Learning from the Living [Class] Room > Other relevant postings and pieces of the puzzle
AI Tutors Double Rates of Learning in Less Learning Time — by drphilippahardman.substack.com Dr. Philippa Hardman
Inside Harvard’s new groundbreaking study
Conclusion
This Harvard study provides robust evidence that AI tutoring, when thoughtfully designed, can significantly enhance learning outcomes. The combination of doubled learning gains, increased engagement, and reduced time to competency suggests we’re seeing just the beginning of AI’s potential in education and that its potential is significant.If this data is anything to go by, and if we – as humans – are open and willing to acting on it, it’s possible AI will have a significant and for some deeply positive impact on how we design and deliver learning experiences.
That said, as we look forward, the question shouldn’t just be, “how AI can enhance current educational methods?”, but also “how it might AI transform the very nature of learning itself?”. With continued research and careful implementation, we could be moving toward an era of education that’s more effective but also more accessible than ever before.
The Tutoring Revolution — from educationnext.org by Holly Korbey
More families are seeking one-on-one help for their kids. What does that tell us about 21st-century education?
Recent research suggests that the number of students seeking help with academics is growing, and that over the last couple of decades, more families have been turning to tutoring for that help.
…
What the Future Holds
Digital tech has made private tutoring more accessible, more efficient, and more affordable. Students whose families can’t afford to pay $75 an hour at an in-person center can now log on from home to access a variety of online tutors, including Outschool, Wyzant, and Anchorbridge, and often find someone who can cater to their specific skills and needs—someone who can offer help in French to a student with ADHD, for example. Online tutoring is less expensive than in-person programs. Khan Academy’s Khanmigo chatbot can be a student’s virtual AI tutor, no Zoom meeting required, for $4 a month, and nonprofits like Learn to Be work with homeless shelters and community centers to give virtual reading and math tutoring free to kids who can’t afford it and often might need it the most.
“The Broken Mirror: Rethinking Education, AI, and Equity in America’s Classrooms” — from nickpotkalitsky.substack.com by JC Price
It’s not that AI is inherently biased, but in its current state, it favors those who can afford it. The wealthy districts continue to pull ahead, leaving schools without resources further behind. Students in these underserved areas aren’t just being deprived of technology—they’re being deprived of the future.
But imagine a different world—one where AI doesn’t deepen the divide, but helps to bridge it. Technology doesn’t have to be the luxury of the wealthy. It can be a tool for every student, designed to meet them where they are. Adaptive AI systems, integrated into schools regardless of their budget, can provide personalized learning experiences that help students catch up and push forward, all while respecting the limits of their current infrastructure. This is where AI’s true potential lies—not in widening the gap, but in leveling the field.
...
But imagine if, instead of replacing teachers, AI helped to support them. Picture a world where teachers are freed from the administrative burdens that weigh them down. Where AI systems handle the logistics, so teachers can focus on what they do best—teaching, mentoring, and inspiring the next generation. Professional development could be personalized, helping teachers integrate AI into their classrooms in ways that enhance their teaching, without adding to their workload. This is the future we should be striving toward—one where technology serves to lift up educators, not push them out.
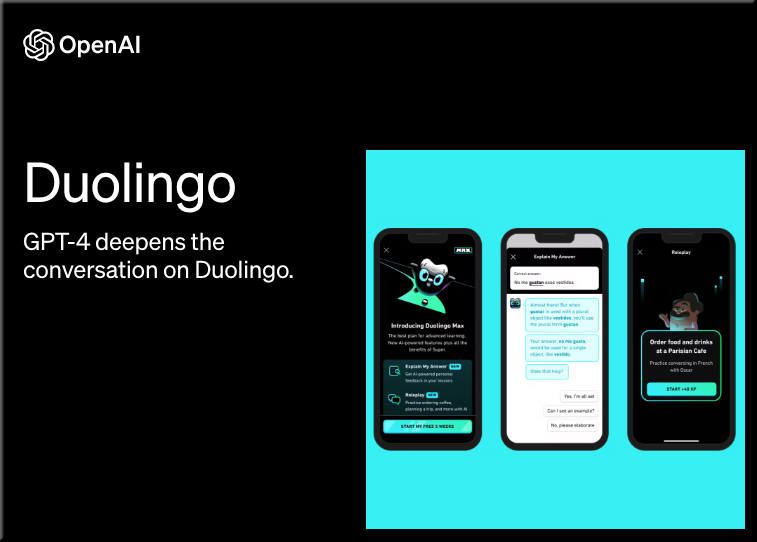
Duolingo Introduces AI-Powered Innovations at Duocon 2024 — from investors.duolingo.com
Duolingo’s new Video Call feature represents a leap forward in language practice for learners. This AI-powered tool allows Duolingo Max subscribers to engage in spontaneous, realistic conversations with Lily, one of Duolingo’s most popular characters. The technology behind Video Call is designed to simulate natural dialogue and provides a personalized, interactive practice environment. Even beginner learners can converse in a low-pressure environment because Video Call is designed to adapt to their skill level. By offering learners the opportunity to converse in real-time, Video Call builds the confidence needed to communicate effectively in real-world situations. Video Call is available for Duolingo Max subscribers learning English, Spanish, and French.
Workera’s CEO was mentored by Andrew Ng. Now he wants an AI agent to mentor you. -- from techcrunch.com by Maxwell Zeff
On Tuesday, Workera announced Sage, an AI agent you can talk with that’s designed to assess an employee’s skill level, goals, and needs. After taking some short tests, Workera claims Sage will accurately gauge how proficient someone is at a certain skill. Then, Sage can recommend the appropriate online courses through Coursera, Workday, or other learning platform partners. Through chatting with Sage, Workera is designed to meet employees where they are, testing their skills in writing, machine learning, or math, and giving them a path to improve.
From DSC:
This is very much akin to what I've been trying to get at with this vision. And as learning agents come onto the scene, this type of vision should take off!
Average Student Loan Debt -- from educationdata.org
Report Highlights. The total average student loan debt (including private loan debt) may be as high as $40,681.
- The average federal student loan debt is $37,853 per borrower.
- Outstanding private student loan debt totals $128.8 billion.
- The average student borrows over $30,000 to pursue a bachelor’s degree.
- A total of 42.8 million borrowers have federal student loan debt.
- It may take borrowers close to 20 years to pay off their student loans.
From DSC:
In other words, we are approaching the end of the line in terms of following the status quo within higher education. Institutions of traditional higher education can no longer increase their cost of tuition by significantly more than the rate of inflation. Increasingly, K-12 students (and families) are looking for other pathways and alternatives. Higher ed better stop trying to change around the edges...they need new, more cost-effective business models as well as being able to be much more responsive in terms of their curricula. If these changes aren't made, alternatives like the ones mentioned on this portion of my website are going to gain significant steam/ momentum.
The Progressive Case for Reforming Higher Ed — from insidehighered.com by Michael D. Smith
Customized, digital education offers a path for progressive reform, Michael D. Smith writes.
That’s the bad news. But there’s good news, too. New digital technologies have arrived during the past decade for delivering instruction and evaluating individual student learning at scale. If we embrace them, they can make real reform possible and allow us to imagine a fairer, more accessible system of higher education—one that will enable us to better serve the many students who are left out of our existing scarcity-based model.
…
I think it should be to reform our educational system in ways that will benefit society. And with the advent of new digital technologies, we have a once-in-a-generation opportunity to do just that. If we embrace those technologies now, we can democratize access to the knowledge that students from all socioeconomic backgrounds need to discover and develop their talents, and we can make it possible for them to earn the credentials they need to signal their knowledge to employers—all so that they can use their talents to make a difference in the world.But in the years ahead, thanks to these new technologies, the broader ecosystem that these institutions exist in is going to expand and change dramatically. Gradually, elite residential colleges and universities will lose their dominant place in that ecosystem, and customized digital learning will first disrupt and then come to dominate a new system of higher education—one that reaches more people, and generates greater benefits for society, than ever before.
School 3.0: Reimagining Education in 2026, 2029, and 2034 — from davidborish.com by David Borish
The landscape of education is on the brink of a profound transformation, driven by rapid advancements in artificial intelligence. This shift was highlighted recently by Andrej Karpathy’s announcement of Eureka Labs, a venture aimed at creating an “AI-native” school. As we look ahead, it’s clear that the integration of AI in education will reshape how we learn, teach, and think about schooling altogether.
…
Traditional textbooks will begin to be replaced by interactive, AI-powered learning materials that adapt in real-time to a student’s progress.
…
As we approach 2029, the line between physical and virtual learning environments will blur significantly.Curriculum design will become more flexible and personalized, with AI systems suggesting learning pathways based on each student’s interests, strengths, and career aspirations.
…
The boundaries between formal education and professional development will blur, creating a continuous learning ecosystem.
Deep Learning: Five New Superpowers of Higher Education — from jeppestricker.substack.com by Jeppe Klitgaard Stricker
How Deep Learning is Transforming Higher EducationWhile the traditional model of education is entrenched, emerging technologies like deep learning promise to shake its foundations and usher in an age of personalized, adaptive, and egalitarian education. It is expected to have a significant impact across higher education in several key ways.
…
…deep learning introduces adaptivity into the learning process. Unlike a typical lecture, deep learning systems can observe student performance in real-time. Confusion over a concept triggers instant changes to instructional tactics. Misconceptions are identified early and remediated quickly. Students stay in their zone of proximal development, constantly challenged but never overwhelmed. This adaptivity prevents frustration and stagnation.
Introducing Eureka Labs -- from eurekalabs.ai
We are Eureka Labs and we are building a new kind of school that is AI native.
How can we approach an ideal experience for learning something new? For example, in the case of physics one could imagine working through very high quality course materials together with Feynman, who is there to guide you every step of the way. Unfortunately, subject matter experts who are deeply passionate, great at teaching, infinitely patient and fluent in all of the world's languages are also very scarce and cannot personally tutor all 8 billion of us on demand.
However, with recent progress in generative AI, this learning experience feels tractable. The teacher still designs the course materials, but they are supported, leveraged and scaled with an AI Teaching Assistant who is optimized to help guide the students through them. This Teacher + AI symbiosis could run an entire curriculum of courses on a common platform. If we are successful, it will be easy for anyone to learn anything, expanding education in both reach (a large number of people learning something) and extent (any one person learning a large amount of subjects, beyond what may be possible today unassisted).
⚡️ Excited to share that I am starting an AI+Education company called Eureka Labs.
— Andrej Karpathy (@karpathy) July 16, 2024
The announcement:
---
We are Eureka Labs and we are building a new kind of school that is AI native.
How can we approach an ideal experience for learning something new? For example, in the case… pic.twitter.com/RHPkqdjB8R
Mary Meeker wants AI and higher education to be partners — from axios.com by Dan Primack; via Robert Gibson on LinkedIn
Mary Meeker has written her first report in over four years, focused on the relationship between artificial intelligence and U.S. higher education.
Why it matters: Meeker’s annual “Internet Trends” reports were among Silicon Valley’s most cited and consumed documents.
- Each one dug deep into the new tech economy, with hundreds of pages of slides. The last one was published in 2019.
- Meeker’s new effort is a shorter attempt (16 pages!) at reconciling tech’s brave new world and America’s economic vitality, with higher ed as the connective tissue.
Excerpts from Meeker’s report:
Actions taken in the next five years will be consequential. It’s important for higher education to take a leadership role, in combination with industry and government. The ramp in artificial intelligence – which leverages the history of learning for learning – affects all forms of learning, teaching, understanding, and decision making. This should be the best of times…
Our first-pass observations on these topics follow. We begin with an overview, followed by thoughts on the unprecedented ramp in AI usage and the magnitude of investment in AI from America’s leading global technology companies. Then we explore ways that this rapidly changing AI landscape may drive transformations in higher education. We hope these add to the discussion.
Claude can now use tools — from anthropic.com
Tool use, which enables Claude to interact with external tools and APIs, is now generally available across the entire Claude 3 model family on the Anthropic Messages API, Amazon Bedrock, and Google Cloud’s Vertex AI. With tool use, Claude can perform tasks, manipulate data, and provide more dynamic—and accurate—responses.
Define a toolset for Claude and specify your request in natural language. Claude will then select the appropriate tool to fulfill the task and, when appropriate, execute the corresponding action:
- Extract structured data from unstructured text…
- Convert natural language requests into structured API calls…
- Answer questions by searching databases or using web APIs…
- Automate simple tasks through software APIs…
- Orchestrate multiple fast Claude subagents for granular tasks…
From DSC: The above posting reminds me of this other posting…as AGENTS are likely going to become much more popular and part of our repertoire:
Forget Chatbots. AI Agents Are the Future — from wired.com by Will Knight
Startups and tech giants are trying to move from chatbots that offer help via text, to AI agents that can get stuff done. Recent demos include an AI coder called Devin and agents that play videogames.Devin is just the latest, most polished example of a trend I’ve been tracking for a while—the emergence of AI agents that instead of just providing answers or advice about a problem presented by a human can take action to solve it. A few months back I test drove Auto-GPT, an open source program that attempts to do useful chores by taking actions on a person’s computer and on the web. Recently I tested another program called vimGPT to see how the visual skills of new AI models can help these agents browse the web more efficiently.
The above item is out here on LinkedIn.
A major step towards much more natural human-computer interaction: OpenAI introduces GPT-4o
Hello GPT-4o — from openai.com
We’re announcing GPT-4o, our new flagship model that can reason across audio, vision, and text in real time.This demo is insane.
— Mckay Wrigley (@mckaywrigley) May 13, 2024
A student shares their iPad screen with the new ChatGPT + GPT-4o, and the AI speaks with them and helps them learn in *realtime*.
Imagine giving this to every student in the world.
The future is so, so bright. pic.twitter.com/t14M4fDjwV
Khan Academy and Microsoft partner to expand access to AI tools that personalize teaching and help make learning fun — from news.microsoft.com
[On 5/21/24] at Microsoft Build, Microsoft and Khan Academy announced a new partnership that aims to bring these time-saving and lesson-enhancing AI tools to millions of educators. By donating access to Azure AI-optimized infrastructure, Microsoft is enabling Khan Academy to offer all K-12 educators in the U.S. free access to the pilot of Khanmigo for Teachers, which will now be powered by Azure OpenAI Service.
The two companies will also collaborate to explore opportunities to improve AI tools for math tutoring in an affordable, scalable and adaptable way with a new version of Phi-3, a family of small language models (SLMs) developed by Microsoft.
This has been my two-device work setup (plus monitor usually) for months.
— Allie K. Miller (@alliekmiller) May 21, 2024
Example: when I’m in a zoom meeting, I’ll mute myself, dictate a crazy fast question to chatgpt, get the answer, and skim it.
Basically enriching my work in real-time. pic.twitter.com/H7n9UwEiVh
From DSC: There are likely to be many more industry-specific AI-based assistants like this:
Microsoft introduces the world to a new category of Windows PCs designed for AI –> Copilot+ PCs

A Guide to the GPT-4o ‘Omni’ Model — from aieducation.substack.com by Claire Zau
The closest thing we have to “Her” and what it means for education / workforce
Announcements from Google I/O re: their AI-based offerings
Google I/O 2024: An I/O for a new generation — from blog.google
The Gemini era
A year ago on the I/O stage we first shared our plans for Gemini: a frontier model built to be natively multimodal from the beginning, that could reason across text, images, video, code, and more. It marks a big step in turning any input into any output — an “I/O” for a new generation.Google just announced huge Gemini updates, a Sora competitor, AI agents, and more.
— Rowan Cheung (@rowancheung) May 15, 2024
The 12 most impressive announcements at Google I/O:
1. Project Astra: An AI agent that can see AND hear what you do live in real-time.pic.twitter.com/sA2YT80O5G
Synthetic Video & AI Professors — from drphilippahardman.substack.com by Dr. Philippa Hardman
Are we witnessing the emergence of a new, post-AI model of async online learning?TLDR: by effectively tailoring the learning experience to the learner’s comprehension levels and preferred learning modes, AI can enhance the overall learning experience, leading to increased “stickiness” and higher rates of performance in assessments.
