The jobs that AI can’t replace — from bbc.com by Erik Brynjolfsson & Andrew McAfee
At the heart of capitalism is the concept of creative destruction. And this phenomenon is turbocharged by technological progress. Innovations from the cotton gin to electricity to the computer have created dramatic changes in the way that we work and the jobs that are available.
Excerpt:
Current advances in robots and other digital technologies are stirring up anxiety among workers and in the media. There is a great deal of fear, for example, that robots will not only destroy existing jobs, but also be better at most or all of the tasks required in the future.
Our research at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) has shown that that’s at best a half-truth. While it is true that robots are getting very good at a whole bunch of jobs and tasks, there are still many categories in which humans perform better.
Get ready for ‘The Economy Of Things’ — from forbes.com by Veena Pureswaran
Excerpt:
The IoT is not just about smart homes that light up when you arrive or washing machines that text you when the cycle is done. The IoT will turn physical assets into participants in real-time global digital markets. As the Internet of Things continues to turn physical assets into participants in new real-time, digital marketplaces, it’s creating what we describe as a new “Economy of Things.”
These types of assets will become as easily indexed, searched and traded as any online commodity. In fact, such digital marketplaces represent huge economic opportunities for growth and advancement.
Who’s the boss? Hitachi looks to promote artificial intelligence — from blogs.wsj.com by Jun Hongo; with thanks to Norma Owen for this resource
Excerpt:
Hitachi Ltd. is looking to promote artificial intelligence to management.
The Japanese electronics maker said it has developed a new artificial intelligence program that will enable robots to deliver instructions to employees based on analyses of big data and the workers’ routines.
“Work efficiency improved by 8% in warehouses with the new artificial intelligence program, compared to those without them,” a Hitachi spokeswoman said. “The program can examine an extremely large amount of data to provide the most efficient instruction, which is impossible for human managers to handle.”
Hitachi last month unveiled a fast-moving two-armed robot which it says may replace humans in performing basic functions like retrieving items in warehouses.
Tomorrow’s workers want mobile, but are employers ready? — from domo.com
70 percent of future workforce expect a bring-your-own-device culture; value technology perks nearly five times more than a stocked kitchen

Excerpt:
The study, which polled more than 2,000 college students, confirmed what many have assumed: that millennials are a mobile-first generation. Not surprisingly, the survey confirms that millennials spend most of their time accessing the Internet via a mobile device, 46 percent via a mobile phone and 43 percent on a tablet or laptop. Additionally, the report uncovers how much time millennials spend on various mobile activities. More than 97 percent use their phones to send or receive text messages, 96 percent use them to access the Internet, and 68 percent turn to a mobile device to stream music and send or receive pictures.
The findings also affirm how critical it is for companies to adjust to the ever-changing mobile-centric business world in order to attract top talent, which will increasingly be comprised of the millennial generation.
‘Transformer in chief’: The new chief digital officer — from mckinsey.com by Tuck Rickards, Kate Smaje, and Vik Sohoni
The CDO role is changing dramatically. Here are the skills today’s world demands.
Excerpt:
In the alphabet soup that is today’s crowded C-suite, few roles attract as much attention as that of the chief digital officer, or CDO. While the position isn’t exactly new, what’s required of the average CDO is. Gone are the days of being responsible for introducing basic digital capabilities and perhaps piloting a handful of initiatives. The CDO is now a “transformer in chief,” charged with coordinating and managing comprehensive changes that address everything from updating how a company works to building out entirely new businesses. And he or she must make progress quickly.
According to social forecasts in the U.S., U.K. and Australia, the point at which our labor market has more freelancers than full-time employees is between 5 to 10 years away. The growing automation of knowledge work means that, globally, we are expected to lose around 2 billion jobs by 2030. Some of that loss will be softened by new jobs created, but they’re going to be of the low-paid, temporary, variety. Today’s university graduates are facing what has been termed a “high skills/low income” future. The recent rapid growth in “knowledge process outsourcing” — the breaking up of salaried jobs into bid-for tasks, through websites like Elance.com and Freelancer. com — may well be transforming economies of developing countries like India, but it is causing futurists in the west to predict “the end of job.”
