From DSC:
Are we neglecting to ask some key questions within higher education? I’ll get to those questions in a moment, the ones that came to my mind after seeing the following posting:
The robots are coming for your job! Why digital literacy is so important for the jobs of the future — from theconversation.com
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
In a report released this week, the Foundation for Young Australians (FYA) claims that up to 70% of young people are preparing for jobs that will no longer exist in the future. The report also raises concerns about decreasing entry-level occupations for school leavers and the impacts of automation.
In another recent report, the Committee for Economic Development of Australia predicts that:
almost five million Australian jobs – around 40% of the workforce – face the high probability of being replaced by computers in the next 10 to 15 years.
…
The FYA report also makes the case for increased emphasis on developing digital literacy and the implementation of a digital technologies curriculum in primary school.
Digital literacy includes skills such as coding, data synthesis and manipulation, as well as the design, use and management of computerised, digital and automated systems. Success in the new work order requires these skills alongside lateral thinking, innovation, problem-solving, collaboration and entrepreneurship. Add these to the traditional literacy skills of reading and writing and you have a very complex picture of what literacy is.
With automation a real threat to future jobs, school curricula have to keep up with the times.
From DSC:
The article raises an important point: “At the same time, the question of how we are preparing students in our schools for the new work order also bears serious consideration.”
I couldn’t agree more, as there are enormous ramifications to this topic/question: Are we, in fact, preparing our students for the future that they will inherit?
I suppose I could have also titled this posting, “More reasons to support the liberal arts,” as the liberal arts lay a strong foundation for many of the twists and turns that our students (and ourselves) will encounter down the road.
However, I fear that even within our liberal arts programs, we aren’t offering quite enough new courses that would help our students deal with a rapidly changing world. For example, I would like to see more courses on futurism offered — training students to look up and pulse check a variety of items that could impact them, their families, or their businesses in the future. Also, I don’t think they are going to know how to run their own businesses or to effectively freelance, something that 30-50% of them are going to need to do (depending upon which articles and reports one reads).
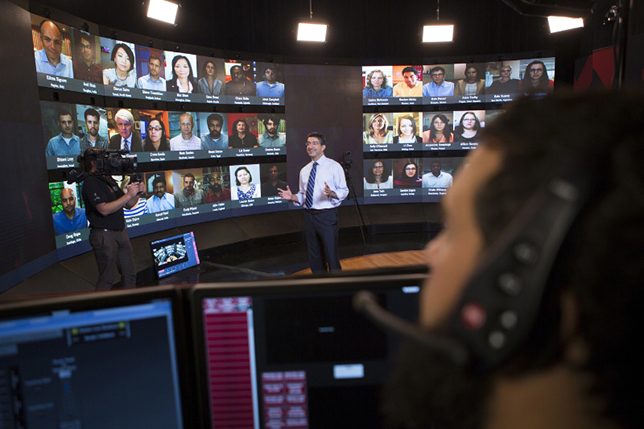
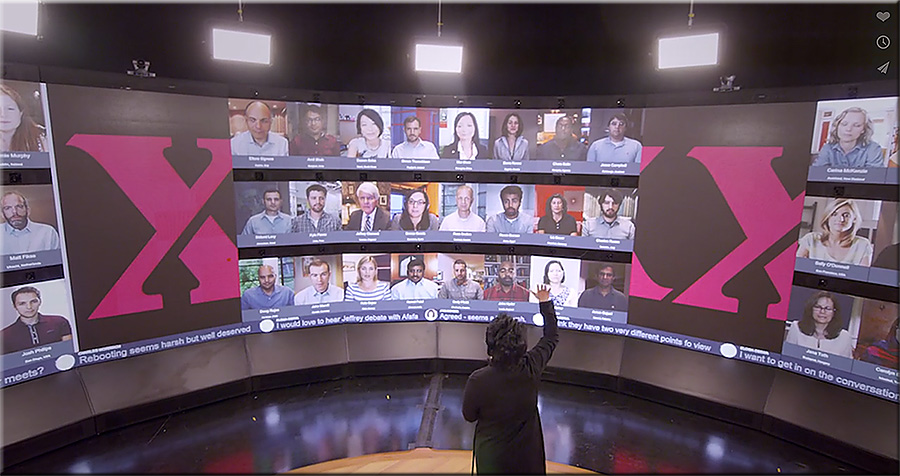
Also, why aren’t we offering more online-based opportunities for students to encounter learning opportunities and discussions that involve people from all over the globe? Won’t they be on project teams like that in the future? Isn’t that occurring already?
What do you think…how are we doing here? How are things in your city, state, or country?