…
TLDR: AI enables us to scale responsive, personalised “always on” feedback and support in a way that might help to solve one of the most wicked problems of online async learning – isolation and, as a result, disengagement.
…
In the last year we have also seen the rise of an unprecedented number of “always on” AI tutors, built to provide coaching and feedback how and when learners need it.Perhaps the most well-known example is Khan Academy’s Khanmigo and its GPT sidekick Tutor Me. We’re also seeing similar tools emerge in K12 and Higher Ed where AI is being used to extend the support and feedback provided for students beyond the physical classroom.
Closing The Skills Gap: An Inside Look At The Achievement Wallet — from forbes.com by Dr. Sarah DeMark
In the dynamic realm of today’s workforce, skills gaps are increasing. Highly skilled talent is out there, but information gaps and traditional hiring methods make it challenging for skilled talent and employers to find one another. While digital recruiting systems have made it more efficient to find prospective candidates, qualified candidates are often vetted out of the hiring process when they do not match the exact criteria, according to a study conducted by Harvard Business School.
Skills and information gaps are not merely abstractions, but tangible forces that influence career trajectories, organizational competitiveness, the lack of underrepresented populations in high growth areas of the workforce, and the fabric of student and professional success. The need for more agency for both learners and employers to bridge these gaps and take advantage of opportunities has never been more pressing.
...
With the rapid pace of change — think automation, new technology, and artificial intelligence — businesses must innovate and think about the best ways to create career mobility and career pathways for their workforces into the roles of tomorrow.
...
In Pursuit of Agency
Imagine a future where learners can instantly see where they stand in a crowded job market, assess their abilities and gaps, and identify opportunities for growth. Or where employers can identify candidates with specific, often hard-to-spot competencies and skills. Possible? Yes. Western Governors University (WGU), the country’s largest competency-based, workforce-relevant online university, is reimagining that future by deploying the Achievement Wallet for WGU students nationally and working students at educational institutions across the state of Indiana.
A Cautionary AI Tale: Why IBM’s Dazzling Watson Supercomputer Made a Lousy Tutor — from the74million.org by Greg Toppo
With a new race underway to create the next teaching chatbot, IBM’s abandoned 5-year, $100M ed push offers lessons about AI’s promise and its limits.
For all its jaw-dropping power, Watson the computer overlord was a weak teacher. It couldn’t engage or motivate kids, inspire them to reach new heights or even keep them focused on the material — all qualities of the best mentors.
It’s a finding with some resonance to our current moment of AI-inspired doomscrolling about the future of humanity in a world of ascendant machines. “There are some things AI is actually very good for,” Nitta said, “but it’s not great as a replacement for humans.”
His five-year journey to essentially a dead-end could also prove instructive as ChatGPT and other programs like it fuel a renewed, multimillion-dollar experiment to, in essence, prove him wrong.
...To be sure, AI can do sophisticated things such as generating quizzes from a class reading and editing student writing. But the idea that a machine or a chatbot can actually teach as a human can, he said, represents “a profound misunderstanding of what AI is actually capable of.”
Nitta, who still holds deep respect for the Watson lab, admits, “We missed something important. At the heart of education, at the heart of any learning, is engagement. And that’s kind of the Holy Grail.”
**************************************
From DSC:
This is why this vision has always said that HUMAN BEINGS will be necessary -- they are key to realizing this vision.
Along these lines, here's a relevant quote:
Another crucial component of a new learning theory for the age of AI would be the cultivation of "blended intelligence." This concept recognizes that the future of learning and work will involve the seamless integration of human and machine capabilities, and that learners must develop the skills and strategies needed to effectively collaborate with AI systems. Rather than viewing AI as a threat to human intelligence, a blended intelligence approach seeks to harness the complementary strengths of humans and machines, creating a symbiotic relationship that enhances the potential of both.
Per Alexander "Sasha" Sidorkin, Head of the National Institute on AI in Society at California State University Sacramento.
**************************************
The New Academic Arms Race | Competition over amenities is over. The next battleground is technology. — from chronicle.com by Jeffrey J. Selingo
Now, after the pandemic, with the value of the bachelor’s degree foremost in the minds of students and families, a new academic arms race is emerging. This one is centered around academic innovation. The winners will be those institutions that in the decade ahead better apply technology in teaching and learning and develop different approaches to credentialing.
Sure, technology is often seen as plumbing on campuses — as long as it works, we don’t worry about it. And rarely do prospective students on a tour ever ask about academic innovations like extended reality or microcredentials. Campus tours prefer to show off the bells and whistles of residential life within dorms and dining halls.
That’s too bad.
...
The problem is not a lack of learners, but rather a lack of alignment in what colleges offer to a generation of learners surrounded by Amazon, Netflix, and Instagram, where they can stream entertainment and music anytime, anywhere.
How Generative AI Owns Higher Education. Now What? -- from forbes.com by Steve Andriole
[A prompt] Develop a syllabus for a marketing course for graduate students that covers the fundamental principles of marketing, marketing cases, readings that include some theory and practice – with an emphasis on practice – with requirements that include projects, essays, tests and in-class conversations that illuminate theory and practice. Also develop lecture notes for me with bullet points – derived from the readings – that will focus the students class-by-class on the right topics. Please also assume that the class is 15 weeks long with readings, assignments and 5 salient topics (captured in the bullet points) per week. Use only current readings: nothing older that 2015. I’d also like some learning outcomes I should expect the course to generate.”
...
What about course videos? Professors can create them (by lecturing into a camera for several hours hopefully in different clothes) from the readings, from their interpretations of the readings, from their own case experiences – from anything they like. But now professors can direct the creation of the videos by talking – actually describing – to a CustomGPT about what they’d like the video to communicate with their or another image. Wait. What? They can make a video by talking to a CustomGPT and even select the image they want the “actor” to use? Yes. They can also add a British accent and insert some (GenAI-developed) jokes into the videos if they like. All this and much more is now possible. This means that a professor can specify how long the video should be, what sources should be consulted and describe the demeanor the professor wants the video to project.
Meet Ed: Ed is an educational friend designed to help students reach their limitless potential. — from lausd.org (Los Angeles School District, the second largest in the U.S.)
What is Ed?
An easy-to-understand learning platform designed by Los Angeles Unified to increase student achievement. It offers personalized guidance and resources to students and families 24/7 in over 100 languages.
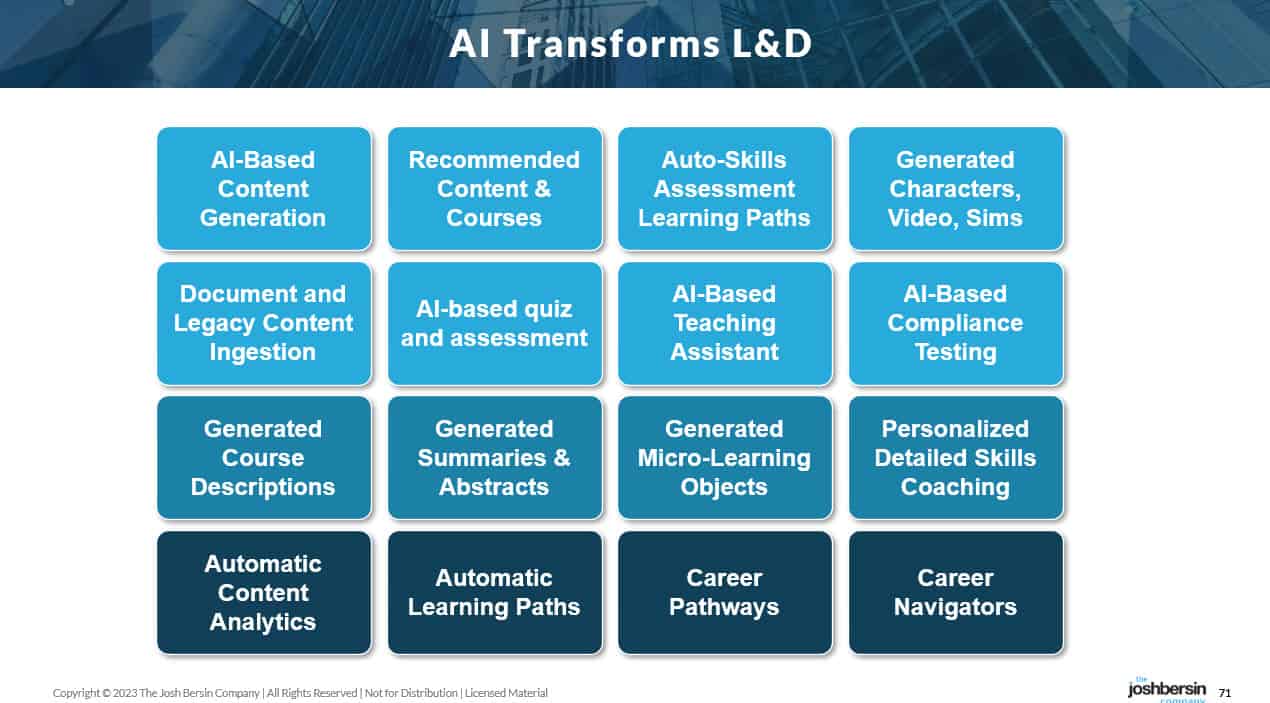
The $340 Billion Corporate Learning Industry Is Poised For Disruption -- from joshbersin.com by Josh Bersin
What if, for example, the corporate learning system knew who you were and you could simply ask it a question and it would generate an answer, a series of resources, and a dynamic set of learning objects for you to consume? In some cases you’ll take the answer and run. In other cases you’ll pour through the content. And in other cases you’ll browse through the course and take the time to learn what you need.
And suppose all this happened in a totally personalized way. So you didn’t see a “standard course” but a special course based on your level of existing knowledge?
This is what AI is going to bring us. And yes, it’s already happening today.
A Notre Dame Senior’s Perspective on AI in the Classroom — from learning.nd.edu — by Sarah Ochocki
At this moment, as a college student trying to navigate the messy, fast-developing, and varied world of generative AI, I feel more confused than ever. I think most of us can share that feeling. There’s no roadmap on how to use AI in education, and there aren’t the typical years of proof to show something works. However, this promising new tool is sitting in front of us, and we would be foolish to not use it or talk about it.
…
I’ve used it to help me understand sample code I was viewing, rather than mindlessly trying to copy what I was trying to learn from. I’ve also used it to help prepare for a debate, practicing making counterarguments to the points it came up with.AI alone cannot teach something; there needs to be critical interaction with the responses we are given. However, this is something that is true of any form of education. I could sit in a lecture for hours a week, but if I don’t do the homework or critically engage with the material, I don’t expect to learn anything.
Accenture to acquire Udacity to build a learning platform focused on AI — from techcrunch.com by Ron Miller
Accenture announced today that it would acquire the learning platform Udacity as part of an effort to build a learning platform focused on the growing interest in AI. While the company didn’t specify how much it paid for Udacity, it also announced a $1 billion investment in building a technology learning platform it’s calling LearnVantage.
“The rise of generative AI represents one of the most transformative changes in how work gets done and is driving a growing need for enterprises to train and upskill people in cloud, data and AI as they build their digital core and reinvent their enterprises,” Kishore Durg, global lead of Accenture LearnVantage said in a statement.
Affordability and Microcredentials — from the-job.beehiiv.com by Paul Fain
Cutting costs for short-term credentials with course sharing and, perhaps, federal money.
‘Bespoke, e-Commerce-Enabled Storefronts’
Demand for nondegree credentials has risen. But it can be expensive and tricky for colleges to create their own workforce-relevant courses and certifications. Homegrown microcredentials also may be more likely to fall flat with students and employers, particularly in competition with professional certificates from big brands like Salesforce or AWS.Acadeum, an online course-sharing company, is betting that a networked marketplace will be a better option for its 460 college and university partners, which include a growing number of community colleges. Beginning last month, those colleges can tap into 380+ online certificates, certifications, and skills-training courses.
“Skills Marketplace lowers the barrier of entry for institutions to self-select only the certifications that align their program offerings to meet student and workforce demand,” says David Daniels, Acadeum’s president and CEO.
6 work and workplace trends to watch in 2024 — from weforum.org by Kate Whiting
The world of work is changing fast.
By 2027, businesses predict that almost half (44%) of workers’ core skills will be disrupted.
Technology is moving faster than companies can design and scale up their training programmes, found the World Economic Forum’s Future of Jobs Report.
…
The Forum’s Global Risks Report 2024 found that “lack of economic opportunity” ranked as one of the top 10 biggest risks among risk experts over the next two years. 5. Skills will become even more important With 23% of jobs expected to change in the next five years, according to the Future of Jobs Report, millions of people will need to move between declining and growing jobs.
...
5. Skills will become even more important
With 23% of jobs expected to change in the next five years, according to the Future of Jobs Report, millions of people will need to move between declining and growing jobs.
From DSC:
Skills need to be updated -- big time, and quickly. Curriculum needs to change -- big time, and quickly. Neither higher education nor K-12 can keep up with this pace, and we'll see if the corporate L&D world will be able to keep up with this blazingly fast pace of change.
Conversational & Experiential: The New Duality of Learning — from learningguild.com by Markus Bernhardt
The future of corporate learning and development (L&D) is being profoundly reshaped by the progress we are witnessing in artificial intelligence (AI). The increasing availability of new technologies and tools is causing L&D leaders and their teams to rethink their strategy and processes, and even their team structure. The resulting shift, already gaining momentum, will soon move us toward a future where learning experiences are deeply personal, interactive, and contextually rich.
...
We are already seeing signs of the immediate future—one where AI will adapt not only content but the entire learner experience, on-the-fly and aligned with the needs and requirements of the learner at a specific moment of need.
Instructure Completes Acquisition of Parchment, the World’s Largest Academic Credential Management Platform and Network — from prnewswire.com
Expands Instructure’s market-leading teaching and learning ecosystem by providing learners with a lifelong record of their journey
SALT LAKE CITY, Feb. 1, 2024 /PRNewswire/ — Instructure Holdings, Inc. (Instructure) (NYSE: INST), the leading learning ecosystem and maker of Canvas, announced today it has completed the acquisition of Parchment, the world’s largest credential management platform and network. Parchment has over 13,000 customers and has exchanged more than 165 million credentials over two decades. This acquisition is expected to significantly expand Instructure’s existing customer base and unlock exciting new growth opportunities.
“The addition of Parchment to the Instructure ecosystem enables our customers to offer flexible lifelong learning experiences to meet the needs of the ever-growing sector of non-traditional learners,” said Steve Daly, CEO of Instructure. “By providing a verifiable and comprehensive digital passport of achievement records and outcomes for learners, we’ll be able to help our customers navigate skill mastery, transfer credits, provide proof of prior learning, and much more.”
From DSC:
Instructure’s purchase here represents an important piece of our future learning ecosystems— a way to document/prove the learning a person has done throughout their ***lifelong learning*** journey.
Slow Shift to Skills — from the-job.beehiiv.com by Paul Fain
Real progress in efforts to increase mobility for nondegree workers is unlikely during the next couple years, Joseph Fuller, a professor at Harvard University’s business school who co-leads its Managing the Future of Work initiative, recently told me.
Yet Fuller is bullish on skills-based hiring becoming a real thing in five to 10 years. That’s because he predicts that AI will create the data to solve the skills taxonomy problem Kolko describes. And if skills-based hiring allows for serious movement for workers without bachelor’s degrees, Fuller says the future will look like where Texas is headed.
Below is an excerpt from AI & “Un-Personalised” Learning -- from drphilippahardman.substack.com by Dr. Philippa Hardman
Exploring the full potential of AI to improve human learning, beyond the 1:1 AI tutor
AI for “Un-Personalised” Learning
The next question is, of course: how could we use AI to scale the positive outcomes of “un-personalised”, communal learning?