— What the Future Economy Means for How Kids Learn Today
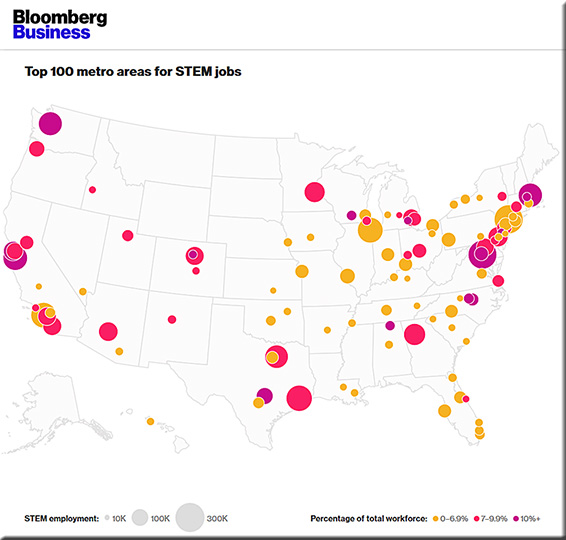
The unlikely cities that will power the U.S. economy — from bloomberg.com
Excerpt:
Huntsville is one of a growing number of smaller U.S. cities, far from Silicon Valley, that are seeking to replace dwindling factory jobs by reinventing themselves as tech centers. Across the Midwest, Northeast, and South, mayors and governors are competing to attract tech companies and workers.
How freelancers are fighting for their labor rights — from fastcompany.com by Dillon Baker
In the absence of unions, creative freelancers are finding new ways to work collectively.
Excerpt:
“On average, our members are owed over $10,000 in unpaid invoices and spend 36 hours tracking down each missing payment,” says Freelancers Union founder and labor lawyer Sara Horowitz. She explains that nearly half (44%) of their members report issues in getting paid.
But getting paid on time is just one of the hurdles that the growing independent workforce faces.
For example, the Internet has lowered the bar to entry for professional writing and created more opportunities than ever, which on one hand is good news for entry-level writers, but shrunken profits have also hollowed out freelance rates at many publications.
4 ways to prepare for the workplace of the future — from fastcompany.com by Erin Palmer
Millennials face a much more volatile workplace than ever. Here are four ways to adapt.
The workplace of the future will be a world of contradictions—which the next generations that enter it will need to master.
Charting a career path in a mercurial workforce means staying focused and adaptive in equal measure. That’s something millennials and their younger generation Z counterparts will need to be able to do more successfully than their elders ever had to.
For now, though, the learning curve still looks steep. A recent study by the online work company Upwork found that despite the millions of millennials looking for work, 53% of hiring managers said that they struggle to find and retain millennial employees.
Today’s leaders have gotten to where they are by adapting to what’s now and what’s next, not blindly clinging to one specific path.
Addendum on 9/15/15:
- APIs Are The New FTEs — from techcrunch.comby Gaurav Jain
Excerpt:
A decade ago, a VP of engineering at a startup might have evaluated the resumes of five solid front-end engineers. Five years ago that VP would have looked at GitHub profiles. Today, they are just as likely to evaluate a front-end framework like Ionic, Meteor or Aurelia and build it themselves.
It’s not just front-end options. We’ve seen a massive proliferation in frameworks, libraries and other tools that allow a single talented engineer to do the work of a team.
Companies and products like Heroku, Celery, RabbitMQ, Mandrill, Fastly, Chartio, Chargebee, Shipwire, Docker, Codeship, Rainforest QA, Replicated and Chartbeat have changed the nature of tech development. These are just a small subset of services that replace the work of individuals or entire teams.
WordPress Ate Webmasters
This trend has pros and cons. It will make life harder for those with only mid-tier technical knowledge. Look at what WordPress has done to “webmasters.” The blogging platform turned CMS has colonized the web, and accounts for ~23 percent of Internet traffic.