomes unavoidable: records alone are not enough. Value emerges only when trusted records can be interpreted through shared skill languages, reused across contexts, and embedded into the systems and marketplaces where decisions are made.
Learning and Employment Records are not a product category. They are a data layer—one that reshapes how learning, work, and opportunity connect over time.
This report is written for anyone seeking to understand how LERs are beginning to move from concept to practice. Whether readers are new to the space or actively exploring implementation, the report focuses on observable signals, emerging patterns, and the practical conditions required to move from experimentation toward durable infrastructure.
…
…
“The building blocks for a global, interoperable skills ecosystem are already in place. As education and workforce alignment accelerates, the path toward trusted, machine-readable credentials is clear. The next phase depends on credentials that carry value across institutions, industries, states, and borders; credentials that move with learners wherever their education and careers take them. The question now isn’t whether to act, but how quickly we move.”
– Curtiss Barnes, Chief Executive Officer, 1EdTech
The above item was from Paul Fain’s recent posting, which includes the following excerpt:
SmartResume just published a guide for making sense of this rapidly expanding landscape. The LER Ecosystem Report was produced in partnership with AACRAO, Credential Engine, 1EdTech, HR Open Standards, and the U.S. Chamber of Commerce Foundation. It was based on interviews and feedback gathered over three years from 100+ leaders across education, workforce, government, standards bodies, and tech providers.
The tools are available now to create the sort of interoperable ecosystem that can make talent marketplaces a reality, the report argues. Meanwhile, federal policy moves and bipartisan attention to LERs are accelerating action at the state level.
“For state leaders, this creates a practical inflection point,” says the report. “LERs are shifting from an innovation discussion to an infrastructure planning conversation.”
The US wants more apprenticeships. The UK figured out how to make them coveted roles — from hechingerreport.org by Kelly Field
‘Degree apprenticeships’ that pair bachelor’s with jobs can be harder to get into than elite colleges
Most students here and in the United States wouldn’t get access to expensive equipment like this until graduate school. Goshawk — a 21-year-old undergraduate student and one of 149 “degree apprentices” employed by AstraZeneca across the U.K. — started using them his second week in.
“It shows the trust we’ve been given,” said Goshawk, who is working nearly full time while studying toward a degree in chemical science at Manchester Metropolitan University that his employer is paying for. By the time he graduates next spring, he will have earned roughly 100,000 pounds (approximately $130,000) in wages, on top of the tuition-free education.
Degree apprenticeships like Goshawk’s have exploded across England since their introduction a decade ago. More than 60,000 apprentices began programs leading to the U.K. equivalent of bachelor’s and master’s degrees in the 2024-25 academic year, in fields as varied as engineering, digital technology, health care, law and business.
Community colleges are training the next generation of manufacturing workers — from manufacturingdive.com by Michelle No
Rutgers University explored how community colleges are responding to regional workforce training demands. Clark State College and Columbus State Community College are among those leading the way.
One underrated option may hold the most promise for workforce growth: the local community college.
That’s according to a series of reports by The Rutgers Education and Employment Research Center released in October, which examines the “hidden innovative structure” of America’s community colleges.
Community colleges excel in ways conducive to a successful manufacturing career, said Shalin Jyotishi, founder of the Future of Work & Innovation Economy Initiative at think tank New America.
Rebuilding The First Rung Of The Opportunity Ladder — from forbes.com by Bruno V. Manno
Two-thirds of employers say most new hires are not fully prepared for their roles, citing “experience,” not technical skill, as the greatest shortfall. At the same time, 61% of companies have raised their experience requirements.
As a result, many so-called entry-level roles now demand two to five years of prior work experience. The first rung of the career ladder has been pulled even farther out of reach for new job seekers. A portfolio—or full-spectrum—model of work-based learning is one promising way to rebuild that rung.
Experience has become what Deloitte calls “the new currency of employability.” But the places where young people once earned that currency are disappearing.
