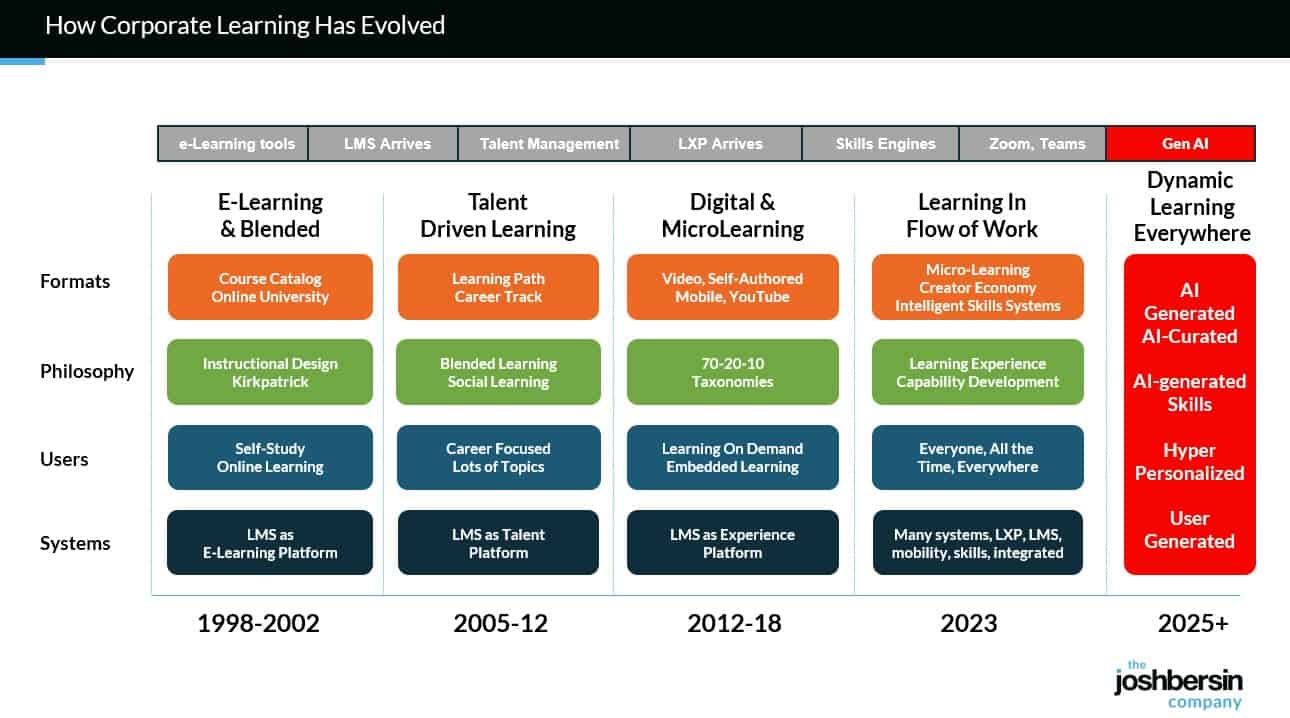
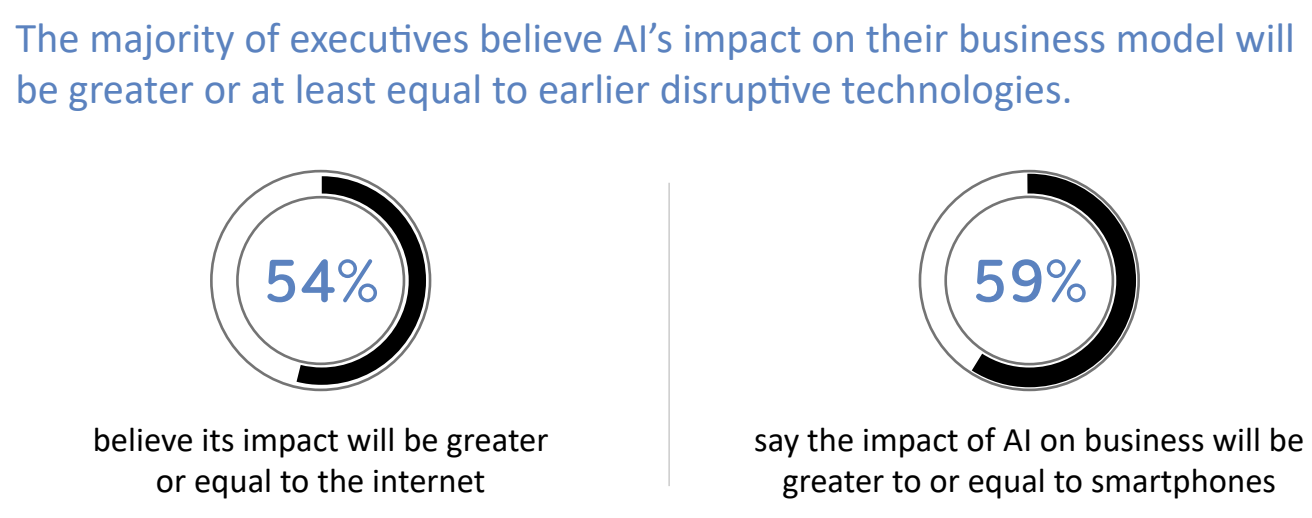
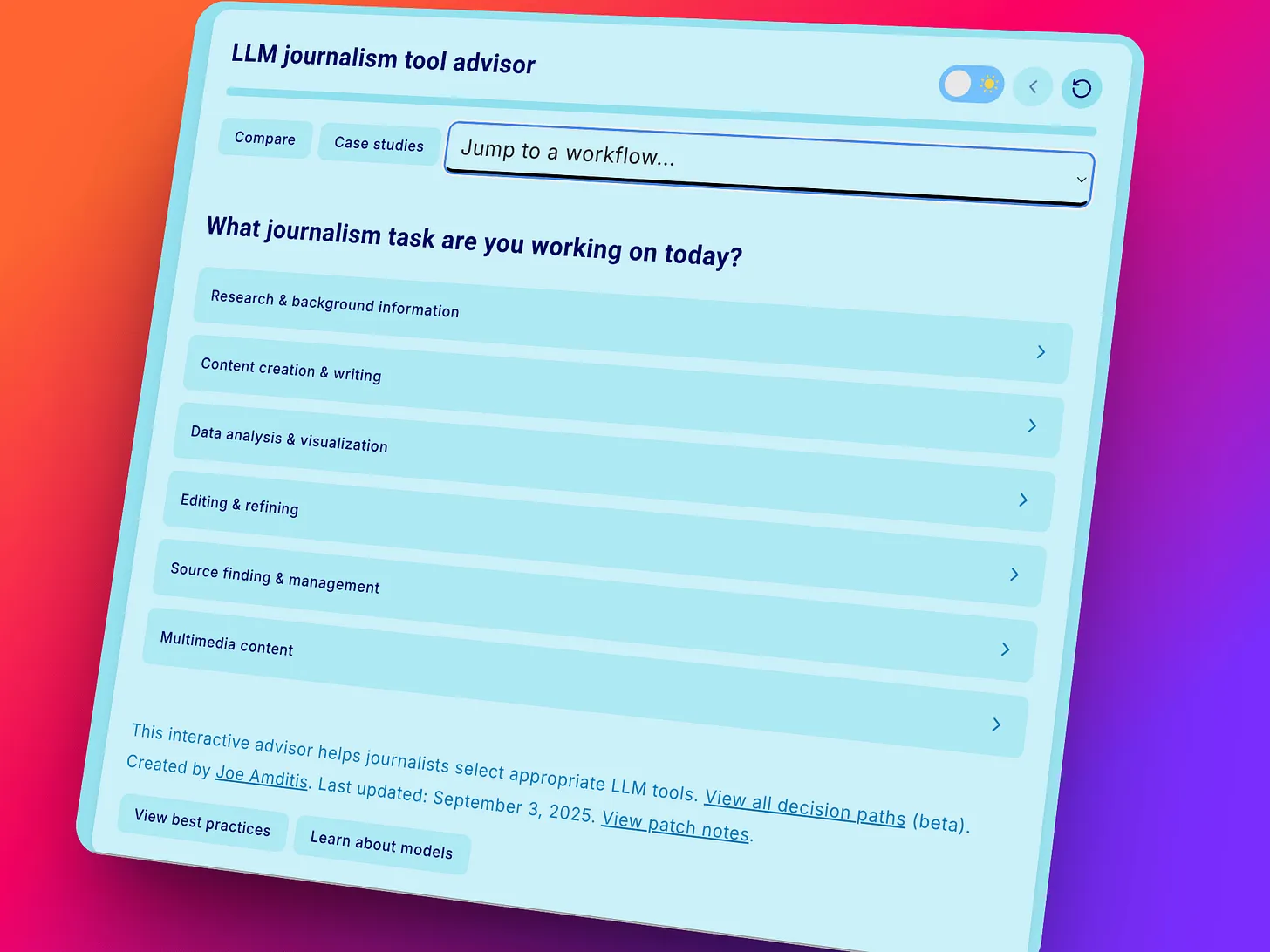
From EdTech to TechEd: The next chapter in learning’s evolution — from linkedin.com by Lev Gonick

A day in the life: The next 25 years
A learner wakes up. Their AI-powered learning coach welcomes them, drawing their attention to their progress and helping them structure their approach to the day. A notification reminds them of an upcoming interview and suggests reflections to add to their learning portfolio.
