A Space for Learning: A review of research on active learning spaces — from by Robert Talbert and Anat Mor-Avi
Abstract:
Active Learning Classrooms (ALCs) are learning spaces specially designed to optimize the practice of active learning and amplify its positive effects in learners from young children through university-level learners. As interest in and adoption of ALCs has increased rapidly over the last decade, the need for grounded research in their effects on learners and schools has grown proportionately. In this paper, we review the peer-reviewed published research on ALCs, dating back to the introduction of “studio” classrooms and the SCALE-UP program up to the present day. We investigate the literature and summarize findings on the effects of ALCs on learning outcomes, student engagement, and the behaviors and practices of instructors as well as the specific elements of ALC design that seem to contribute the most to these effects. We also look at the emerging cultural impact of ALCs on institutions of learning, and we examine the drawbacks of the published research as well as avenues for potential future research in this area.
1: Introduction
1.1: What is active learning, and what is an active learning classroom?
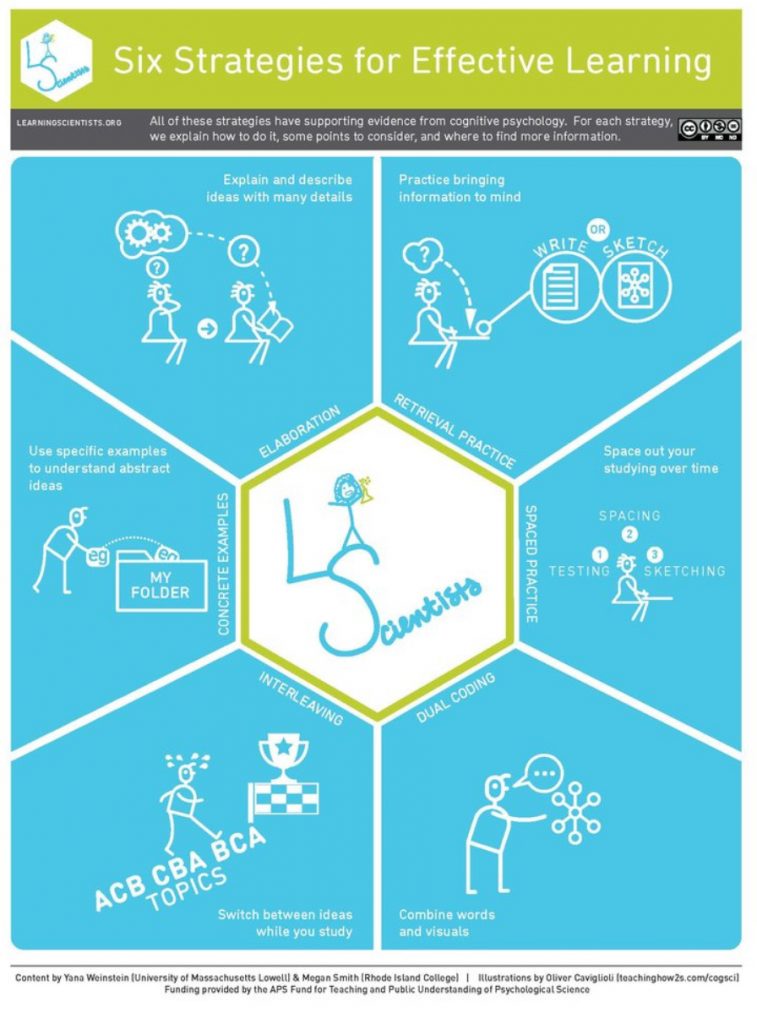
Active learning is defined broadly to include any pedagogical method that involves students actively working on learning tasks and reflecting on their work, apart from watching, listening, and taking notes (Bonwell & Eison, 1991). Active learning has taken hold as a normative instructional practice in K12 and higher education institutions worldwide. Recent studies, such as the 2014 meta-analysis linking active learning pedagogies with dramatically reduced failure rates in university-level STEM courses (Freeman et al., 2014) have established that active learning drives increased student learning and engagement across disciplines, grade levels, and demographics.