Caring for Patients for 26 Years—and Still Not a Nurse — from workshift.org/ by Colleen Connolly
Arnett’s experience spending decades in a job she intended as a first step is common among CNAs, medical assistants, and other entry-level healthcare workers, many of them women of color from low-income backgrounds. Amid a nationwide nursing shortage, elevating those workers seems like an obvious solution, but the path from CNA to nurse isn’t so much a ladder as it is a huge leap.
And obstacle after obstacle is strewn in the way. The high cost of nursing school, lengthy prerequisite requirements, rigid schedules, and unpaid clinical hours make it difficult for many CNAs to advance in their careers, despite their willingness and ability and the dire need of healthcare facilities.
While there are no national statistics about the number of entry-level healthcare workers who move on to higher-paid positions, a study of federal grants for CNA training showed that only 3% of those who completed the training went on to pursue further education to become an LPN or RN. Only 1% obtained an associate degree or above. A similar study in California showed that 22% of people who completed CNA certificate programs at community colleges went on to get a higher-level educational credential in health, but only 13% became registered nurses within six years.
That reality perpetuates chronic shortages in nursing, and it also keeps hundreds of thousands of healthcare workers locked below a living wage, often for decades.
…the above posting links to:
Higher Ed Is Sleepwalking Toward Obsolescence— And AI Won’t Be the Cause, Just the Accelerant — from substack.com by Steven Mintz
AI Has Exposed Higher Ed’s Hollow Core — The University Must Reinvent Itself or Fade
It begins with a basic reversal of mindset: Stop treating AI as a threat to be policed. Start treating it as the accelerant that finally forces us to build the education we should have created decades ago.
A serious institutional response would demand — at minimum — six structural commitments:
- Make high-intensity human learning the norm. …
- Put active learning at the center, not the margins. …
- Replace content transmission with a focus on process. …
- Mainstream high-impact practices — stop hoarding them for honors students. …
- Redesign assessment to make learning undeniable. …
And above all: Instructional design can no longer be a private hobby.
Teaching with AI: From Prohibition to Partnership for Critical Thinking — from facultyfocus.com by Michael Kiener, PhD, CRC
How to Integrate AI Developmentally into Your Courses
- Lower-Level Courses: Focus on building foundational skills, which includes guided instruction on how to use AI responsibly. This moves the strategy beyond mere prohibition.
- Mid-Level Courses: Use AI as a scaffold where faculty provide specific guidelines on when and how to use the tool, preparing students for greater independence.
- Upper-Level/Graduate Courses: Empower students to evaluate AI’s role in their learning. This enables them to become self-regulated learners who make informed decisions about their tools.
- Balanced Approach: Make decisions about AI use based on the content being learned and students’ developmental needs.
Now that you have a framework for how to conceptualize including AI into your courses here are a few ideas on scaffolding AI to allow students to practice using technology and develop cognitive skills.
80 per cent of young people in the UK are using AI for their schoolwork — from aipioneers.org by Graham Attwell
What was encouraging, though, is that students aren’t just passively accepting this new reality. They are actively asking for help. Almost half want their teachers to help them figure out what AI-generated content is trustworthy, and over half want clearer guidelines on when it’s appropriate to use AI in their work. This isn’t a story about students trying to cheat the system; it’s a story about a generation grappling with a powerful new technology and looking to their educators for guidance. It echoes a sentiment I heard at the recent AI Pioneers’ Conference – the issue of AI in education is fundamentally pedagogical and ethical, not just technological.
Is An Internship In College More Important Than The Degree Itself? — from forbes.com by Brandon Busteed
While confidence in higher education has eroded and more Americans are questioning the importance of a degree, the demand for internships among college students is skyrocketing and the odds of getting an internship at a major company are now lower than getting into the Ivy League. This begs the question: are we at a point where an internship is as valuable – or perhaps more so – than a degree itself?
