From DSC: I’d like to thank Ryan Craig for mentioning several interesting articles and thoughts in a recent Gap Letter. At least 2-3 of the articles he mentioned got me to thinking…
With a degree no longer enough, job candidates are told to prove their skills in tests — from hechingerreport.org by Jon Marcus
Instead of relying on credentials, more employers want applicants to show their stuff
Excerpts (emphasis DSC):
Among the many frustrations ahead for millions of Americans thrown out of work by the pandemic is one that may surprise them: To get a new job, it’s increasingly likely they will have to take a test.
As the number of candidates balloons while health risks make it hard for hiring managers to meet with them in person, a trend toward “pre-hiring assessments” — already under way before Covid-19 — is getting a huge new push.
Skeptical that university degrees are the best measure of whether candidates have the skills they need, employers were already looking for ways that applicants could prove it — including in fields where that was not previously required.
“It’s like try before you buy,” said Price.
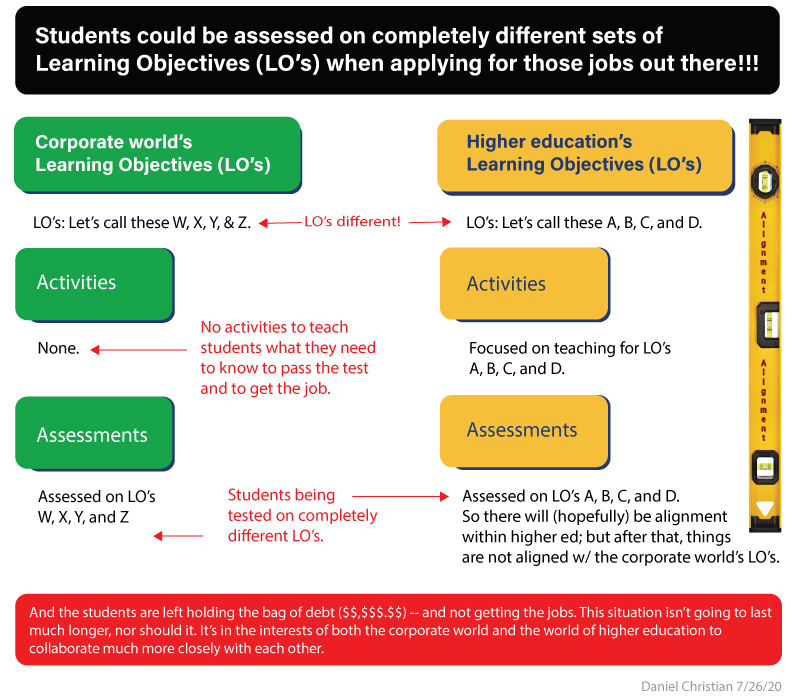
PDF version here.
Also see:
From DSC:
There is a huge misalignment between the Learning Objectives (LO’s) that the corporate world supports — and ultimately hires by — as compared to the LO’s that faculty, provosts, & presidents support.
This happened to me a while back when I was looking for a new job. I traveled to another city — upon the company’s request (though they never lifted a finger to help me with the travel-related expenses). Plus, I dedicated the time and got my hopes up, yet again, in getting the job. But the test they gave me (before I even saw a human being) blew me away! It was meant for PhD-level candidates in Computer Science, Programming, or Statistics. It was ridiculously hard.
The article above got me to thinking….
Higher education increasingly puts a guerrilla of debt on many students’ backs, which adds to the dispiriting struggle to overcome these kinds of tests. Also, the onslaught of the Applicant Tracking Systems that students have to conquer (in order to obtain that sought after interview) further adds to this dispiriting struggle.
How can we achieve better alignment here? Students are getting left holding the bag…a situation that will likely not last much longer. If higher ed doesn’t address this situation, we shouldn’t be surprised to see a mass exodus when effective alternatives pick up steam even further. Last call to address this now before the exodus occurs.
Along these lines see:
Better Connecting College and Career — from insidehighered.com by Steven Mintz
How to improve career readiness.
Excerpt:
How can colleges best prepare students for careers in a volatile, uncertain environment? This is the question recently asked by Marie Cini, the former provost at University of Maryland University College and former president of CAEL.
Career service offices, she observes, are first and foremost job search centers: reviewing résumés, publicizing job openings and arranging interviews. What they are not about, for the most part, is career preparation, a longer and more intense process involving self-analysis, skills building and genuine insights into the job market.