Here are some initial ideas:
-
AI algorithms could be used to analyse students' backgrounds, and performance data to create optimised learning cohorts.
-
AI-powered features like real-time language translation could be used to create and connect diverse groups.
-
AI tutors could be built to serve learning groups by stimulating discussion, answering questions, providing explanations and ensuring that all group members are on the same page.
-
AI-facilitated spaces could be built to enable virtual brainstorming sessions, group discussions & collaborative project work.
-
AI could be used to create groups with shared interests or challenges and suggest connections to foster collective learning and innovation.
-
AI could also be used to help generate resources to support ideation and to analyse and give feedback on the quality of ideas.
-
AI could be used to match learners with others who have similar interests and learning goals, enabling peer mentorship and knowledge exchange.
-
AI could be used to manage the logistics of peer instruction sessions, including organising discussion groups and timing activities.
-
Within Peer-to-Peer networks, AI could be used to immediate feedback to students based on their responses, analyse and give feedback on the effectiveness of peer instruction methods and assess changes in student understanding and behaviour.
-
AI can be used to generate scenarios and guide learners through them.
-
Learners could be allocated different roles in a historical or hypothetical scenarios and AI could coach the group to negotiate and make collective decisions, providing a dynamic learning environment that emphasises teamwork, leadership and decision-making skills.
How Workers Rise — from the-job.beehiiv.com by Paul Fain
A look forward at skills-based hiring and AI’s impacts on education and work.
Impacts of AI: Fuller is optimistic about companies making serious progress on skills-based hiring over the next five to 10 years. AI will help drive that transformation, he says, by creating the data to better understand the skills associated with jobs.
The technology will allow for a more accurate matching of skills and experiences, says Fuller, and for companies to “not rely on proxies like degrees or grade point averages or even the proxy of what someone currently makes or how fast they’ve gotten promoted on their résumé.”
Another example of where we're headed:

Learners’ Edition: AI-powered Coaching, Professional Certifications + Inspiring conversations about mastering your learning & speaking skills — from linkedin.com by Tomer Cohen
1. Your own AI-powered coaching
Learners can go into LinkedIn Learning and ask a question or explain a challenge they are currently facing at work (we’re focusing on areas within Leadership and Management to start). AI-powered coaching will pull from the collective knowledge of our expansive LinkedIn Learning library and, instantaneously, offer advice, examples, or feedback that is personalized to the learner’s skills, job, and career goals.What makes us so excited about this launch is we can now take everything we as LinkedIn know about people’s careers and how they navigate them and help accelerate them with AI.
…
3. Learn exactly what you need to know for your next job
When looking for a new job, it’s often the time we think about refreshing our LinkedIn profiles. It’s also a time we can refresh our skills. And with skill sets for jobs having changed by 25% since 2015 – with the number expected to increase by 65% by 2030– keeping our skills a step ahead is one of the most important things we can do to stand out.There are a couple of ways we’re making it easier to learn exactly what you need to know for your next job:
When you set a job alert, in addition to being notified about open jobs, we’ll recommend learning courses and Professional Certificate offerings to help you build the skills needed for that role.
When you view a job, we recommend specific courses to help you build the required skills. If you have LinkedIn Learning access through your company or as part of a Premium subscription, you can follow the skills for the job, that way we can let you know when we launch new courses for those skills and recommend you content on LinkedIn that better aligns to your career goals.
2024 Edtech Predictions from Edtech Insiders — from edtechinsiders.substack.com by Alex Sarlin, Ben Kornell, and Sarah Morin
Omni-modal AI, edtech funding prospects, higher ed wake up calls, focus on career training, and more!
Alex: I talked to the 360 Learning folks at one point and they had this really interesting epiphany, which is basically that it’s been almost impossible for every individual company in the past to create a hierarchy of skills and a hierarchy of positions and actually organize what it looks like for people to move around and upskill within the company and get to new paths.
Until now. AI actually can do this very well. It can take not only job description data, but it can take actual performance data. It can actually look at what people do on a daily basis and back fit that to training, create automatic training based on it.
From DSC:
I appreciated how they addressed K-12, higher ed, and the workforce all in one posting. Nice work. We don’t need siloes. We need more overall design thinking re: our learning ecosystems — as well as more collaborations. We need more on-ramps and pathways in a person’s learning/career journey.
Notebook LM (experiment): Collaborate with a virtual research assistant
From DSC:
Google hopes that this personalized AI/app will help people with their note-taking, thinking, brainstorming, learning, and creating.
It reminds me of what Derek Bruff was just saying in regards to Top Hat’s Ace product being able to work with a much narrower set of information — i.e., a course — and to be almost like a personal learning assistant for the course you are taking. (As Derek mentions, this depends upon how extensively one uses the CMS/LMS in the first place.)
When Educators and Employers Work Together, Students Succeed — from hbsp.harvard.edu by Joseph Fuller and Manjari Raman
(Emphasis below from DSC)
Last year, in “The Partnership Imperative,” we put forth a set of more than 40 best practices that employers and educators can use to develop a close collaboration. As part of that effort, we identified three main goals and laid out strategies for achieving each.
- Partner with each other to offer training and education that is aligned with industry needs. (DSC: Similar to how Instructional Designers want alignment with learning objectives, learning activities, and assessments of learning.)
- Establish relationships with each other that result in the recruitment and hiring of students and graduates.
- Make supply-and-demand decisions that are informed by the latest data and trends.
Under #1, their strategies include:
Cocreate and regularly update college curriculums so that they reflect relevant technical and foundational skills based on industry needs. Codesign programs that fit with students’ lives and industry hiring cycles. Incorporate classroom experiences that simulate real-world settings and scenarios.
***I see AI being able to identify what those changing, currently sought-after, and foundational skills are based on industry needs (which shouldn’t be hard, and vendors like Microsoft are already doing this by combing through the posted job descriptions on their platforms). These findings/results will help build regularly updated learning playlists.***
LERs Are Hot. What Are States Going To Do With Them? -- from National Governors Association

Governors and state leaders are concerned about the current labor shortage, occurring during a time when many skilled workers are underemployed or even unemployed. Skills-based approaches to hiring and recruiting can shift that dynamic—making pathways to good careers accessible to a wider segment of the workforce and opening up new pools of talent for employers. They do so by focusing on what workers know and can do, not on the degrees or credentials they’ve earned.
That’s the theory. But a lot hinges on how things actually play out on the ground.
Technology will play a key role, and many states have zeroed in on learning and employment records—essentially digital resumes with verified records of people’s skills, educational experiences, and work histories—as an essential tool. A lot of important work is going into the technical design and specifications.
This project, on the other hand, aims to take a step back and look at the current state of play when it comes to the use cases for LERs. Just a few of the key questions:
- How might employers, education providers, government agencies, and workers themselves actually use them? Will they?
- In what areas do state policymakers have the most influence over key stakeholders and the most responsibility to invest?
- What actions are needed now to ensure that LERs, and skills-based hiring more broadly, actually widen access to good jobs—rather than setting up a parallel system that perpetuates many of today’s inequities?
Exploring blockchain’s potential impact on the education sector — from e27.co by Moch Akbar Azzihad M
By the year 2024, the application of blockchain technology is anticipated to have a substantial influence on the education sector
Areas mentioned include:
- Credentials that are both secure and able to be verified
- Records of accomplishments that are not hidden
- Enrollment process that is both streamlined and automated
- Storage of information that is both secure and decentralised
- Financing and decentralised operations
The Vision for Project Chiron:
From DSC: This future learning platform will also focus on developing skills and competencies. Along those lines, see:
Scale for Skills-First — from the-job.beehiiv.com by Paul Fain
An ed-tech giant’s ambitious moves into digital credentialing and learner records.
A Digital Canvas for Skills
Instructure was a player in the skills and credentials space before its recent acquisition of Parchment, a digital transcript company. But that $800M move made many observers wonder if Instructure can develop digital records of skills that learners, colleges, and employers might actually use broadly.
…Ultimately, he says, the CLR approach will allow students to bring these various learning types into a coherent format for employers.
Instructure seeks a leadership role in working with other organizations to establish common standards for credentials and learner records, to help create consistency. The company collaborates closely with 1EdTech. And last month it helped launch the 1EdTech TrustEd Microcredential Coalition, which aims to increase quality and trust in digital credentials.
Paul also links to 1EDTECH’s page regarding the Comprehensive Learning Record
New models and developer products announced at DevDay -- from openai.com
GPT-4 Turbo with 128K context and lower prices, the new Assistants API, GPT-4 Turbo with Vision, DALL·E 3 API, and more.
Today, we shared dozens of new additions and improvements, and reduced pricing across many parts of our platform. These include:
- New GPT-4 Turbo model that is more capable, cheaper and supports a 128K context window
- New Assistants API that makes it easier for developers to build their own assistive AI apps that have goals and can call models and tools
- New multimodal capabilities in the platform, including vision, image creation (DALL·E 3), and text-to-speech (TTS)
Introducing GPTs -- from openai.com You can now create custom versions of ChatGPT that combine instructions, extra knowledge, and any combination of skills.
I'm genuinely blown away by this.
The leap from text descriptions straight to 3D models? It's next-level. Think about the possibility: a stream of prompts turns into a treasure trove of 3D pieces. Gather them, and you've got a full scene ready to come to life. The thought… pic.twitter.com/x79WEeY1iq — Linus (???) (@LinusEkenstam) November 8, 2023
OpenAI's New Groundbreaking Update -- from newsletter.thedailybite.co Everything you need to know about OpenAI's update, what people are building, and a prompt to skim long YouTube videos...
But among all this exciting news, the announcement of user-created "GPTs" took the cake.
That's right, your very own personalized version of ChatGPT is coming, and it's as groundbreaking as it sounds.
OpenAI's groundbreaking announcement isn't just a new feature - it's a personal AI revolution.
The upcoming customizable "GPTs" transform ChatGPT from a one-size-fits-all to a one-of-a-kind digital sidekick that is attuned to your life's rhythm.
Home schooling’s rise from fringe to fastest-growing form of education -- from washingtonpost.com by Peter Jamison, Laura Meckler, Prayag Gordy, Clara Ence Morse and Chris Alcantara A district-by-district look at home schooling’s explosive growth, which a Post analysis finds has far outpaced the rate at private and public schools
Examination of the data reveals:
-
In states with comparable enrollment figures, the number of home-schooled students increased 51 percent over the past six school years, far outpacing the 7 percent growth in private school enrollment. Public school enrollment dropped 4 percent in those states over the same period, a decline partly attributable to home schooling.
-
Home schooling’s surging popularity crosses every measurable line of politics, geography and demographics. The number of home-schooled kids has increased 373 percent over the past six years in the small city of Anderson, S.C.; it also increased 358 percent in a school district in the Bronx.
...
The Learning & Employment Records (LER) Ecosystem Map — with thanks to Melanie Booth on LinkedIn for this resource
Driving Opportunity and Equity Through Learning & Employment Records
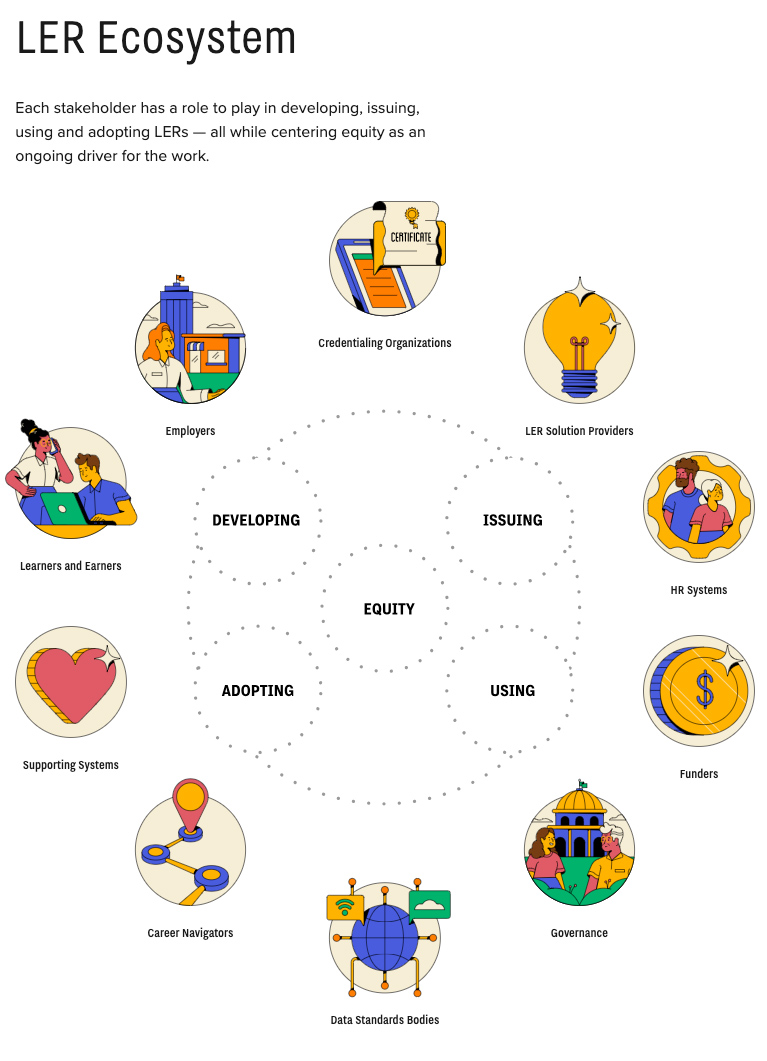
Imagine A World Where…
- Everyone is empowered to access learning and earning opportunities based on what they know and can do, whether those skills and abilities are obtained through degrees, work experiences, or independent learning.
- People can capture and communicate the skills and competencies they’ve acquired across their entire learning journey — from education, experience and service — with more ease, confidence, and clarity than a traditional resume.
- Learners and earners control their information and can curate their skills to take advantage of every opportunity they are truly qualified to pursue, opening up pathways that help address systemic inequities.
- Employers can tap into a wider talent pool and better match applicants to opportunities with verifiable credentials that represent skills, competencies, and achievements.
This is the world that we believe can be created by Learning and Employment Records (LERs), i.e. digital records of learning and work experiences that are linked to and controlled by learners and earners. An interoperable, well-governed LER ecosystem has the potential to transform the future of work so that it is more equitable, efficient, and effective for everyone involved— individuals, training and education providers, employers, and policymakers.
The Public Is Giving Up on Higher Ed — from chronicle.com by Michael D. Smith
Our current system isn’t working for society. Digital alternatives can change that.
Excerpts:
I fear that we in the academy are willfully ignoring this problem. Bring up student-loan debt and you’ll hear that it’s the government’s fault. Bring up online learning and you’ll hear that it is — and always will be — inferior to in-person education. Bring up exclusionary admissions practices and you’ll hear something close to, “Well, the poor can attend community colleges.”
On one hand, our defensiveness is natural. Change is hard, and technological change that risks making traditional parts of our sector obsolete is even harder. “A professor must have an incentive to adopt new technology,” a tenured colleague recently told me regarding online learning. “Innovation adoption will occur one funeral at a time.”
But while our defense of the status quo is understandable, maybe we should ask whether it’s ethical, given what we know about the injustice inherent in our current system. I believe a happier future for all involved — faculty, administrators, and students — is within reach, but requires we stop reflexively protecting our deeply flawed system. How can we do that? We could start by embracing three fundamental principles.
1. Digitization will change higher education.
…
2. We should want to embrace this change.
…
3. We have a way to embrace this change.
Why Shaquille O’Neal led edtech startup Edsoma’s $2.5M seed round — from techcrunch.com by Kirsten Korosec; via GSV
Edsoma is an app that uses an AI reading assistant to help people learn or improve their reading and communication.