While concerns about degree ROI were on the rise, the value of internships and other work-integrated learning opportunities was becoming increasingly apparent. New research and analysis have shown us how valuable it is for a student to have an internship during college: it doubles the odds they have a good job waiting for them upon graduation and doubles their odds of being engaged in their work over their lifetime. Although there are some variations in those outcomes by choice of college or academic major, those variations pale in comparison to the impact of having an internship. In short, a collegiate internship experience is a more important indicator of these outcomes than alma mater or major.
Entrepreneurship: The New Core Curriculum — from gettingsmart.com by Tom Vander Ark
Key Points
- Entrepreneurship education fosters resilience, creativity, and financial literacy—skills critical for success in an unpredictable, tech-driven world.
- Programs like NFTE, Junior Achievement, and Uncharted Learning empower students by offering real-world entrepreneurial experiences and mentorship.
“Entrepreneurship is the job of the future.”
— Charles Fadel, Education for the Age of AI
This shift requires a radical re-evaluation of what we teach. Education leaders across the country are realizing that the most valuable skill we can impart is not accounting or marketing, but the entrepreneurial mindset. This mindset—built on resilience, creative problem-solving, comfort with ambiguity, and the ability to pivot—is essential in startups, as an intrapreuer in big organizations, or as a citizen working for the common good.
Why Co-Teaching Will Be A Hot New Trend In Higher Education — from forbes.com by Brandon Busteed
When it comes to innovation in higher education, most bets are being placed on technology platforms and AI. But the innovation students, faculty and industry need most can be found in a much more human dimension: co-teaching. And specifically, a certain kind of co-teaching – between industry experts and educators.
While higher education has largely embraced the value of interdisciplinary teaching across different majors or fields of study, it has yet to embrace the value of co-teaching between industry and academia. Examples of co-teaching through industry-education collaborations are rare and underutilized across today’s higher ed landscape. But they may be the most valuable and relevant way to prepare students for success. And leveraging these collaborations can help institutions struggling to satisfy unfulfilled student demand for immersive work experiences such as internships.
From DSC:
It’s along these lines that I think that ADJUNCT faculty members should be highly sought after and paid much better — as the up-to-date knowledge and experience they bring into the classroom is very valuable. They should have equal say in terms of curriculum/programs and in the way a college or university is run.
Provosts Are a ‘Release Valve’ for Campus Controversy — from insidehighered.com by Emma Whitford
According to former Western Michigan provost Julian Vasquez Heilig, provosts are stuck driving change with few, if any, allies, while simultaneously playing crisis manager for the university.
After two years, he stepped down, and he now serves as a professor of educational leadership, research and technology at Western Michigan. His frustrations with the provost role had less to do with Western Michigan and more to do with how the job is designed, he explained. “Each person sees the provost a little differently. The faculty see the provost as administration, although, honestly, around the table at the cabinet, the provost is probably the only faculty member,” Heilig said. “The trustees—they see the provost as a middle manager below the president, and the president sees [the provost] as a buffer from issues that are arising.”
Inside Higher Ed sat down with Heilig to talk about the provost job and all he’s learned about the role through years of education leadership research, conversations with colleagues and his own experience.
Brandeis University launches a new vision for American higher education, reinventing liberal arts and emphasizing career development — from brandeis.edu
Levine unveiled “The Brandeis Plan to Reinvent the Liberal Arts,” a sweeping redesign of academic structures, curricula, degree programs, teaching methods, career education, and student support systems. Developed in close partnership with Brandeis faculty, the plan responds to a rapidly shifting landscape in which the demands on higher education are evolving at unprecedented speed in a global, digital economy.
“We are living through a time of extraordinary change across technology, the economy, and society,” Levine said. “Today’s students need more than knowledge. They need the skills, experiences, and confidence to lead in a world we cannot yet predict. We are advancing a new model. We need reinvention. And that’s exactly what Brandeis is establishing.”