As schools, colleges, and universities increasingly seek to implement active learning, concerns about the learning spaces used for active learning have naturally arisen. Attempts to implement active learning pedagogies in spaces that are not attuned to the particular needs of active learning — for example, large lecture halls with fixed seating — have resulted in suboptimal results and often frustration among instructors and students alike. In an effort to link architectural design to best practices in active learning pedagogy, numerous instructors, school leaders, and architects have explored how learning spaces can be differently designed to support active learning and amplify its positive effects on student learning. The result is a category of learning spaces known as Active Learning Classrooms (ALCs).
While there is no universally accepted definition of an ALC, the spaces often described by this term have several common characteristics:
- ALCs are classrooms, that is, formal spaces in which learners convene for educational activities. We do not include less-formal learning spaces such as faculty offices, library study spaces, or “in-between” spaces located in hallways or foyers.
- ALCs include deliberate architectural and design attributes that are specifically intended to promote active learning. These typically include moveable furniture that can be reconfigured into a variety of different setups with ease, seating that places students in small groups, plentiful horizontal and/or vertical writing surfaces such as whiteboards, and easy access to learning
technologies (including technological infrastructure such as power outlets).
- In particular, most ALCs have a “polycentric” or “acentric” design in which there is no clearly-defined front of the room by default. Rather, the instructor has a station which is either
movable or located in an inconspicuous location so as not to attract attention; or perhaps there is no specific location for the instructor.
- Finally, ALCs typically provide easy access to digital and analog tools for learning , such as multiple digital projectors, tablet or laptop computers, wall-mounted and personal whiteboards, or classroom response systems.
2.1: Research questions
The main question that this study intends to investigate is: What are the effects of the use of ALCs on student learning, faculty teaching, and institutional cultures? Within this broad overall question, we will focus on four research questions:
- What effects do ALCs have on measurable metrics of student academic achievement? Included in such metrics are measures such as exam scores, course grades, and learning gains on pre/post-test measures, along with data on the acquisition of “21st Century Skills”, which we will define using a framework (OCDE, 2009) which groups “21st Century Skills” into skills pertaining to information, communication, and ethical/social impact.
- What effects do ALCs have on student engagement? Specifically, we examine results pertaining to affective, behavioral, and cognitive elements of the idea of “engagement” as well as results that cut across these categories.
- What effect do ALCs have on the pedagogical practices and behaviors of instructors? In addition to their effects on students, we are also interested the effects of ALCs on the instructors who use them. Specifically, we are interested in how ALCs affect instructor attitudes toward and implementations of active learning, how ALCs influence faculty adoption of active learning pedagogies, and how the use of ALCs affects instructors’ general and environmental behavior.
- What specific design elements of ALCs contribute significantly to the above effects? Finally, we seek to identify the critical elements of ALCs that contribute the most to their effects on student learning and instructor performance, including affordances and elements of design, architecture, and technology integration.
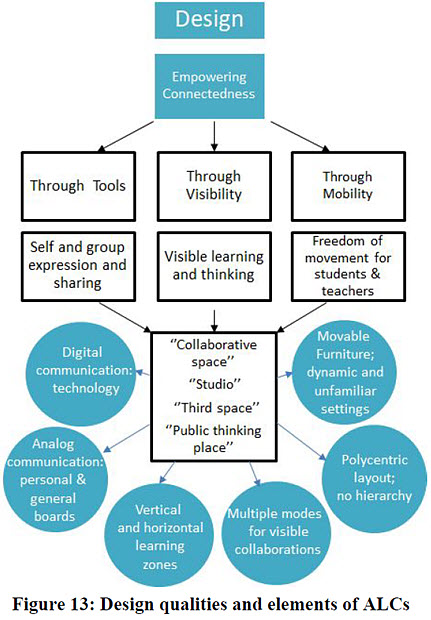
The common denominator in the larger cultural effects of ALCs and active learning on students and instructors is the notion of connectedness, a concept we have already introduced in discussions of specific ALC design elements. By being freer to move and have physical and visual contact with each other in a class meeting, students feel more connected to each other and more connected to their instructor. By having an architectural design that facilitates not only movement but choice and agency — for example, through the use of polycentric layouts and reconfigurable furniture — the line between instructor and students is erased, turning the ALC into a vessel in which an authentic community of learners can take form.