…
For now, the company is targeting users in grades kindergarten to fourth grade based on the content that it has today. Wallgren noted that the Edsoma’s technology will work right through into university and he has ambitions to become the No. 1 literacy resource in the United States.
Outschool launches an AI-powered tool to help teachers write progress reports — from techcrunch.com by Lauren Forristal; via GSV
Outschool, the online learning platform that offers kid-friendly academic and interest-based classes, announced today the launch of its AI Teaching Assistant, a tool for tutors to generate progress reports for their students. The platform — mainly popular for its small group class offerings — also revealed that it’s venturing into one-on-one tutoring, putting it in direct competition with companies like Varsity Tutors, Tutor.com and Preply.
From DSC:
Interesting.
Learners can now seamlessly transition between AI-powered assistance (AI Tutor) and Live Expert support to get access to instant support, whether through AI-guided learning or real-time interactions with a human expert.
From Brainly Enrolls New AI-Powered Tools for More
Personalized and Accessible Learning (businesswire.com)
So far, high-profile ventures in the instruction realm, such as Kyron Learning, have fused teacher-produced, recorded content with LLM-powered conversational UX. The micro-learning tool Nolej references internet material when generating tasks and tests, but always holds the language model closely to the ground truth provided by teachers. Both are intriguing takes on re-imagining how to deliver core instruction and avoid hallucinations (generated content that is nonsensical).
-- Generative AI in Schools: A Closer Look and Future Predictions -- from thejournal.com by Ted Mo Chen
***
DC: This Tweet addresses a likely component of our future learning ecosystems:
Excited to introduce YouPro for Education—your AI study buddy.
— Richard Socher (@RichardSocher) August 30, 2023
Access unlimited AI chat + search, unlimited AI writing generations, unlimited AI art generations, supercharged with GPT-4 and Stable Diffusion XL at just $6.99/month for students and teachers. pic.twitter.com/0t8zf0AaLr
DC: What if we had an AI that could practice some digital Socratic Methods with us? The following item from Google made me wonder about this possibility.
Google’s AI-powered note-taking app is the messy beginning of something great — from theverge.com by David Pierce; via AI Insider
NotebookLM is a neat research tool with some big ideas. It’s still rough and new, but it feels like Google is onto something.
Excerpts (emphasis DSC):
What if you could have a conversation with your notes? That question has consumed a corner of the internet recently, as companies like Dropbox, Box, Notion, and others have built generative AI tools that let you interact with and create new things from the data you already have in their systems.
Google’s version of this is called NotebookLM. It’s an AI-powered research tool that is meant to help you organize and interact with your own notes.
DC: That got me to thinking…
What if the presenter/teacher/professor/trainer/preacher provided a set of notes for the AI to compare to the readers’ notes?That way, the AI could see the discrepancies between what the presenter wanted their audience to learn/hear and what was actually being learned/heard. In a sort of digital Socratic Method, the AI could then generate some leading questions to get the audience member to check their thinking/understanding of the topic.
The end result would be that the main points were properly communicated/learned/received.
From DSC: If this is true, how will we meet this type of demand?!?
- RESKILLING NEEDED FOR 40% OF WORKFORCE BECAUSE OF AI, REPORT FROM IBM SAYS -- from staffingindustry.com
Generative AI will require skills upgrades for workers, according to a report from IBM based on a survey of executives from around the world. One finding: Business leaders say 40% of their workforces will need to reskill as AI and automation are implemented over the next three years. That could translate to 1.4 billion people in the global workforce who require upskilling, according to the company.
***
Excerpt from From Toasters to Ties: The AI Takeover -- by Linus Ekenstam
The fusion of short and long-term memory will be a game-changer for LLMs. Wrap this in an intuitive API, make it accessible for all, and the potential is boundless. Let users interconnect their data across platforms using this shared layer, and the digital realm will truly come alive.
DC: Is the future of one of our powerful learning ecosystems more like adding your own desired groups/cohorts, topics, items, etc. to your server? Like a learning-focused type of Discord service? (https://t.co/Vq4dZamBf2)#future #learningecosystems #personalizedlearning pic.twitter.com/wVMWYBN3R1
— Daniel Christian (he/him/his) (@dchristian5) August 17, 2023
TLDR section from AIxEducation Day 1: My Takeaways
* There was a lot of talk about learning bots. This talk included the benefits of 1:1 tutoring, access to education for those who don’t currently have it (developing world), the ability to do things for which we currently don’t have enough teachers and support staff (speech pathology), individualized instruction (it will be good at this soon), and stuff that it is already good at (24/7 availability, language tutoring, immediate feedback regarding argumentation and genre (not facts :), putting students on the right track, comprehensive feedback, more critical feedback).
* Students are united. The student organizers and those who spoke at the conference have concerns about future employment, want to learn to use generative AI, and express concern about being prepared for the “real world.” They also all want a say in how generative AI is used in the college classroom. Many professors spoke about the importance of having conversations with students and involving them in the creation of AI policies as well.
* I think it’s fair to say that all professors who spoke thought students were going to use generative AI regardless of whether or not it was permitted, though some hoped for honesty.* No professor who spoke thought using a plagiarism detector was a good idea.
* Everyone thought that significant advancements in AI technology were inevitable.
* Almost everyone expressed being overwhelmed by the rate of change.
***
A relevant excerpt from The future of learning and skilling with AI in the picture -- from chieflearningofficer.com by Janice Burns
Recommending and personalizing
Other forms of AI, like recommendation engines, will be able to suggest L&D content to individuals based on their existing skills, skills gaps (identified through their career goals or business needs), learning preferences, role and interests. With AI, learning will become more relevant and tailored to each person, which also levels the playing field for those from non-traditional academic backgrounds, neurodiverse employees and those who haven’t had time or access to traditional learning opportunities.
DC: If true, this could be huge.
#Linkedin is working on LinkedIn Coach!
— Nima Owji (@nima_owji) July 27, 2023
It's an AI ASSISTANT that helps you apply for JOBS, learn new SKILLS, and find more ways to CONNECT with your network! pic.twitter.com/jKBrPmEFJt
DC: Sounds very useful for learning-related items.
“Custom instructions allow you to add preferences or requirements that you’d like ChatGPT to consider when generating its responses.” https://t.co/n0WOJnmDIY — Daniel Christian (he/him/his) (@dchristian5) July 21, 2023
For example, a teacher crafting a lesson plan no longer has to repeat that they're teaching 3rd grade science. A developer preferring efficient code in a language that’s not Python – they can say it once, and it's understood. Grocery shopping for a big family becomes easier, with the model accounting for 6 servings in the grocery list.
The Future Of Education: Embracing AI For Student Success — from forbes.com by Dr. Michael Horowitz
Unfortunately, too often attention is focused on the problems of AI—that it allows students to cheat and can undermine the value of what teachers bring to the learning equation. This viewpoint ignores the immense possibilities that AI can bring to education and across every industry.
The fact is that students have already embraced this new technology, which is neither a new story nor a surprising one in education. Leaders should accept this and understand that people, not robots, must ultimately create the path forward. It is only by deploying resources, training and policies at every level of our institutions that we can begin to realize the vast potential of what AI can offer.

DC: Something I created via Adobe Firelfy (Beta version)
It's only a matter of time before A.I. chatbots are teaching in primary schools -- from cnbc.com by Mikaela Cohen
Key Points
- Microsoft co-founder Bill Gates saying generative AI chatbots can teach kids to read in 18 months rather than years.
- Artificial intelligence is beginning to prove that it can accelerate the impact teachers have on students and help solve a stubborn teacher shortage.
- Chatbots backed by large language models can help students, from primary education to certification programs, self-guide through voluminous materials and tailor their education to specific learning
stylespreferences.
Massive Disruption Now: What AI Means for Students, Educators, Administrators and Accreditation Boards
— from stefanbauschard.substack.com by Stefan Bauschard
The choices many colleges and universities make regarding AI over the next 9 months will determine if they survive. The same may be true for schools.
Just for a minute, consider how education would change if the following were true –
- AIs “hallucinated” less than humans
- AIs could write in our own voices
- AIs could accurately do math
- AIs understood the unique academic (and eventually developmental) needs of each student and adapt instruction to that student
- AIs could teach anything any student wanted or need to know any time of day or night
- AIs could do this at a fraction of the cost of a human teacher or professor
PowerSchool Announces Collaboration with Microsoft Azure OpenAI Service to Provide Personalized Learning at Scale in K-12 Education -- from powerschool.com
Large-scale language models integrated within PowerSchool Performance Matters and PowerSchool LearningNav products will empower educators in delivering transformative personalized learning pathways
The implementation of generative AI within these products will dramatically improve educators’ ability to deliver personalized learning to students at scale by enabling the application of personalized assessments and learning pathways based on individual student needs and learning goals. K-12 educators will also benefit from access to OpenAI technology...
We Might Finally Get AI That “Remembers” Us -- from theneurondaily.com by Noah Edelman & Pete Huang
Why it matters: The best AI assistants will be the ones that require the least prompting. They’ll get to know who you are, what you need, and your modus operandi. Profiles are a good starting point, but we believe the game-changer will be larger context windows (that’s nerd-speak for the amount of context ChatGPT can handle).
From DSC:
And my point with this vision is to ask how about taking this type of thing a step further and remembering — or being able to access — our constantly updated Cloud-Based Learning Profiles?
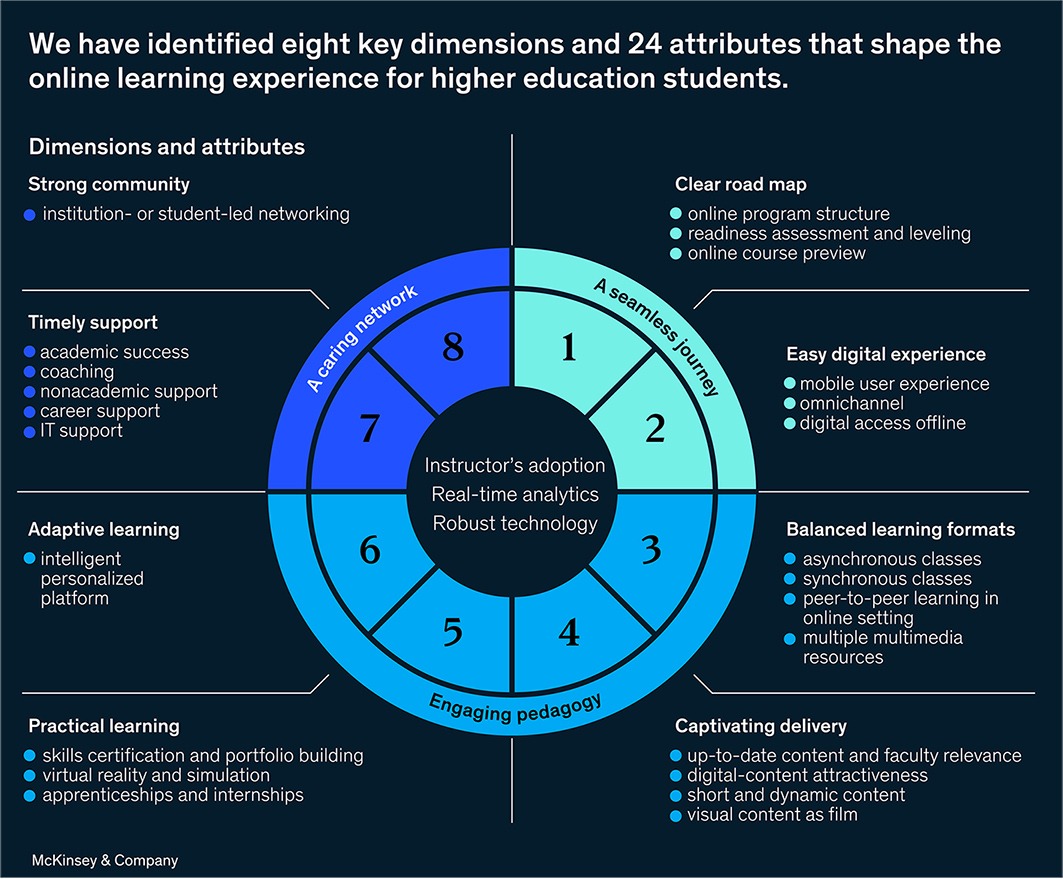
What do higher education students want from online learning? -- from McKinsey's Child, Frank, Law, & Sarakatsannis
Our AI in Edtech Takeaways -- from The Cambrian Explosion of AI Edtech Is Here
After chronicling 160+ AI tools (which is surely only a small fraction of the total), we’re seeing a few clear patterns among the tools that have come out so far- here are 10 categories that are jumping out!
-
Virtual Teaching Assistants: tools designed to save teachers time when lesson planning, creating IEPs, writing curriculum, giving feedback and more (Playlab, Brisk Teaching, Roshi)
-
Virtual Tutors: student-facing AI bots designed to be personalized tutors (Salley for career coaching, Quizlet’s Q-Chat, Trellis)
-
AI-Powered Study Tools: tools designed to instantly turn media resources like websites or videos into traditional ‘study materials’ like notes, flashcards or practice quizzes (Wisdolia, Cognii, Studyable)
-
Educational Content Creation: tools to rapidly create educational content, especially video creation and quizzes, for independent course creators, educational publishers and L&D teams (Prof Jim, Synthesia, Prep.ai)
-
Educational Search: AI-enhanced search tools that surface information in new and unexpected ways (Perplexity, Heuristi.ca, Transvribe, AskBooks)
-
Auto-generated Learning Paths: tools that, given a subject or question, will create an instant, personalized ‘course’ (Learn.xyz, Nolej, LearnGPT)
-
AI-Powered Research: tools that help navigate research papers or journals to find citations and rapid answers (Elicit, Scite, Consensus)
-
Speak to Characters: ability to speak to AI bots that simulate the personalities of famous people, historical figures or characters (Khanmigo, Duolingo Max’s Roleplay, Character.ai)
-
Grammar and Writing: tools to support writing and grammar skills (Quillbot, Trinka, Writefull, Smodin)
-
AI Cheating Detection: tools that can detect AI in student submissions and track cheating (GPTZero, Turnitin, Originality.ai)
Changed by Our Journey: Engaging Students through Simulive Learning -- from er.educause.edu by Lisa Lenze and Megan Costello
'Megan Costello: I took a different approach to remote synchronous online learning at the start of the pandemic. Instead of using traditional videoconferencing software to hold class, I prerecorded, edited, and uploaded videos of my lectures to a streaming website. This website allowed me to specify a time and date to broadcast my lectures to my students. Because the lectures were already prepared, I could watch and participate in the chat with my students as we encountered the materials together during the scheduled class time. I drove conversations in chat, asked questions, and got students engaged as we covered materials for the day. The students had my full attention.
Although I've been using this teaching method since the start of the pandemic, I didn't find out until much later that this event format is referred to as "simulive." This catchy term is a mashup of the words "simulated" and "live" because of its pre-recorded and live elements. I had seen this event format applied in the entertainment industry and to online conferences, but I had never seen it used for teaching. Because I was using simulive in an educational context, I called my implementation "simulive learning." Since inventing this term, I've become aware of others who have implemented similar teaching practices. Some call it "watch party lecturing," and others are still looking for an appropriate term.
Comment from DSC:
So the Subject Matter Expert -- or better yet, a TEAM of specialists -- has previously recorded the lecture. Then the SME is able to participate in real-time with the learners. Very interesting...and possibly a part of our future learning ecosystems.
Bill Gates says AI is poised to destroy search engines and Amazon — from futurism.com by Victor Tangermann
Who will win the AI [competition]?
Gates has been bullish on the topic of AI for a while now. Just last month, he told an audience during a keynote speech that AI could eventually teach kids how to read. Even within "the next 18 months, the AIs will come in as a teacher’s aide and give feedback on writing," he said. "And then they will amp up what we’re able to do in math."
EdX launches ChatGPT-powered plugin, learning assistant
-- from edscoop.com
The online learning firm edX introduced two new tools powered by ChatGPT, the "first of many innovations" in generative AI for the platform.