The Brandeis Plan transforms the student experience by integrating career preparation into every stage of a student’s education, requiring internships or apprenticeships, sustaining career counseling, and implementing a core curriculum built around the skills that employers value most. The plan also reimagines teaching. It will be more experiential and practical, and introduce new ways to measure and showcase student learning and growth over time.
Tuition Tracker from the Hechinger Report
1 in 2 graduates believe their college major didn’t prepare them for today’s market — from hrdive.com by Carolyn Crist
Respondents said they felt unprepared in numerous ways, especially finding a job after graduation and navigating student debt and personal finances.
As today’s college graduates struggle to start a steady career, 1 in 2 Americans say their college major didn’t prepare them for the job market, according to a June 18 report from Preply.
Beyond that, 1 in 6 Americans who went to college said they regret it. When thinking about their college experience, college graduates said their top regrets included taking out student loans, not networking more and not doing internships.
College graduates said they felt unprepared in numerous ways, especially finding a job after graduation and navigating student debt and personal finances.
From DSC:
The Career Placement Office at Northwestern University did not help build my skills to get a job, at all. I had no clue what I was doing. I had no idea what networking was even about, nor the power of it, and why it would be useful throughout my career. They provided conference rooms for interviews to occur…and that was about it, at least in my experience. In terms of my education, I didn’t get any real-world experience (such as apprenticeships, internships, capstone courses, etc.), nor did I pick up many practical or technical skills.
Driving Culture Change in Higher Education — from jeffselingo.com by Jeff Selingo
The call for transformation in higher education has never been louder, yet the path forward remains unclear for many institutions. Leaders often struggle with the “how” of meaningful change. This five-part playbook by higher education author and strategist Jeff Selingo as well as other experts draws on proven methodologies to provide clear, actionable guidance from mapping current institutional culture to sustaining long-term momentum.
Employers’ emphasis on skilled trades lost on Gen Z: Harris poll — from facilitiesdive.com
Young workers don’t realize going into the trades can offer good pay more quickly than pursuing a college-based career, the report says.
A mismatch exists between the importance employers are putting on skilled trades and how the generation that’s newly joining the workforce views those jobs, a Harris poll finds.
Gen Z, the oldest members of which are 28, is the age cohort least focused on skilled trades, in part because they’re misinformed about the jobs, says the report based on 2,200 respondents to survey questions posted online in June.
“Only 38% of Gen Z says skilled trades offer the best job opportunities today” and “only 36% strongly agree skilled trades offer a faster and more affordable path to a good career,” the report says.
From DSC:
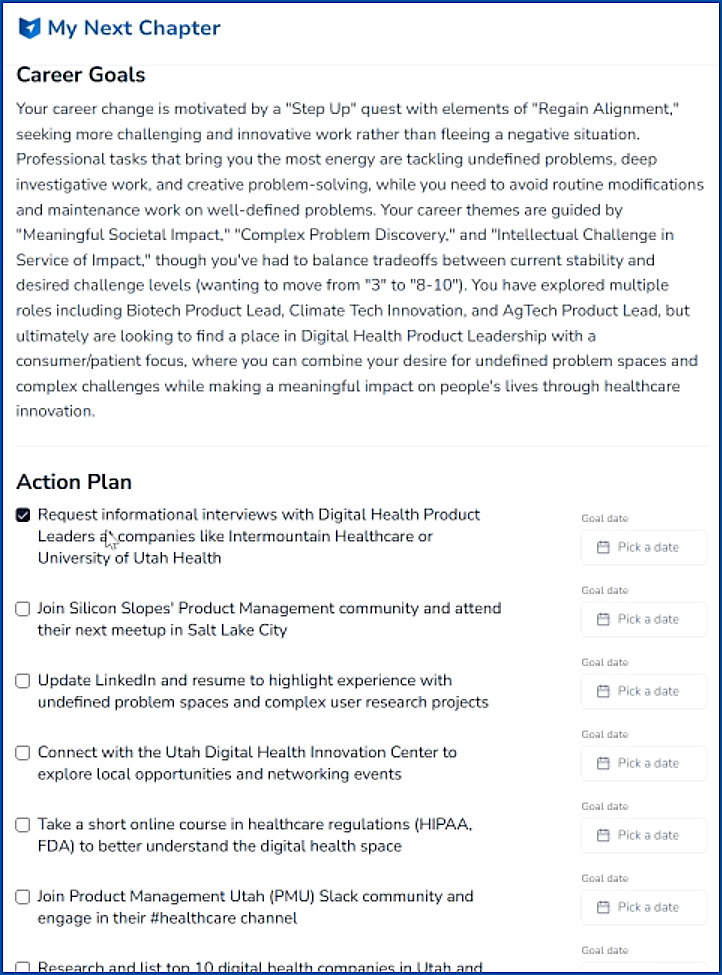
In looking at MyNextChapter.ai — THIS TYPE OF FUNCTIONALITY of an AI-based chatbot talking to you re: good fits for a future job — is the kind of thing that could work well in this type of vision/learning platform. The AI asks you relevant career-oriented questions, comes up with some potential job fits, and then gives you resources about how to gain those skills, who to talk with, organizations to join, next steps to get your foot in the door somewhere, etc.
