Retailers cut tens of thousands of jobs. Again. — from money.cnn.com by Paul R. La Monica
The dramatic reshaping of the American retail industry has, unfortunately, led to massive job losses in the sector.
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
The federal government said Friday that retailers shed nearly 30,000 jobs in March. That follows a more than 30,000 decline in the number of retail jobs in the previous month.
So-called general merchandise stores are hurting the most.
That part of the sector, which includes struggling companies like Macy’s, Sears, and J.C. Penney, lost 35,000 jobs last month. Nearly 90,000 jobs have been eliminated since last October.
…
“There is no question that the Amazon effect is overwhelming,” said Scott Clemons, chief investment strategist of private banking for BBH. “There has been a shift in the way we buy things as opposed to a shift in the amount of money spent.”
To that end, Amazon just announced plans to hire 30,000 part-time workers.
From DSC:
One of the reasons that I’m posting this item is for those who say disruption isn’t real…it’s only a buzz word…
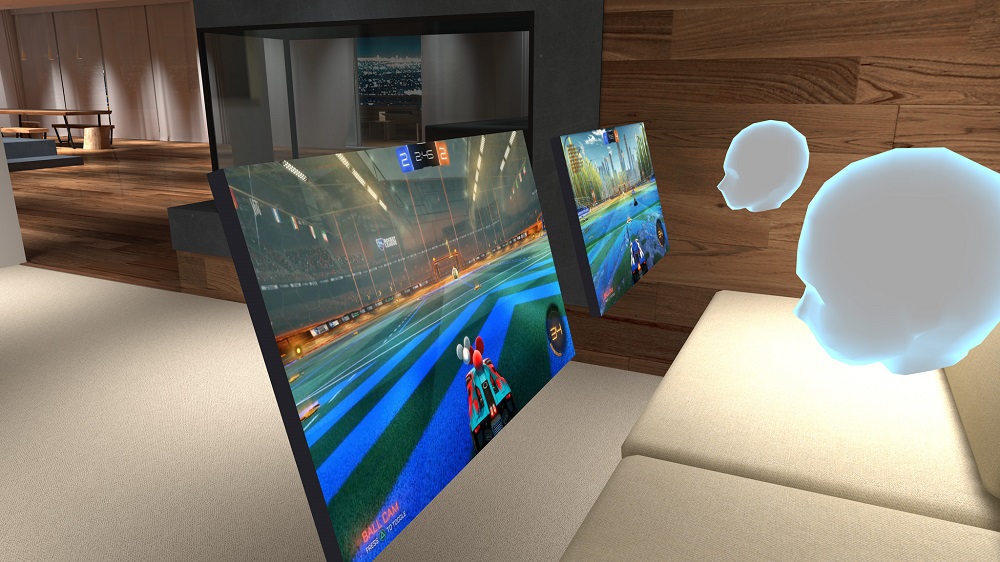
A second reason that I’m posting this item is because those of us working within higher education should take note of the changes in the world of retail and learn the lesson now before the “Next Amazon.com of Higher Education*” comes on the scene. Though this organization has yet to materialize, the pieces of its foundation are beginning to come together — such as the ingredients, trends, and developments that I’ve been tracking in my “Learning from the Living [Class] Room” vision.
This new organization will be highly disruptive to institutions of traditional higher education.
If you were in an influential position at Macy’s, Sears, and/or at J.C. Penney today, and you could travel back in time…what would you do?
We in higher education have the luxury of learning from what’s been happening in the retail business. Let’s be sure to learn our lesson.
* Effective today, what I used to call the “Forthcoming Walmart of Education“ — which has already been occurring to some degree with things such as MOOCs and collaborations/partnerships such as Georgia Institute of Technology, Udacity, and AT&T — I now call the “Next Amazon.com of Higher Education.”
Cost. Convenience. Selection. Offering a service on-demand (i.e., being quick, responsive, and available 24×7). <– These all are powerful forces.
P.S. Some will say you can’t possibly compare the worlds of retail and higher education — and that may be true as of 2017. However, if:
- the costs of higher education keep going up and we continue to turn a deaf ear to the struggling families/students/adult learners/etc. out there
- alternatives to traditional higher education continue to come on the landscape
- the Federal Government continues to be more open to financially supporting such alternatives
- technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, deep learning continue to get better and more powerful — to the point that they can effectively deliver a personalized education (one that is likely to be fully online and that utilizes a team of specialists to create and deliver the learning experiences)
- people lose their jobs to artificial intelligence, robotics, and automation and need to quickly reinvent themselves
…I can assure you that people will find other ways to make ends meet. The Next Amazon.com of Education will be just what they are looking for.










![The Living [Class] Room -- by Daniel Christian -- July 2012 -- a second device used in conjunction with a Smart/Connected TV](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian-July-2012.jpg)