The online learning platform edX introduced two new tools on Friday based on OpenAI’s ChatGPT technology: an edX plugin for ChatGPT and a learning assistant embedded in the edX platform, called Xpert.
According to the company, its plugin will enable ChatGPT Plus subscribers to discover educational programs and explore learning content such as videos and quizzes across edX’s library of 4,200 courses.
Also see:
The amazing AI super tutor for students and teachers -- from ted.com by Sal Kahn
EdTech Is Going Crazy For AI — from joshbersin.com by Josh Bersin
This week I spent a few days at the ASU/GSV conference and ran into 7,000 educators, entrepreneurs, and corporate training people who had gone CRAZY for AI.
No, I’m not kidding. This community, which makes up people like training managers, community college leaders, educators, and policymakers is absolutely freaked out about ChatGPT, Large Language Models, and all sorts of issues with AI. Now don’t get me wrong: I’m a huge fan of this. But the frenzy is unprecedented: this is bigger than the excitement at the launch of the i-Phone.
Imagining what’s possible in lifelong learning: Six insights from Stanford scholars at ASU+GSV -- from acceleratelearning.stanford.edu by Isabel Sacks
High-quality tutoring is one of the most effective educational interventions we have – but we need both humans and technology for it to work. In a standing-room-only session, GSE Professor Susanna Loeb, a faculty lead at the Stanford Accelerator for Learning, spoke alongside school district superintendents on the value of high-impact tutoring. The most important factors in effective tutoring, she said, are (1) the tutor has data on specific areas where the student needs support, (2) the tutor has high-quality materials and training, and (3) there is a positive, trusting relationship between the tutor and student. New technologies, including AI, can make the first and second elements much easier – but they will never be able to replace human adults in the relational piece, which is crucial to student engagement and motivation.
Interoperability: Scaling Statewide Talent Development Systems: the Alabama Model -- from talentplaybook.org
No workforce or education digital tool that seeks to facilitate mobility can succeed if it operates in isolation. Interoperability, the ability of data systems to work together, exchange, and make use of information from other systems, is the key to success, scale, and impact.
The same is true for Learning and Employment Records (LERs), which use open data standards in order to be portable, verified records of an individual’s education and work-based earned skills, credentials, and experience. LERs are designed to free education and workforce data from static resumes, proprietary systems, and education providers’ file cabinets, ensuring smooth transfer of data between education providers, employers, and learners.
The top online learning statistics in 2023 -- from Devlin Peck's Online Learning Statistics: The Ultimate List in 2023
- Worldwide, 49% of students have completed some sort of online learning
- Online learning is the fastest-growing market in the education industry – it has grown 900% since its creation in 2000
- 70% of students say online learning is better than traditional classroom learning
- The number of online learning users is expected to increase to 57 million by 2027
- 80% of businesses now offer online learning or training solutions
- 63% of students in the US engage in online learning activities daily
- Online learning can increase student and employee retention to as much as 50%
- Online learning can reduce the time needed to learn a subject by 40% to 60%
- The online learning industry is projected to be worth more than $370 billion by 2026
- Online learning and training can improve employee performance by 15% to 25%
The Future of Teaching is Here -- from Sam Chaltain, 180 studio
It's not sexy, but I feel like Sal Khan’s recent video introducing his Academy’s GPT-fueled AI tutor augurs the future of the teaching profession — and not just at Khan Academy.
The video is twenty minutes long, although I recommend watching the whole thing. But even if you only duck in for a few minutes, you’ll see what I mean.
The tutor is already fully capable of offering personalized feedback, hints and suggestions for just about any topic for which there are already clearly established answers -- from solving math equations with parentheses to digesting John Locke’s political philosophy.
And therein lies the rub.
...
But now we’ve entered a new chapter — dare I say, a Technological Singularity (20 years early) — one in which Chat-GPT in particular, and the daily flood of AI tools more generally, has changed the nature of the teacher/student relationship even more irrevocably than before.As a result, from this day forward, the job of a teacher REALLY needs to stop being about transmission.
So what should it start being instead?
...
In which case, the future of teaching is not about transmission, but it is about the other trans- words: transmedia exploration, transdisciplinary weaving, transcultural understanding, and, yes, personal and societal transformation.
A Spotify model of personalised higher education — from timeshighereducation.com by Michael Rosemann and Martin Betts
With technology offering greater potential for a personalised approach to higher education, Michael Rosemann and Martin Betts look at what universities can learn from the ubiquitous music platform Spotify
Selection, or the P(upil)-route as educationalist Dan Buckley calls it, means personalisation driven by the learner. This is the fastest-moving form of personalised learning. Not only do students benefit from true omnichannel education – choosing between face to face and online – they also independently navigate the internet’s resources and online databases in search of the knowledge that will help them to achieve their learning targets.
…
Automation, or the A-route, is the new enabler of personalised learning. As with personalised medicine, finance or entertainment, education is starting to use digital technologies to unlock new models of tailored engagement. While for most universities, AI-driven, personalised education is not an option as the required capabilities are missing and significant investments would be necessary, there is a range of alternative forms of automated personalised learning. For this, we look to providers outside the sector for inspiration.
***
Though the following article is from 2021, note the five new realities for higher education that are mentioned (emphasis DSC):
- New content producers and distributors will continue to enter the marketplace, driving up competition and consumer choice while driving down prices.
- Institutional control of higher education will decrease, and the power of higher education consumers will increase.
- With near universal access to digital devices and the internet, students will seek from colleges the same things they are getting from the music, movie and newspaper industries.
- A knowledge economy model based on outcomes will eclipse the industrial era model of higher education based on process.
- The dominance of time-bound degrees and "just-in-case" education will diminish.
***
GPT4. GPT4. GPT4. ChatGPT. ChatGPT plugins. Generative AI. Accelerated Computing. A slew of new AI-based products has hit the scene recently! Below are some relevant articles/items/resources:
Acceleration -- from Ethan Mollick
So, first what happened in the last seven days? Two major new AI models were released to the public (one mind-blowing, on disappointing); the world of AI image creation leapt forward; and a whole lot of large companies put out specialized products that would have been absolutely disruptive just a few weeks ago, but which are barely noticeable with the background buzz of accelerating technology.
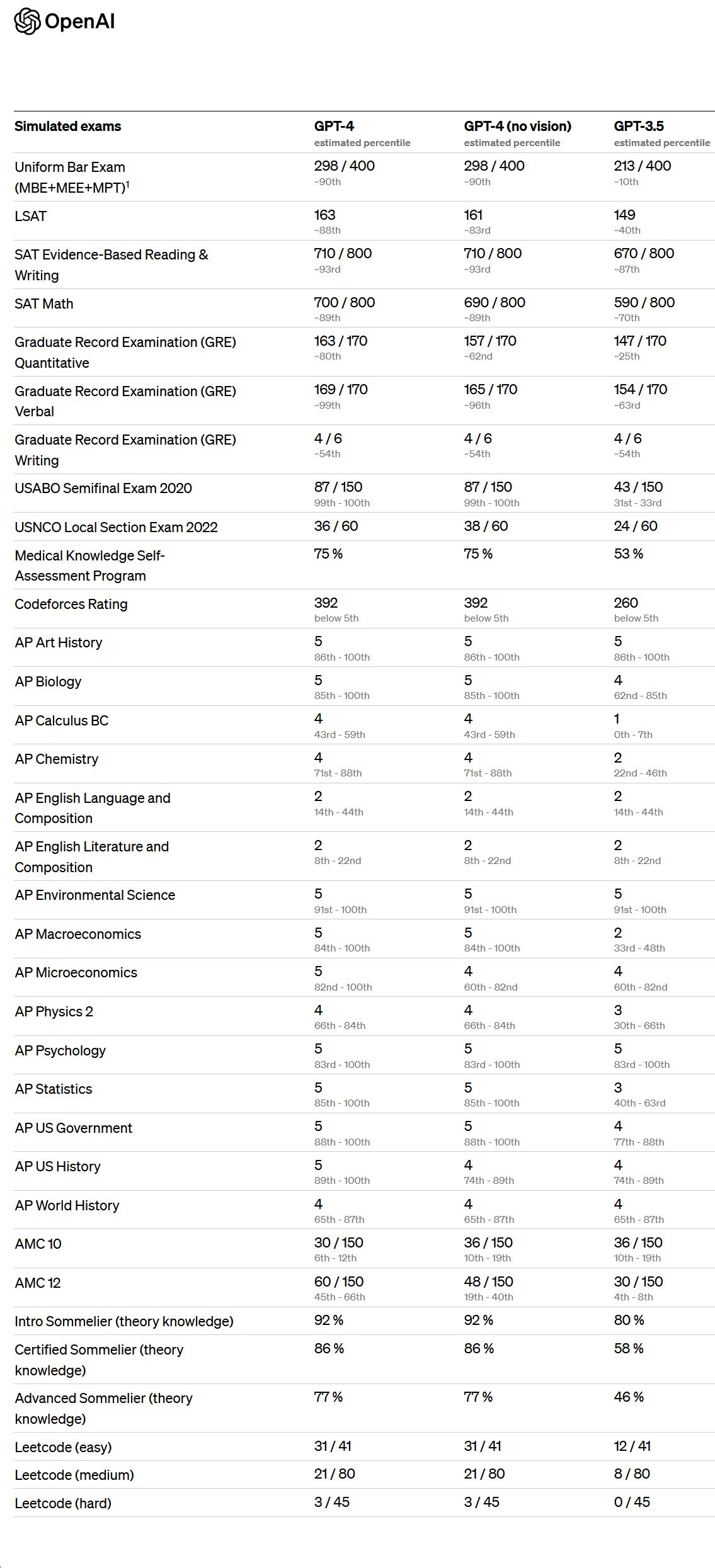
GPT-4 passes basically every exam. And doesn't just pass... The Bar Exam: 90% LSAT: 88% GRE Quantitative: 80%, Verbal: 99% Every AP, the SAT... (Per Ethan's Tweet of 3/14/23)
Introducing Mozilla.ai: Investing in trustworthy AI — from blog.mozilla.org by Mark Surman
We’re committing $30M to build Mozilla.ai: A startup — and a community — building a trustworthy, independent, and open-source AI ecosystem.
ChatGPT plugins — from openai.com
10 gifts we unboxed at Canva Create — from canva.com
Earlier this week we dropped 10 unopened gifts onto the Canva homepage of 125 million people across the globe. Today, we unwrapped them on the stage at Canva Create.
How AI will revolutionize the practice of law — from brookings.edu by John Villasenor
Begun, the AI lawsuits have — from bloomberg.com by Brad Stone
Meet Adobe Firefly. — from adobe.com
Experiment, imagine, and make an infinite range of creations with Firefly, a family of creative generative AI models coming to Adobe products.

Gen-2: The Next Step Forward for Generative AI — from research.runwayml.com
A multi-modal AI system that can generate novel videos with text, images, or video clips.
Realistically and consistently synthesize new videos. Either by applying the composition and style of an image or text prompt to the structure of a source video (Video to Video). Or, using nothing but words (Text to Video). It’s like filming something new, without filming anything at all.
Explore Breakthroughs in AI, Accelerated Computing, and Beyond at GTC — from nvidia.com
The Conference for the Era of AI and the Metaverse
Nvidia will bring AI to every industry, says CEO Jensen Huang in GTC keynote: ‘We are at the iPhone moment of AI’ — from venturebeat.com by Sharon Goldman
Generative AI for Enterprises — from nvidia.com
Custom-built for a new era of innovation and automation.
GPT-4 has arrived. It will blow ChatGPT out of the water. — from washingtonpost.com by Drew Harwell and Nitasha Tiku
The long-awaited tool, which can describe images in words, marks a huge leap forward for AI power — and another major shift for ethical norms
Introducing Our Virtual Volunteer Tool for People who are Blind or Have Low Vision, Powered by OpenAI’s GPT-4 — from bemyeyes.com
We are thrilled to announce Be My Eyes Virtual Volunteer™, the first-ever digital visual assistant powered by OpenAI’s new GPT-4 language model.
OpenAI releases GPT-4 on March 14, 2023
We’ve created GPT-4, the latest milestone in OpenAI’s effort in scaling up deep learning. GPT-4 is a large multimodal model (accepting image and text inputs, emitting text outputs) that, while less capable than humans in many real-world scenarios, exhibits human-level performance on various professional and academic benchmarks. For example, it passes a simulated bar exam with a score around the top 10% of test takers; in contrast, GPT-3.5’s score was around the bottom 10%. We’ve spent 6 months iteratively aligning GPT-4 using lessons from our adversarial testing program as well as ChatGPT, resulting in our best-ever results (though far from perfect) on factuality, steerability, and refusing to go outside of guardrails.
***
Duolingo turned to OpenAI’s GPT-4 to advance the product with two new features: Role Play, an AI conversation partner, and Explain my Answer, which breaks down the rules when you make a mistake, in a new subscription tier called Duolingo Max. “We wanted AI-powered features that were deeply integrated into the app and leveraged the gamified aspect of Duolingo that our learners love,” says Bodge.
***
The whole idea of AI as a useful teacher is here. Honestly it's astounding. [Duoling has] provided a Socratic approach to an algebra problem that is totally on point. Most people learn in the absence of a teacher or lecturer. They need constant scaffolding, someone to help them move forward, with feedback. This changes our whole relationship with what we need to know, and how we get to know it. Its reasoning ability is also off the scale. We now have human teachers, human learners but also AI teachers and AI that learns. It used to be a diad, it is now a tetrad - that is the basis of the new pedAIgogy. Personalised, tutor-led learning, in any subject, anywhere, at any time for anyone. That has suddenly become real.
***
***
“It’s driven by artificial intelligence,” Barnes said of IBM’s training and reskilling effort. “It’s a Netflix-like interface that pushes content.
...
“Employers were saying, ‘We have job openings we can’t fill, and we want to work with the education system, but it is so unbelievably frustrating because they’re very rigid, and they don’t want to customize to our needs,’” Hansen said. These employers sought workforce training that could produce a pipeline of learners-turned-employees, and Hansen said they told him, “If you can do that, I’ll pay you.”
Challenging ‘Bad’ Online Policies and Attitudes — from insidehighered.com by Susan D’Agostino
Introducing Q-Chat, the world’s first AI tutor built with OpenAI’s ChatGPT — from quizlet.com by Lex Bayer
Excerpt:
Modeled on research demonstrating that the most effective form of learning is one-on-one tutoring1, Q-Chat offers students the experience of interacting with a personal AI tutor in an effective and conversational way. Whether they’re learning French vocabulary or Roman History, Q-Chat engages students with adaptive questions based on relevant study materials delivered through a fun chat experience. Pulling from Quizlet’s massive educational content library and using the question-based Socratic method to promote active learning, Q-Chat has the ability to test a student’s knowledge of educational content, ask in-depth questions to get at underlying concepts, test reading comprehension, help students learn a language and encourage students on healthy learning habits.
Industry insight: Blockchaining to track current and potential employees’ skills — from chieflearningofficer.com by Tanya Boyd
Excerpts:
A learner who is aware of their unique strengths and development needs, as well as their preferred approach for gaining new skills, is often able to find the learning opportunities that they need more effectively and efficiently.
A global language for skills
While we might be tempted to focus within, looking for ways to address our own company’s talent challenges in isolation, this common concern invites a more global solution. We would all be better off if we could build a global language for skills. It’s at least one step toward achieving global processes for evaluating and developing them.
…
The top three challenges with skills and skill-based practices, as cited by McKinsey’s 2021 state of hiring survey, are: the ability to validate skills, sourcing job seekers with the right skills and scaling this approach.
Having a validated “chain” of skills for an employee helps not only in the selection process, but also as L&D departments seek to personalize learning. Blockchain creates a more valid approach to personalizing learning based on each employee’s competencies and skills gathered across their career, rather than just the skills they are demonstrating in their current organization and role.