The next gen learning platform would provide links to online-based courses, blogs, peoples’ names on LinkedIn, courses from L&D organizations or from institutions of higher education or from other entities/places to obtain those skills (similar to the ” Action Plan” below from MyNextChapter.ai).
Astronaut one day, artist the next: How to help children explore the world of careers — from apnews.com by Cathy Bussewitz
Sometimes career paths follow a straight line, with early life ambitions setting us on a clear path to training or a degree and a specific profession. Just as often, circumstance, luck, exposure and a willingness to adapt to change influence what we do for a living.
…
Developmental psychologists and career counselors recommend exposing children to a wide variety of career paths at a young age.
“It’s not so that they’ll pick a career, but that they will realize that there’s lots of opportunities and not limit themselves out of careers,” said Jennifer Curry, a Louisiana State University professor who researches career and college readiness.
Preparing for a world of AI
In addition to exposing children to career routes through early conversations and school courses, experts recommend teaching children about artificial intelligence and how it is reshaping the world and work.
Boys Are Struggling in School. What Can Be Done? — from edweek.org by Rick Hess
Scholar Richard Reeves says it’s time to take a hard look at gender equity
Rick: What kinds of strategies do you think would help?
Richard: In education, we should expand the use of male-friendly teaching methods, such as more hands-on and active learning approaches. We should also consider redshirting boys—starting them in school a year later—to account for developmental differences between boys and girls. We should also introduce more male mentors and role models in schools, particularly in elementary education, where male teachers are scarce. In the workforce, apprenticeship and vocational training programs need to be expanded to create pathways into stable employment for young men who may not pursue a four-year degree. Career counseling should also emphasize diverse pathways to ensure that boys who may not thrive in a traditional academic setting still have opportunities for success. Additionally, fatherhood policies should recognize the importance of male engagement in family life, supporting fathers in their role as caregivers and providers.
While on the topic of K12 education, also see:
How Electives Help All Students Succeed — from edutopia.org by Miriam Plotinsky
Giving students a choice of electives increases engagement and allows them to develop skills outside of core academic subjects.
I recently conducted a student focus group on the topic of school attendance. One of the participants, a high school junior who admitted to being frequently late or absent, explained why she still came to school: “I never want to miss Drama. My teacher is awesome. Her class is the reason I show up every day.” As the rest of the focus group chimed in with similar thoughts, I reflected on the power that elective courses hold for students of all ages.
These courses, from jazz band to yoga, cement students’ sense of self not just in their primary and secondary years, but also in their journey toward adulthood. In these tight economic times, schools or districts often slash electives to save money on staffing, which is highly detrimental to student success. Instead, not only should budget cuts be made elsewhere, but also elective offerings should increase to heighten student choice and well-being.