Faculty Predict Virtual/Augmented/Mixed Reality Will Be Key to Ed Tech in 10 Years — from campustechnology.com by Rhea Kelly
Faculty in our 2017 Teaching with Technology Survey believe tech will play a positive role in the future of higher education — but some technologies will be more important than others.
Excerpt:
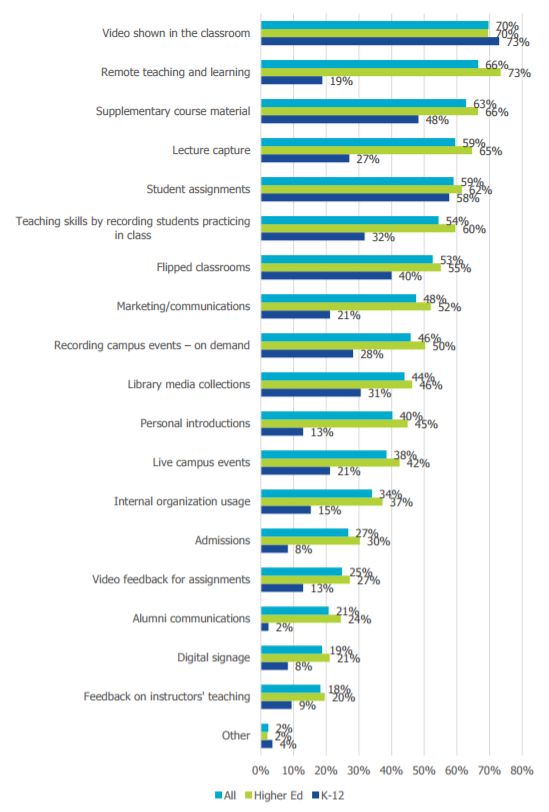
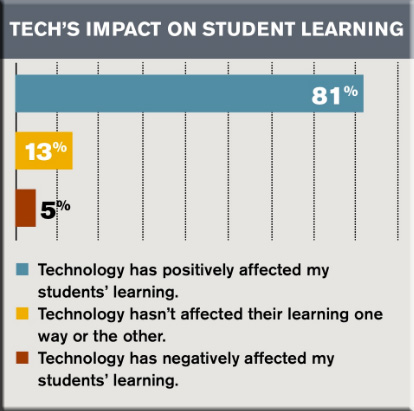
What technologies do faculty think will be important in education over the next decade? The most popular answer to that question by far was virtual/augmented/mixed reality, garnering 81 percent of responses (it topped the list last year as well). Mobile devices and apps, 3D modeling/scanning/printing, adaptive/personalized learning and video/streaming all rounded out the top five.
From DSC:
Great to see several of these items made the list. I would also add:
- The use of Natural Language Processing (NLP) to allow more voice-enabled and voice-driven applications
- Learning agents/bots (for example, a learning-related bot could go find out the top 50-100 jobs that employers are hiring for and present a list of potential digital playlists from a variety of providers that would help potential employees be able to do the work in those positions)
- Blockchain and the use of web-based learner profiles
- Artificial Intelligence / cognitive computing (which could be argued is already mentioned in the item re: adaptive, personalized learning)
- Moving towards providing up-to-date streams of content (for purposes of lifelong learning and microlearning)
Finally, it was great to see #9 on the list as I, too, believe that a next gen learning platform is needed:










![The Living [Class] Room -- by Daniel Christian -- July 2012 -- a second device used in conjunction with a Smart/Connected TV](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian-July-2012.jpg)