Five Predictions for the Future of Learning in the Age of AI — from a16z.com by Anne Lee Skates
Excerpts:
Seeing as education is one of AI’s first consumer use cases, and programs like ChatGPT are how millions of kids, teachers, and administrators will be introduced to AI, it is critical that we pay attention to the applications of AI and its implications for our lives. Below, we explore five predictions for AI and the future of learning, knowledge, and education.

From DSC:
And more ChaptGPT, GPT-3, and AI!
The following links provide a sampling of the types of articles that we are seeing in early 2023. NOTE: They RELATE DIRECTLY to this vision, whereby AI will be a component of our future learning ecosystems. The pieces continue to come together for this vision!
- Introducing: ChatGPT Edu-Mega-Prompts — from drphilippahardman.substack.com by Dr. Philippa Hardman;
- Whispers of A.I.’s Modular Future — from newyorker.com by James Somers
- Microsoft Teams Premium: Cut costs and add AI-powered productivity — from microsoft.com by Nicole Herskowitz
- Everything that happened in AI this January. -- from Lior on Twitter
- Meet MathGPT: a Chatbot Tutor Built Specific to a Math Textbook — from thejournal.com by Kristal Kuykendall
- Educator considerations for ChatGPT — from platform.openai.com
- The practical guide to using AI to do stuff — from oneusefulthing.substack.com by Ethan Mollick; with thanks to Sam DeBrule for this resource. Ethan Mollick is a professor at the Wharton School of the University of Pennsylvania where he studies entrepreneurship & innovation, as well as how we can better learn and teach.
A resource for students in my classes (and other interested people).
***
Back to Living Room Home>>
***
3 Trends That May Unlock AI’s Potential for L&D in 2023 — from learningguild.com by Juan Naranjo
Excerpts:
1. Meta-learning
Meta-learning, in the context of this article, refers to AI tools that serve up experiences to learners based on their preferences, needs, and goals. It is the superstructure behind the content assets (e.g., programs, courses, articles, videos, etc.) that assembles everything in a coherent, and purposeful, body of knowledge to be accessed by the user.
...
2. AI-assisted design and development work
This is the trend most likely to have a dramatic evolution this year.
...
IDs will be doing more curation and less creation:
- Many IDs will start pulling raw material from content generators (built using natural language processing platforms like Open AI’s GPT-3, Microsoft’s LUIS, IBM’s Watson, Google’s BERT, etc.) to obtain ideas and drafts that they can then clean up and add to the assets they are assembling. As technology advances, the output from these platforms will be more suitable to become final drafts, and the curation and clean-up tasks will be faster and easier.
- Then, the designer can leverage a solution like DALL-E 2 (or a product developed based on it) to obtain visuals that can (or not) be modified with programs like Illustrator or Photoshop (see image below for Dall-E's “Cubist interpretation of AI and brain science.”)
- If the asset requires a video, IDs will be able to quickly create one by leveraging existing footage, without having to go through each video in a library (using a program like Pictory) or from scratch by feeding text to a video generator (as it is the case with Lumen5).
...
3. Ultra-personalized learning
Unbundled: Designing Personalized Pathways for Every Learner — from gettingsmart.com by Nate McClennen “with contributions from the Getting Smart team and numerous friends and partners in the field”
Excerpts:
In this publication, we articulate the critical steps needed to unbundle the learning ecosystem, build core competencies, design learning experiences, curate new opportunities, and rebundle these experiences into coherent pathways.
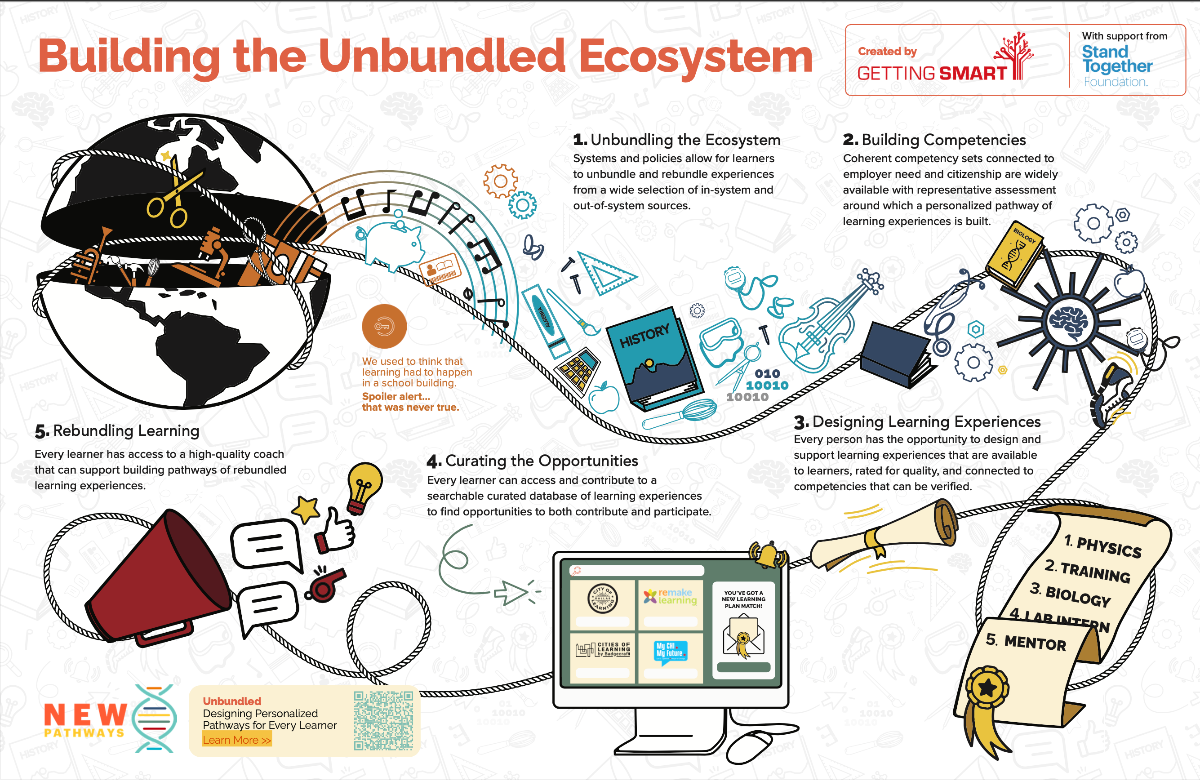
Recommendations
Solutions already exist in the ecosystem and need to be combined and scaled. Funding models (like My Tech High), badging/credentialing at the competency level (like VLACS), coaching models (like Big Thought), and open ecosystems (like NH Learn Everywhere) provide an excellent foundation. Thus, building unbundled systems has already begun but needs systemic changes to become widely available and accepted.
- Build a robust competency-based system.
- Create a two-way marketplace for unbundled learning.
- Implement policy to support credit for out-of-system experiences.
- Invest in technology infrastructure for Learning and Employment Records.
- Design interoperable badging systems that connect to credentials.
From DSC:
ChaptGPT. ChatGPT. ChatGPT. From late 2022 and into 2023, ChatGPT has exploded onto the scene (along with other things related to Artificial Intelligence).
The following links provide a sampling of the types of articles that we are seeing. NOTE: They RELATE DIRECTLY to this vision, whereby AI will be a component of our future learning ecosystems. The pieces continue to come together for this vision!
- Microsoft Plans to Build OpenAI, ChatGPT Features Into All Products” + other AI-related items
- Resources and “big deals” about ChatGPT and AI
- 9 ways ChatGPT saves me hours of work every day, and why you’ll never outcompete those who use AI effectively. [Valdarrama]
- Education is about to radically change: AI for the masses [McClennen & Dené Poth]
- To chat or not to chat…
- Several resources re: ChatGPT and teaching/learning implications from McMurtrie, Mills, & Co.
- Playing with ChatGPT: now I’m scared (a little) [Bates] AI & digital video: Likely some plusses & minuses ahead of us [Christian]
- “AI is going to be transformative as a teacher” [Lockyer]
- GPT to likely pass the Bar Exam in the near future [Bommarito & Katz]
- What’s next for AI [Heikkilä and Douglas Heaven] + several other items re: AI and the future
- ChatGPT and The Professional’s Guide to Using AI [Miller]
Trend No. 7 — Blockchain (source)
Today, much of the national discussions around blockchain center on cryptocurrencies. However, this breakthrough technology creates new opportunities to reimagine credential management for the learner, institutions and organizations.
Two initiatives are underway at ASU Enterprise Technology to bring credentials into the 21st century using distributed technology, including blockchain. The first focuses on creating a network — both digital infrastructure and community — to build a validated and immutable repository of learning.
To do so, the Trusted Learner Network is working to reimagine the traditional digital credential model by placing learners and their data at the center.
Utilizing distributed, web 3.0 semantic technologies, the Trusted Learner Network creates a durable, immutable ledger of learning that allows learners to easily view and manage their credentials.
And in order for learners to capture their diverse records of learning as verified credentials, they need a digital wallet. Enter ASU Pocket.
The digital wallet and portfolio is being designed and developed by teams at Enterprise Technology. Learners will be able to capture evidence of their learning inside their wallet and connect their skills to future jobs.
Both ASU Pocket and the TLN were featured in the 2023 SmartReport Ecosystem Map, released by iDatafy; the map (included above) reflects a current landscape of digital wallet and learner educational records (LER).
Unschooler: Your AI Vocational Mentor -- from techacute.com by Gabriel Scharffenorth
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
AI to help realize your dream career
The Unschooler mentor helps you understand what you need to do to achieve your dream career. You can select one of six broad areas of expertise: science, people, tech, info, art, and business. The platform will then ask questions related to your future career.It also has some other useful features. Unschooler keeps track of your skills by adding them to a skill map that’s unique to you. You can also ask it to expand on the information it has already given you. This is done by selecting the text and clicking one of four buttons: more, example, how to, explain, and a question mark icon that defines the selected text. There’s also a mobile app that analyzes text from pictures and explains tasks or concepts.
A New Generation Of Mastery-Based Learning Platforms Has Arrived — from joshbersin.com by Josh Bersin
Excerpt:
The $330 billion corporate training market is enormous, fragmented, and complex. For years it was dominated by Learning Management Systems (LMS) and content providers, each pioneered in the early 2000s. These systems served well, but the needs of employees and organizations moved ahead.
Today companies want not only a place to find and administer learning, they want a “Learning Platform” that creates mastery. And this market, that of “Learning Delivery Platforms,” is far more complex than you think. Let me put it straight: video-based chapter by chapter courses don’t teach you much. Companies want a solution that is expert-led, engaging, includes assignments and coaching, and connects employees to experts and peers.
Well there’s a new breed of platforms focused in this area, and I call them Capability Academy systems.
These are platforms explicitly to bring together expert teachers, AI-enabled collaboration, assignments, and coaching to drive mastery. They can train thousands of people in small cohorts, offering hands-on support for technical or PowerSkills topics. And the results are striking: these vendors achieve 90% completion rates and netPromoter scores above 60 (far above traditional content libraries).
DSC: An interesting idea and likely a component of our future learning ecosystems/platforms --> A “GPS for your career” -- FutureFit AI
An excerpt from their website:
Using AI to help workers navigate their careers
We use advanced labor market data and ethical machine learning algorithms to identify an individual’s ‘starting point’ in the labor market, recommend best fit career path ‘destinations’, and build a personalized roadmap of learning, resources, and work opportunities to successfully guide them from point A to point B in their career
Automation & Higher Ed -- from prawfsblawg.blogs.com by Orly Lobel
Excerpt:
I was delighted to see this thoughtful review of my new book The Equality Machine in Inside Higher Ed focused on some of the questions nearest and dearest to prawfs' hearts: the future of the professor and higher education as AI becomes more and more part of our learning and teaching. In The Equality Machine, I have a chapter that considers robots and automation in education but does not delve into universities and higher ed. Here's the review:
If the dream of creating high-quality/low-cost scaled online programs is ever to be realized, artificial intelligence—AI—will likely be the key enabling technology. The job of the AI in a scaled (high-enrollment) online course will be to optimally connect the instructor to the learner. The AI will determine when the human instructor should coach, encourage and engage with the learner—and when to hold back. The professor and the AI will collaborate to scale the relational model of learning that is the secret sauce of effective instructional practices.
Integrating faculty and AI to scale quality online learning is, to my knowledge, today more an idea than a reality. After reading The Equality Machine, however, I’m more hopeful than ever that this vision will come to fruition. While not focusing on higher education, the book provides enough examples of the transformative powers of digital technology to enhance human flourishing that some level of academic techno-optimism may be warranted.
Excerpt from QAA Report on Badging and Micro-Credentialing: How Education and Employment Can Benefit from Using Skills Profiles
Key report takeaways for educators and employers:
- Skills profiles enable us to better link education to employment.
- Accommodating badging and microcredential within formal education supports diversity both within learning and for learners.
- Personalized learning supports a more adaptable, better-aligned workforce and enables learner-earners to perform better in education, employment, and life.
Instructure Research Reveals Higher Education’s New Directive as Students Demand Flexibility and Return on Investment — from prnewswire.com by Instructure
“We are seeing a growing group of non-traditional students that demand change in the way institutions offer courses,” said Melissa Loble, chief customer experience officer at Instructure. “Learners are looking for flexibility and an emphasis on career skills in preparation for entering the workforce. Institutions that offer holistic solutions, such as mental health resources and mentoring programs, will go a long way in ensuring student success.”In its third year, the "State of Higher Education" research reflects a survey of over 7,500 current students, administrators and faculty from 23 countries representing a mixture of two-year, four-year, public and private higher education institutions. The report uncovered six key trends:
1. Students are demanding convenience and flexibility. Learners now expect a higher standard of online course design as part of any teaching and learning experience and want options between in-person, online, or hybrid courses.
- Two-thirds of students (62%) want to take some courses fully online and nearly three-quarters of faculty (72%) want to teach some courses fully online.
- As a result of the pandemic, respondents have a more positive attitude towards digital material (69%), open education resources (65%), combined in-person and online instruction (61%), online learning (59%) and online exam proctoring (51%).
- NORAM students are likely to take online (59%) and hybrid classes (57%). NA faculty are also likely to teach online (57%) and hybrid classes (75%).
2. Career readiness is of paramount importance. Preparing students for a career path after graduation, whether they are traditional students, part-time students, or mid-career, is still the primary concern of students, faculty and administrators. However, administrators and students agree that this is the area where institutions struggle most.
- Work/career readiness is the factor respondents say (32%) their institution struggles with most.
- Most respondents (71%) believe work/career readiness (82%), skill competency (87%), and student advancement (83%) are the most important factors when measuring student success.
- North America (27%) and EMEA (23%) are significantly less likely to believe their institution struggles with work/career readiness.
3. Competency-based and skills-based learning is in growing demand.
***
Back to Living Room Home>>
***
Student Preference for Online Learning Up 220% Since Pre-Pandemic — from campustechnology.com by Rhea Kelly
Excerpt:
According to a recent Educause survey, the number of students expressing preferences for courses that are mostly or completely online has increased 220% since the onset of the pandemic, from 9% in 2020 (before March 11) to 29% in 2022. And while many students still prefer learning mostly or completely face-to-face, that share has dropped precipitously from 65% in 2020 to 41% this year.
“These data point to student demand for online instructional elements, even for fully face-to-face courses,” Educause stated.
Also relevant/see:
- A Surge in Young Undergrads, Fully Online — from insidehighered.com by Susan D’Agostino
Tens of thousands of 18- to 24-year-olds are now enrolling at Western Governors, Southern New Hampshire and other national online institutions. Does this represent a change in student behavior?