Rather than a static gradebook, their portfolio is a dynamic, living record, curated by the student, validated by mentors in both industry and education, and enriched through co-creation with maturing modes of AI. It tells a story through essays, code, music, prototypes, journal reflections, and team collaborations. These artifacts are not “submitted”, they are published, shared, and linked to verifiable learning outcomes.
And when it’s time to move, to a new institution, a new job, or a new goal, their data goes with them, immutable, portable, verifiable, and meaningful.
From DSC:
And I would add to that last solid sentence that the learner/student/employee will be able to control who can access this information. Anyway, some solid reflections here from Lev.
AI Could Surpass Schools for Academic Learning in 5-10 Years — from downes.ca with commentary from Stephen Downes
I know a lot of readers will disagree with this, and the timeline feels aggressive (the future always arrives more slowly than pundits expect) but I think the overall premise is sound: “The concept of a tipping point in education – where AI surpasses traditional schools as the dominant learning medium – is increasingly plausible based on current trends, technological advancements, and expert analyses.”
The world’s first AI cabinet member — from therundown.ai by Zach Mink, Rowan Cheung, Shubham Sharma, Joey Liu & Jennifer Mossalgue
The Rundown: In this tutorial, you will learn how to combine NotebookLM with ChatGPT to master any subject faster, turning dense PDFs into interactive study materials with summaries, quizzes, and video explanations.
Step-by-step:
- Go to notebooklm.google.com, click the “+” button, and upload your PDF study material (works best with textbooks or technical documents)
- Choose your output mode: Summary for a quick overview, Mind Map for visual connections, or Video Overview for a podcast-style explainer with visuals
- Generate a Study Guide under Reports — get Q&A sets, short-answer questions, essay prompts, and glossaries of key terms automatically
- Take your PDF to ChatGPT and prompt: “Read this chapter by chapter and highlight confusing parts” or “Quiz me on the most important concepts”
- Combine both tools: Use NotebookLM for quick context and interactive guides, then ChatGPT to clarify tricky parts and go deeperPro Tip: If your source is in EPUB or audiobook, convert it to PDF before uploading. Both NotebookLM and ChatGPT handle PDFs best.
Claude can now create and edit files — from anthropic.com
Claude can now create and edit Excel spreadsheets, documents, PowerPoint slide decks, and PDFs directly in Claude.ai and the desktop app. This transforms how you work with Claude—instead of only receiving text responses or in-app artifacts, you can describe what you need, upload relevant data, and get ready-to-use files in return.
Also see:
- Microsoft to lessen reliance on OpenAI by buying AI from rival Anthropic — from techcrunch.com byRebecca Bellan
Microsoft will pay to use Anthropic’s AI in Office 365 apps, The Information reports, citing two sources. The move means that Anthropic’s tech will help power new features in Word, Excel, Outlook, and PowerPoint alongside OpenAI’s, marking the end of Microsoft’s previous reliance solely on the ChatGPT maker for its productivity suite. Microsoft’s move to diversify its AI partnerships comes amid a growing rift with OpenAI, which has pursued its own infrastructure projects as well as a potential LinkedIn competitor.
Ep. 11 AGI and the Future of Higher Ed: Talking with Ray Schroeder
In this episode of Unfixed, we talk with Ray Schroeder—Senior Fellow at UPCEA and Professor Emeritus at the University of Illinois Springfield—about Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) and what it means for the future of higher education. While most of academia is still grappling with ChatGPT and basic AI tools, Schroeder is thinking ahead to AI agents, human displacement, and AGI’s existential implications for teaching, learning, and the university itself. We explore why AGI is so controversial, what institutions should be doing now to prepare, and how we can respond responsibly—even while we’re already overwhelmed.
Best AI Tools for Instructional Designers — from blog.cathy-moore.com by Cathy Moore
Data from the State of AI and Instructional Design Report revealed that 95.3% of the instructional designers interviewed use AI in their daily work [1]. And over 85% of this AI use occurs during the design and development process.
These figures showcase the immense impact AI is already having on the instructional design world.
If you’re an L&D professional still on the fence about adding AI to your workflow or an AI convert looking for the next best tools, keep reading.
This guide breaks down 5 of the top AI tools for instructional designers in 2025, so you can streamline your development processes and build better training faster.
But before we dive into the tools of the trade, let’s address the elephant in the room:
3 Human Skills That Make You Irreplaceable in an AI World — from gettingsmart.com/ by Tom Vander Ark and Mason Pashia
Key Points
-
Update learner profiles to emphasize curiosity, curation, and connectivity, ensuring students develop irreplaceable human skills.
-
Integrate real-world learning experiences and mastery-based assessments to foster agency, purpose, and motivation in students.