New Mexico College Publishes Report to Advance a National Learning and Employment Record for Skills-based Credentialing and Hiring — from prnewswire.com by Central New Mexico Community College
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
ALBUQUERQUE, N.M., Oct. 11, 2022 /PRNewswire/ — In the current job market, applicants are usually asked to provide a broad résumé that lists the basics of their qualifications including college degrees and past work experience. It’s an outdated and inefficient system and one that Central New Mexico Community College (CNM) is now helping to improve.
Thanks to a grant from Walmart, CNM produced a comprehensive report that researches several independent efforts underway in order to build a model for creating a national Learner and Employment Records (LER) infrastructure. An LER enables the exchange of skills-based digital records that facilitate more efficient pathways from learning to earning.
An LER is more efficient and secure for both employers and job-seekers because it uses blockchain technology to provide security, trust, and transparency.
From DSC:
I still am learning about how secure blockchain-based applications are — or aren’t. But this idea of a Learner and Employment Record — which I’ve referred to as a “cloud-based learner profile” — seems to hold a lot of potential as we move into the future. Especially when the focus is increasingly on which skills a position needs and which skills an individual has.
This Company Aims to Become the Amazon of Lifelong Learning — from edsurge.com by Daniel Mollenkamp
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
The Singapore-based company Genius Group has turned some of its attention to the U.S. edtech market recently.
It’s making acquisitions, and even listed on the New York Stock Exchange in April.
In July, the company bought the for-profit University of Antelope Valley in California, saying it would incorporate it as a portal in the metaverse, part of the voguish effort to link the globe into “one big classroom.” Genius Group also partnered with NASA to help students find opportunities for start-ups to commercialize the agency’s technology patents.
If you listen to the company’s chief executive, it’s thriving because it runs a hybrid model for its entrepreneurship training programs that, the company argues, keeps it growing when a lot of edtech companies have had to struggle with the return to in-person learning. While some companies have seen layoffs, the Genius Group lifelong learning platform is growing among users at a rate of greater than 50 percent, they claim. Currently, it has 2.7 million students across 200 countries, according to its website.
...
But we decided that rather than looking to solve the problem for just some, if we could be one of the companies that was looking to solve it for all, that would be a great market opportunity for us. And at the same time, it would be something which would enable us to attract the best educators, and the best content creators from around the world as well.[The intent was] to really tackle the full, lifelong learning journey that we're on, and to put in place a pathway, and more importantly, a platform that would enable anyone to be able to come and take their curriculum, bring it on board, and in the same way that YouTube allows anyone to be a creator.
MasterClass’s Co-Founder Takes on the Community-College Degree — from wsj.com by Lindsay Ellis
A new, online-only education model promises associate degrees via prerecorded lectures from experts at Yale, NASA and other prestigious institutions

Excerpts (emphasis DSC):
One of the founders of the celebrity-fueled, e-learning platform MasterClass is applying the same approach to the humble community-college degree—one based on virtual, highly produced lectures from experts at prestigious institutions around the country.
…
The two-year degrees—offered in applied computing, liberal studies or business administration—will be issued by Golden Gate University, a nonprofit institution in San Francisco. Golden Gate faculty and staff, not the lecturers, will be the ones to hold office hours, moderate virtual discussions and grade homework, said Outlier, which is announcing the program Wednesday and plans to start courses in the spring.***
From DSC:
I signed up to receive some items from Outlier.org the other day. Here’s one of the emails that I recently received. It seems to me that this type of thing is going to be hard to compete against:
- Professionally-done content
- Created by teams of specialists, including game designers
- Hand-picked professors/SME’s -- from all over the world
- Evidence-based learning tools
Golden Gate University and Outlier.org Reinvent Affordable College with Degrees+ — from prnewswire.com
Excerpt:
For less than one-third the price of the national average college tuition, students will earn an associate degree plus a job-ready certificate from Google, IBM, or Salesforce
NEW YORK, Sept. 7, 2022 /PRNewswire/ — Golden Gate University is launching Degrees+, powered by Outlier.org, with three associate degrees that reimagine the two-year degree for a rising generation of students that demand high quality education without the crushing cost. For annual tuition of $4,470 all-inclusive, students will earn a two-year degree that uniquely brings together the best of a college education with a career-relevant industry certificate.
Beginning today, students can apply to be part of the first class, which starts in Spring 2023.
***
Adobe Live is now on YouTube -- as of 9/6/22. Interesting. Per Adobe on that date (emphasis DSC):
And we’re live! Starting 9:30am pst on Adobe Live’s YouTube Channel
After years of partnering with the Creative Cloud YouTube channel to bring our community inspiration and advice, Adobe Live will be streaming to our own YouTube channel (+Behance!) starting 9/6! This gives the Adobe Live team an exciting opportunity to connect closely with YOU, our community, through tailored content, YouTube’s community tab and, of course, LIVE streams.
...in addition to Adobe:
EdTech Giant Unacademy Launches 50 New Channels On YouTube To Democratise Online Education — from edtechreview.in by Shalini Pathak
Excerpt:
Unacademy, an Indian EdTech unicorn and one of the leading online learning platform, has recently launched 50 new education channels on Google-owned YouTube. The channels significantly help in increasing accessibility for millions of learners across academic and non-academic categories.
Few of these 50 channels are built on the existing content categories as offered by Unacademy. They mark Unacademy’s foray into newer terrains such as ‘Tick Tock Tax’- to simplify the direct and indirect tax concepts, and Life After IIT – a platform to crack JEE and discuss success stories of top rankers.
***
Back to Living Room Home>>
***
What a New Strategy at 2U Means for the Future of Online Higher Education — from edsurge.com by Phil Hill
Excerpt:
The acceleration is that 2U is going all in on the education platform strategy that started with the company’s acquisition of edX last year. The idea at the time was to rely on a flywheel effect, where edX can upsell to its tens of millions of registered learners taking free or low-cost online courses known as MOOCs, thus driving down the marketing costs required for the OPM business, while offering a spectrum of options—from free MOOCs to stackable certificates, to bootcamps and short courses, all the way to full degrees. The flywheel aspect is that the more the strategy succeeds, the more revenue is made by institutional partners and by the company, leading to more free courses and registered learners. It’s a self-reinforcing strategy that is the same one followed by Coursera.
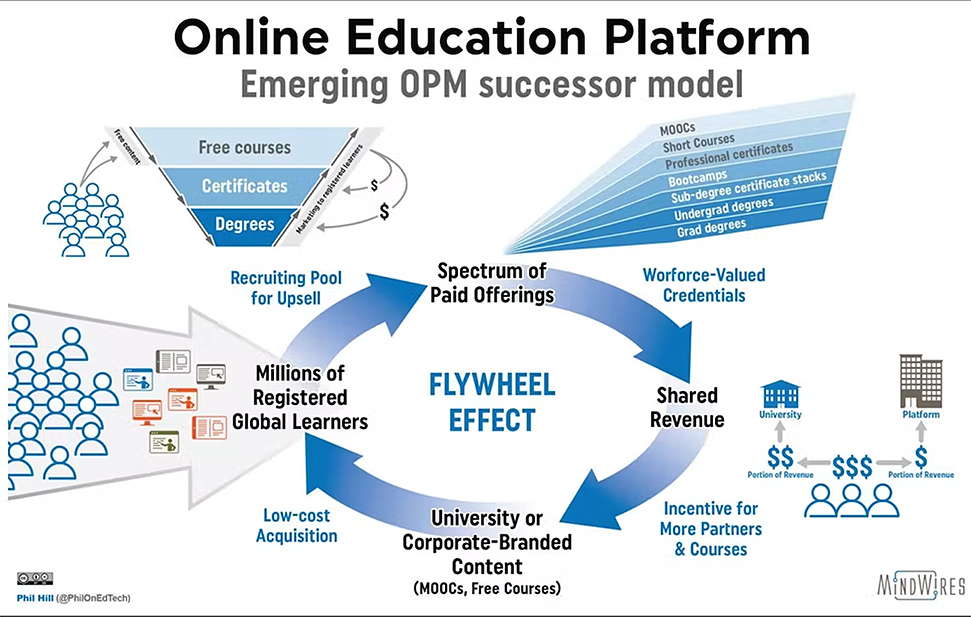
The Metaverse Will Reshape Our Lives. Let's Make Sure It's for the Better -- from time.com by Matthew Ball
Excerpts:
We cannot know in advance exactly how important a 3D internet might be to our global economy, just as we didn’t know the value of the internet. But we do have some view to the answer. As internet connectivity and computer processors have improved, we’ve shifted from colorless text to primitive webpages and web blogs, then online profiles (like a Facebook page) and video-based social networks, emojis, and filters. The volume of content we produce online has grown from a few message board posts, emails, or blog updates a week to a constant stream of multimedia content encapsulating our lives. The next evolution to this trend seems likely to be a persistent and “living” virtual world that is not a window into our life (such as Instagram) nor a place where we communicate it (such as Gmail) but one in which we also exist—and in 3D (hence the focus on immersive VR headsets and avatars).
...
Education is a category we have long expected to be transformed by the digital era, but has thus far resisted it. Since 1983, the cost of higher education has grown over 1,200%; medical care and services, which ranks second for cost increases in the U.S. over that period, is up half as much. The challenge is the real thing requires no fewer resources than it did decades ago, and what is lost when shifting to a remote computer screen. Eye contact. Peers. Hands-on experimentation. Equipment. Zoomschool, YouTube videos, and digital multiple choice are no substitute for the real thing.In the metaverse, the Magic School Bus becomes possible. For decades, students learned about gravity by watching their teacher drop a feather and a hammer, and then seeing a tape of Apollo 15 commander David Scott doing the same on the moon. (Spoiler: They fall at the same speed.) Such demonstrations need not go away, but they can be supplemented by the creation of elaborate virtual Rube Goldberg machines, which students can then test under Earth-like gravity, on Mars, and even under sulfuric rainfalls of the Venusian upper atmospheres. Instead of dissecting a frog, we can travel its circulatory systems not unlike the way we drive the Mushroom Kingdom in Mario Kart. And all of this is available irrespective of geographic location or resources of the local school board.
DSC takeaway -- keep what's happening with the Metaverse on your radar. Among the many industries and areas it will impact, education, higher education, vocational training, as well as training and development within the corporate world will likely be among them.
The Post-Covid New Normal is Looking Bipolar — from philonedtech.com by Phil Hill
I think it is important to deal with evidence on enrollment trends on their own terms and not just in the context of Covid recovery, and not just based on pre-Covid trends. The data we’re seeing recently have some big implications for the health of institutions, for online and hybrid education, and for alternative educational programs (and even alternative scheduling of programs).
Excerpt from The Metaverse in 2040 -- from pewresearch.org by Janna Anderson and Lee Rainie
Daniel D. Bryant, Wales-based VR educator, co-founder of Educators in VR and a leader in the Virtual World Society, predicted, “By 2040 the internet that you now access on a screen will be a place you can enter, visit and explore. Currently we are looking in through windows (literally), but we are soon going to be starting to climb through the windows and into the internet. The word website implies a location. Currently this is mostly in 2D. What if these sites are in 3D and you can get in and interact directly, rather than with a keyboard and a mouse? Think how creative people already get with creating and monetizing content on the 2D internet. Now add a third dimension to this and you have just created what Charlie Fink has referred to as the ‘largest wealth-and-value-creation experience humankind has ever witnessed.’ I can’t imagine the momentum heading anywhere else. When young people can truly get their heads and hands into the ‘metaverse,’ just stand back and watch in wonder. And that is even before AI [artificial intelligence] gets into the mix. AI will soon be able to generate virtual worlds and useful and very convincing AI bots to populate it. It’s a wild ride already. Better get strapped in.”
Below is an excerpted graphic from Gerd Leonhard's presentation The Future of Education (for EduCanada)

...which reminds me of Thomas Frey's reflections out at "A top futurist predicts the largest internet company of 2030 will be an online school."
Boost Usability of Libraries & Knowledge Hubs with Automation — from learningsolutionsmag.com by Markus Bernhardt
Excerpts:
Our article series looks at the top three areas where we see automation and AI revolutionizing the way in which successful L&D teams work: Asset libraries and knowledge hubs; hyper-personalized, truly adaptive learning; and capability mapping. This article examines the impact of AI and automation on maintaining asset libraries and knowledge hubs.
…
Thus, the contextualization engine becomes a powerful content management tool. It is also easy to use and requires no particular subject matter knowledge of the user; the librarian who has read everything does that for the user. And this works, of course, with articles, slide decks, audio, video, and even VR/AR content, and basically any file type.Assets can be mapped to competencies, skills, learning objectives, departments, the requirements of a specific course or workshop, or to the horizontals and verticals of an organization’s internal restructuring model. And this takes place within seconds and minutes, and at scale.
With the ability to map content as well as practice exercises, questions, and assessments automatically into each concept’s complexity tree, it is now possible to use automation and AI to deliver adaptive and truly personalized learning content and learning paths.
Entrepreneur Education Platform GeniusU Raises $1.5M Seed Funding at $250M Valuation -- from edtechreview.in ed by Stephen Soulunii
Excerpt:
Genius Group has recently announced that its EdTech arm, GeniusU Ltd, has raised $1.5 million in a seed round to support the development of its Genius Metaversity virtual learning plans.
...
With the fresh funding, GeniusU plans to extend its courses and programs to interactive learning environments in the metaverse, with students and faculty connecting and learning in global classrooms and virtual 3D environments. It also plans to integrate each student’s AI-based virtual assistant ‘Genie’ into the metaverse as 3D virtual assistants that accompany each student on their personalized journey and integrate its GEMs (Genius Education Merits) student credits into the metaverse. GEMs are earned by students as they learn and can be spent on products and services within GeniusU and counting towards their certifications.
The amazing opportunities of AI in the future of the educational metaverse -- from forbes.com by Rem Darbinyan
Excerpt:
Multilingual Learning Opportunities
Language differences may be a real challenge for students from different cultures as they may not be able to understand and keep up with the materials and assignments. Artificial intelligence, VR and AR technologies can enhance multilingual accessibility for learners no matter where they are in the world. Speech-to-text, text-to-speech and machine translation technologies enrich the learning process and create more immersive learning environments.The true benefit of using AI in a metaverse learning space is the ability to respond to each student’s individual needs. AI can process multiple languages simultaneously and provide real-time translations, enabling learners to engage with the materials in the language of their choice. With the ability to instantly transcribe speech across multiple languages, artificial intelligence removes any language barriers for students, enabling them to be potentially involved, learn and communicate in any language.
Why one university is moving toward a subscription model — a podcast from edsurge.com by Jeffrey R. Young
Excerpt:
“By the end of this decade or before, students should pay for higher ed the way they pay for Netflix or their cell phone bill,” [Maryville University President Mark] Lombardi says.
Momentum builds behind a way to lower the cost of college: A degree in three years — from hechingerreport.org by Jon Marcus
Skepticism about the cost and duration of a higher education drives a need for speed
Excerpt:
A rare brand-new nonprofit university, NewU has a comparatively low $16,500-a-year price that’s locked in for a student’s entire education and majors with interchangeable requirements so students don’t fall behind if they switch.
But the feature that appears to be really winning over applicants is that NewU will offer bachelor’s degrees in three years instead of the customary four.
“We didn’t think the three-year bachelor’s degree was going to be the biggest draw,” said Stratsi Kulinski, president of the startup college. “But it has been, hands-down. Consumers are definitely ready for something different.”
Now we just need a “Likewise TV” for learning-related resources! [Christian]
Likewise TV Brings Curation to Streaming — from lifewire.com by
And it’s available on iOS, Android, and some smart TVsSome noteworthy and interesting features include:
- All your streaming services in one place. One search. One watchlist. Socially powered recommendations.
- Entertainment startup Likewise has launched a new recommendations hub that pulls from all the different streaming platforms to give you personalized picks.
- Likewise TV is a streaming hub powered by machine learning, people from the Likewise community, and other streaming services. The service aims to do away with mindlessly scrolling through a menu, looking for something to watch, or jumping from one app to another by providing a single location for recommendations.
- Note that Likewise TV is purely an aggregator.
Some big numbers from bootcamps!
Tech Bootcamps re-skilled and up-skilled over 100,000 professionals globally in 2021, up from less than 20,000 in 2015. We expect this number to reach over 380,000 by 2025 representing over $3B of expenditure with significant upside as tech up-skilling models and modes overlap and converge. Governments, employers, universities and colleges everywhere are embracing rapid, high ROI training to build capacity in software, marketing, cyber and tech sales to drive their economies and growth.
-- from Accelerated Digital Skills and the ‘Bootcamp Boom’ out at holoniq.com
Excerpted chart from These 3 charts show the global growth in online learning — from weforum.org by Johnny Wood
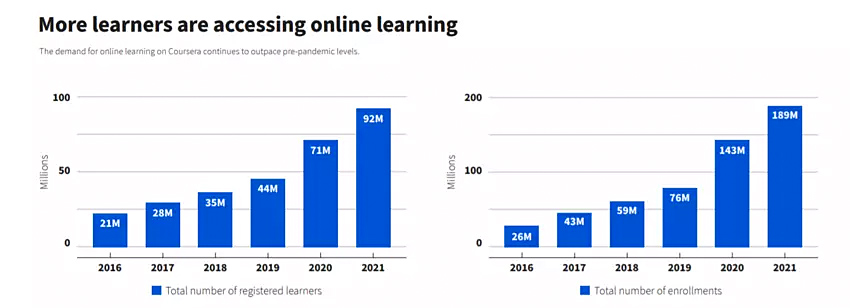
But in the face of an entrenched and growing skills gap, young people are increasingly questioning the status quo and looking for shorter, less expensive, more direct-to-career options.
Shorter Training, Better Skills: Three Predictions For The Future Of
Career And Technical Education -- from forbes.com
In a squiggly career, everyone’s a learner and everyone’s a teacher.
Make Learning a Part of Your Daily Routine -- from hbr.org
by Helen Tupper and Sarah Ellis
“We know, broadly, that learning will become more available, it’ll be more online, and there’ll be a lot more people learning for a lot more of their lives,” said Coursera CEO Jeff Maggioncalda.
School in the metaverse: How tech and the pandemic are changing
online education -- from protocol.com by David Pierce
Deprioritizing our development is a risky career strategy because it reduces our resilience and ability to respond to the changes happening around us.
...
In a squiggly career, everyone’s a learner and everyone’s a teacher.
Make Learning a Part of Your Daily Routine -- from hbr.org
by Helen Tupper and Sarah Ellis
With the addition of Codecademy’s innovative capabilities, we will create an even more immersive online learning experience. When we combine Skillsoft’s enterprise customer base of more than 12,000 corporate customers and over 46 million learners with Codecademy’s 40 million learners, sophisticated digital marketing capability and influential brand, we expect to unlock significant revenue synergies.”
...
Skillsoft has already assembled an expansive set of learning options, including virtual instructor-led training, coaching, micro videos, audio, books, bootcamps, live events, assessments and badges.
Skillsoft to acquire CodeAcademy, a leading platform for
learning high-demand technical skills, creating a worldwide
community of more than 85 million learners -- from skillsoft.com
Among money-courses, the best synthesis to date is found at Reforge. With a subscription model like MasterClass, Reforge organizes courses around business problems like retention and engagement, experimentation and testing, and monetization and pricing. Who builds and leads them? Executives from companies like Tinder, SurveyMonkey, HubSpot and Instacart. Reforge has attracted these experts through MasterClass-like persistence and networking (and presumably an attractive economic model). And as with MasterClass, it’s now at the point where tech leaders are seeking out Reforge.
Beyond branded experts and production values, Reforge has added a critical third element that we haven’t seen in less expensive love-courses: synchronous learning. Reforge casts itself as a membership network where “each has something to offer.” So in addition to 2-3 hours of self-paced material each week, members attend live sessions where instructors apply concepts through work-based scenarios.
MasterClass’s first masterstroke was recognizing that when it comes to conveying expertise online, brand matters a lot.
From Ryan Craig's 11/14/21 Gap Letter
***
Back to Living Room Home>>
***
Millions of jobs lost in the pandemic aren't coming back, and many of those vanished positions were disproportionately held by people of color. As automation and other shifts accelerate, many of these displaced workers will need additional education and training to find new roles, as well as a rapid return on their educational investment. This means more of the short-term credentials that are getting so much attention these days — but it also means faster pathways to an associate or bachelor's degree, both of which have greater proven value in the labor market.
From Competency-based learning can power an equitable recovery -- highereddive.com on 10/21/21
Foster online discussions: Terry Ord, an associate professor in the School of Biological, Earth, and Environmental Sciences at the University of New South Wales, in Australia, moved his class online during the pandemic, where it has stayed. Many of his students are from other countries, so he has had to figure out how to create a lively, asynchronous online community.
Ord created a forum centered on the lecture content. He broke his class of about 70 students into study groups of eight to 10 students, which remained fixed throughout the course. Then he released recorded lectures in groups of three to four at a time. The students had two to three weeks to watch them, post questions, and respond to other students’ questions.
“It was a huge hit,” he writes. “Most students went well beyond the requirements of the Q&A forum, spending time discussing ideas with each other and posting expanded details on content that they’d independently researched online. It was wonderful.”
The quality of discussion is actually better, he says, than in his face-to-face course, and the Q&A is mentioned as one of students’ favorite components, with many saying it pushed them to think for themselves.
From Teaching: Your Pandemic Teaching Tips by Beth McMurtire -- 10/14/21
Here are a couple of recent examples of learning-related platforms:
- UND says it wants to “provide competency-based, online education that provides ‘micro-pathways’ or smaller targeted units of learning to individuals as a way to enhance their skill set and knowledge for advancing in the labor market or reskilling for a new employment opportunity.” -- from It’s like Netflix for education: UND considers subscription tuition model
- Curiosity Stream Is the Streaming Service Tailored for People Who Love To Learn — from
And for less than $20 a year, Curiosity Stream offers something for everyone.
- A pre-pandemic study shows that more than 4 in 10 college degree holders are underemployed and are likely to remain that way for decades to come. This coupled with the astronomical cost of college and mounting student loan debt raises a need for alternative pathways into America’s workforce. The current college system is not putting all Americans to work.
...
Jobtech has the potential to be more effective for job seekers by aligning their aspirations more directly with the needs of employers. Unlike higher education institutions, a jobtech company’s profit and survival depend on people getting placed in good jobs. (Why Tech Companies View the Job Search As Big Business | EdSurge - 5/10/21)
- "Perhaps most significant, this trend represents employers stepping in to fill the skills gap and build learning options to create the digital workforce of the future. It’s clear that these employer-issued credentials are becoming a major part of the broader, significant trend toward skills-based hiring—and alternative, non-degree pathways into careers and professional advancement. Why now? Because online education is now mainstream, and online platforms make it easier for employers to offer education on their own if they wish, separate from the traditional higher education enterprise. And, many companies can’t wait for higher education institutions to develop the shorter term credential programs employers need." (More Employers Are Awarding Credentials. Is A Parallel Higher Education System Emerging? | EdSurge- 3/25/21)
- In fact, the number one thing teens would change about college is the price tag. Their second top concern is making sure the path they take directly connects them to a future career. (source)
- Given the expected concentration of job growth in high-wage occupations and declines in low-wage occupations, the scale and nature of workforce transitions required in the years ahead will be challenging, according to our research. Across the eight focus countries, more than 100 million workers, or 1 in 16, will need to find a different occupation by 2030 in our post-COVID-19 scenario, as shown in Exhibit 4. This is 12 percent more than we estimated before the pandemic, and up to 25 percent more in advanced economies (Exhibit 4). (MckInsey & Co. 2/18/21)
- We are confronted less often with the traditional 18-year-old learner and increasingly with the 60-year learner -- students who return repeatedly through their career seeking upskilling and wholly new competencies. These students need just-in-time learning that addresses the changing needs of employers and entrepreneurs in an AI-rich environment. (source)
- At the moment, “the higher-education value proposition is all around the most inexpensive education and certification that will get me a job,” says Susan Grajek, vice president for communities and research at Educause, a nonprofit organization that advocates for technology in higher education. (source)
- Per Laurie Burruss on LinkedIn: The internet has empowered adult learners by providing new online tools to ramp up education and training. “The need for workers to keep pace with fast-moving economic, cultural and technological changes, combined with longer careers, will add up to great swaths of adults who need to learn more than generations past — and faster than ever,” said Luke Yoquinto, a research associate at the M.I.T. AgeLab and co-author of “Grasp: The Science Transforming How We Learn
- Then some data from MOOC Enrollment Explodes in 2020:
According to a new report by Class Central, a company that tracks massive open online courses, of all learners who have registered for MOOCs throughout their history, a third did so last year. Coursera, the largest MOOC operator, added nearly four times the number of new registered users, exploding from 8 million in 2019 to 31 million in 2020 — a rise of 387 percent. Dhawal Shah, founder of Class Central, estimated that Coursera's total number of users is currently 76 million. The second largest MOOC organization, edX, doubled in size, expanding from 5 million new registered users in 2019 to 10 million in 2020. Shah put the total user base at 35 million. UK-based Future Learn nearly met Coursera's pace of growth, adding 5 million new registered users in 2020, compared to 1.3 million in 2019, a boost of 384 percent. The total user base was estimated to be about 15 million.
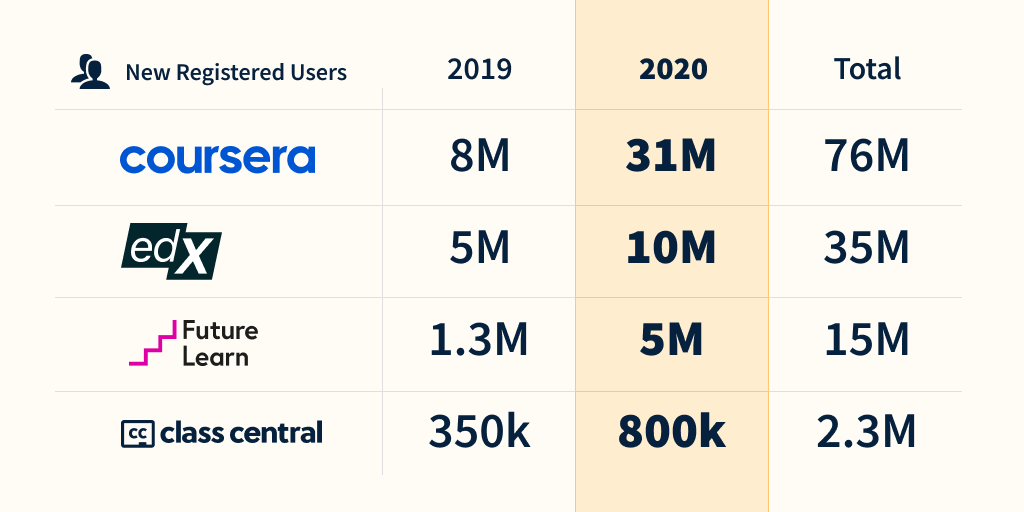
- Digital credentials leader bolsters workforce analytics and skills visibility for the enterprise -- resource from Ryan Craig's Gap Letter Vol III, #3 (Feb 5, 2021)
Credly, the leader in digital credentials, announces Credly 360, a new offering that provides the most reliable workforce analytics and skills visibility available for enterprises. Powered by the world’s largest network of verified skills, Credly 360 allows organizations to better understand, engage and retain talent.
- "Launching a new non-degree credential today is like building a bridge halfway (a pier); the only way to complete it is to build from the other side – from the employer side. And that’s exactly what digital credential apps will do. And once the enterprise has made better hiring decisions, we’ll see apps mapping career pathways, highlighting future managers and leaders and assembling more complete, compatible and diverse teams." Ryan Craig -- Gap Letter Vol III, #3 (Feb 5, 2021)
- ...CuriosityStream is a streaming service for people who love to learn. It hosts numerous award-winning, thought-provoking educational content covering history, science, technology, and sports.
- ...the social and economic imperatives for colleges to serve older students — offering them convenient, affordable academic programs — have never been more compelling.
(Goldie Blumenstyk, from the 11/4/20 edition of The Edge newsletter from The Chronicle of Higher Education)
- What will this new world look like? It’s likely, for one thing, to be more consolidated, with smaller numbers of colleges creating the content that can now be delivered, at scale, online. It’s likely that to be increasingly un-bundled, with the once-standard package (four years, on campus, with education plus everything else) broken into a myriad of more discrete and specific offerings. It’s likely to be distributed over a large segment of a learner’s life.
(Debora Spar , Sr. Associate Dean of Harvard Business School Online, 9/10/20)
- YouTube retains the #1 position that it is has held *for the 5th year running.* (emphasis DSC)
Jane Hart, 9/1/20, Top 200 Tools for Learning
- AI changes everything. It changes how we work, shop, travel, entertain ourselves, socialize, deal with finance and healthcare. When online, AI mediates almost everything – Google, Google Scholar, YouTube, Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, TikTok, Amazon, Netflix. It would be bizarre to imagine that AI will have no role to play in learning – it already has. Both informally and formally, AI is now embedded in many of the tools real learners use for online learning...
-- So what is the book about? (Donald Clark, September 2020); which discusses his book entitled, Artificial Intelligence for Learning: How to use AI to Support Employee Development
- Information technology transforms industries by making scarce resources plentiful, forcing customers to rethink the value of established products.
-- Are universities going the way of CDs and cable TV? (June 2020)
- “Many—perhaps millions—will need quick, job-focused upskilling and reskilling." -- Opportunity America (June 2020)
- The problem lies in an imperfect, incomplete market that does not provide comprehensive information over an individual’s lifetime to encourage a broader awareness of careers. Nor do we help individuals understand that career development is a process and not a destination, while showing them how to develop their lifelong
approach to making a living. -- A New Model for Career Exploration in a VUCA World (July 2020)
- "...it is abundantly apparent that universities must leverage technology to increase educational quality and access. The rapid shift to delivering an education that complies with social distancing guidelines speaks volumes about the adaptability of higher education institutions, but this transition has also posed unique difficultiesfor colleges and universities that had been slow to adopt digital education. The last decade has shown that online education, implemented effectively, can meet or even surpass the quality of in-person instruction. Digital instruction, broadly defined, leverages online capabilities and integrates adaptive learning methodologies, predictive analytics, and innovations in instructional design to enable increased student engagement, personalized learning experiences, and improved learning outcomes. The ability of these technologies to transcend geographic barriers and to shrink the marginal cost of educating additional students makes them essential for delivering education at scale." -- Dr. Micheal Crow, Pres. ASU, 6/25/20
- "The Coronavirus has brought forth the Dawn of the Age of Digital Learning — a time for builders to create the platforms, tools, and technology to propel society forward." -- source, dated 5/6/20
- "As previously noted, in the next 10 years, the number of higher ed students will double from 207M to over 414M. In Before Coronavirus (B.C.), we had expected a lot of this growth to happen online. In After Disease (A.D.), all of this growth will occur online, and many of the students formerly on campuses will also be taking courses online. -- source, dated 5/6/20
- "Millions of working adults must turn to digital degrees to improve their employability in a post-industrial economy that demands higher-level skills than on the assembly line." -- source, dated 3/5/20
- "Technology-enhanced learning can help us keep up with demand and offer pathways for the existing workforce to gain new skills. AI-based learning tools developed in the past decade have incredible potential to personalise education, enhance college readiness and access, and improve educational outcomes." -- source, dated 1/21/20
- "Voice is the most accessible form you can think of when you think about any interface. In education, it’s already started to take off." -- source, dated 3/2/20
Back to Living Class[Room] home
© 2024 | Daniel Christian
However, this vision/idea goes back much further than the date listed on the
graphic below -- and the pieces continue to come together!
![Learning from The Living [Class] Room](images/The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian-July-2012.jpg)